标签:适配器 == bridge 个数 desktop image code pre 独立
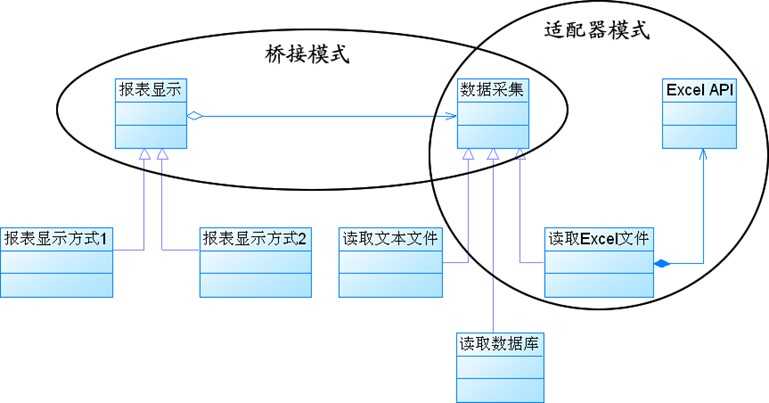
桥接模式
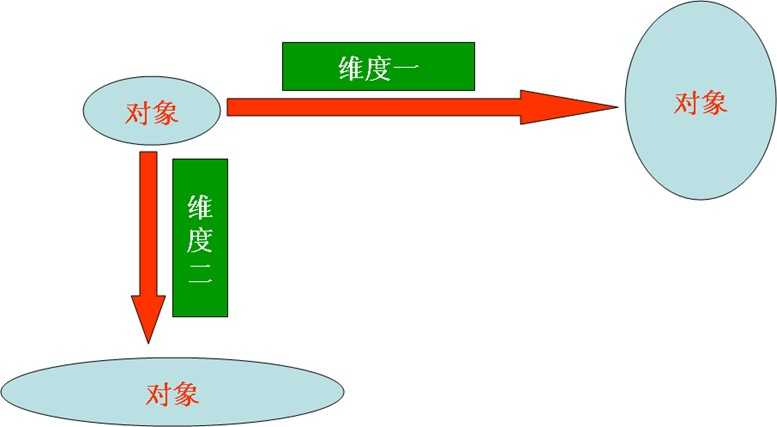
定义:是将抽象部分与它的实现部分分离,使它们都可以独立地变化。它是一种对象结构型模式,又称为柄体(Handler and Body)模式或接口(interface)模式。
图示: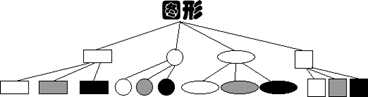 =========》
=========》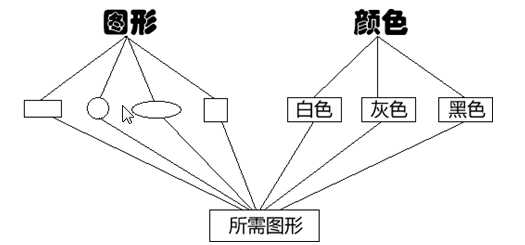
||
||
 《======
《======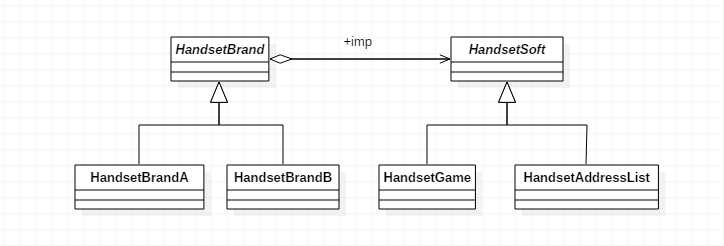
package com.offcn.designpattern.bridgepattern; public class BridgepatternDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { //联想台式机 Computer computer = new Desktop(new Lenovo()); computer.info(); //苹果笔记本 Computer computer1 = new Laptop(new Apple()); computer1.info(); } } //类型抽象类 abstract class Computer{ //组合,品牌
//使用protected,抽象类的子类可以使用该属性
protected Brand brand; public Computer(Brand brand){ this.brand = brand; } public void info(){ brand.info();//自带品牌 } } //类型:台式机 class Desktop extends Computer{ public Desktop(Brand brand) { super(brand);//联想/苹果 } @Override public void info() { super.info(); System.out.println("台式机"); } } //类型:笔记本 class Laptop extends Computer{ public Laptop(Brand brand) { super(brand); } @Override public void info() { super.info(); System.out.println("笔记本"); } } //品牌接口 interface Brand{ void info(); } //联想品牌 class Lenovo implements Brand{ @Override public void info() { System.out.print("联想"); } } //苹果品牌 class Apple implements Brand{ @Override public void info() { System.out.print("苹果"); } }
输出:

优点:
1) 桥接模式类似于多继承方案,但是多继承方案违背了类的单一职责原则,复用性比较差,类的个数也非常多。桥接模式是比多继承方案更好的解决方案,
极大的减少了子类的个数,从而降低管理和维护的成本。
2) 桥接模式提高了系统的可扩充性,在两个变化维度中任意扩展一个维度,都不需要修改原来系统,符合开闭原则。就像一座桥,可以把两个变化的维度连接起来。
缺点:
1) 桥接模式的引入会增加系统的理解与设计难度,由于聚合关联关系建立在抽象层,要求开发者针对抽象设计与编程。
2) 桥接模式要求正确识别出系统中两个独立变化的维度,因此其使用范围具有一定的局限性。
应用场景:
1) java语言通过java虚拟机实现了平台的无关性。
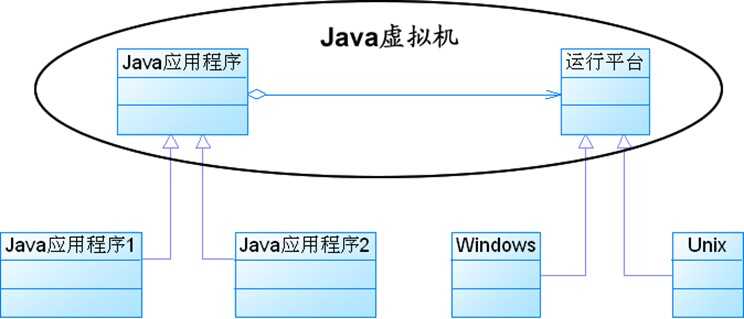
2) AWT中的peer架构。
3) JDBC驱动程序也是桥接模式的应用之一。
标签:适配器 == bridge 个数 desktop image code pre 独立
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/bai3535/p/12316620.html