标签:单个字符 src 字符数组 equals false 大小 mamicode 参数 根据
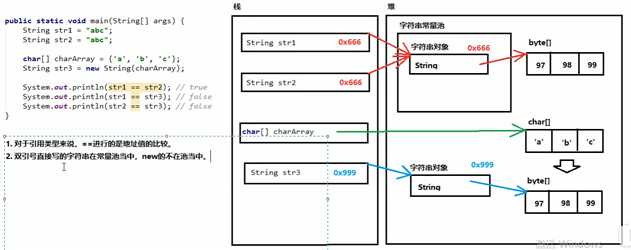
java.lang.String类代表字符串
程序中所有双引号字符串,都是String对象(就算没有new,也是对象)
字符串特点:
1.字符串内容永不改变
2.由于字符串内容不改变,所以字符串可以共享使用(常量池)
3.字符串效果上相当于char[]字符数组,但是底层原理是byte[]字节数组
字符串创建方法:
1.public String():创建一个空白字符串,不含任何内容
String str = new String();
2.public String(char[] array):根据字符数组内容,来创建相应的字符串
char[] array = {‘a‘, ‘b‘, ‘c‘};
String str = new String(array)
3.public String(byte[] array):根据字节数组内容,来创建相应的字符串
byte[] array = {97, 98, 99};
String str = new String(array);
4.直接创建 String str = "abc";
字符串常量池:程序当中直接写上的双引号字符串,就在字符串常量池中。
对于基本类型,==是对进行数值的比较
对于引用类型,==是对进行地址值的比较
String类常用方法:
1.public boolean equals(object obj):参数可以是任何对象,只有参数是一个字符串并且内容相同才会给出true,否则false
任何对象都能被 obejct 接收
str1 = "hello";
char[] array = {‘a‘, ‘b‘, ‘c‘};
String str2 = new String(array);
sout(str1.equals(str2)); //false
sout("hello".equals(str1)); //true
一般常量放前面,变量放后面
这个方法区分大小写
2.public boolean equalsIgnoreCase(object obj):英文不区分大小写的比较
3.public int length():获取字符串中含字符个数,得到字符串长度
4.public String concat(String str):将当前字符串和参数字符串,拼接成为一个新的字符串并返回
String str1 = "hello"
String str2 = "world"
String str3 = str1.concat(str2); helloworld
5.public char charAt(int index):获取指定位置的单个字符(从0开始)
String str1 = "hello";
char ch = str1.charAt(1) // ch = e
6.public int indexOf(String str):查找参数字符串,在本字符串当中首次出现的索引位置,如果没有,返回值为-1
String str1 = "helloworld";
int num = str1.indexOf("llo"); // num = 2
int num = str1.indexOf("abc"); // num = -1
标签:单个字符 src 字符数组 equals false 大小 mamicode 参数 根据
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/aoligei/p/12358299.html