标签:有序 有序链表 地址 nlogn 时间 temp img 递归 技术
题目描述:将两个有序链表合并为一个新的有序链表并返回。新链表是通过拼接给定的两个链表的所有节点组成的。

单链表的定义

思路:思路一,将遍历两个链表存入列表中,对列表进行排序后再输出即可。思路二:递归方法。思路三:迭代方法。
(1)思路一:使用sort函数列表中的元素从小到大排列,然后遍历列表,以链表的形式输出即可。对本人来说不太熟练的地方在于,如何将列表中的元素以链表的形式输出。首先定义一个空链表node作为中间链表 Listnode(Node) , 用一个ans指向这个中间链表的地址。
1 class Solution: 2 def mergeTwoLists(self, l1: ListNode, l2: ListNode) -> ListNode: 3 #用列表的方法 4 if l1 is None or l2 is None: 5 return l2 or l1 6 node = ListNode(None) #创建空链表的空头节点 7 ans = node #ans指向node链表 8 temp_list = [] 9 while l1: 10 temp_list.append(l1.val) 11 l1 = l1.next 12 while l2: 13 temp_list.append(l2.val) 14 l2 =l2.next 15 temp_list.sort() 16 for i in range(len(temp_list)): 17 node.val = temp_list[i] 18 if i < len(temp_list)-1: 19 node.next = ListNode(None) #创建一个新的空next节点 20 node = node.next 21 return ans
时间复杂度:由于sort()函数的时间复杂度为O(nlogn),因此本算法的时间复杂度为O((m+n)log(m+n)) 空间复杂度:O(m+n)
(2)思路二:递归方法。
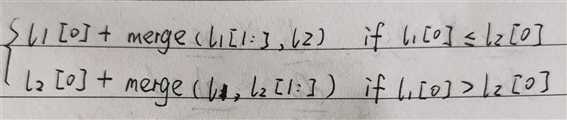
1 class Solution: 2 def mergeTwoLists(self, l1, l2): 3 if l1 == None or l2 == None: 4 return l2 or l1 5 if l1.val < l2.val: 6 l1.next = self.mergeTwoLists(l1.next,l2) 7 return l1 8 else: 9 l2.next = self.mergeTwoLists(l1,l2.next) 10 return l2
递归方法的主要问题在于要找出递归公式。
(3)思路三:迭代法。用指针head指向要返回链表的头节点,pre表示当前节点。当链表l1中节点的值比较小时,则pre.next指向该节点,并更行pre到当前节点,同时l1中的指针也移动到下一个节点。
1 class Solution: 2 def mergeTwoLists(self, l1: ListNode, l2: ListNode) -> ListNode: 3 #迭代方法 4 head = Listnode(-1) 5 pre = head 6 while l1 and l2: 7 if l1.val <= l2.val: 8 pre.next = l1 9 l1 = l1.next 10 else: 11 pre.next = l2 12 l2 = l2.next 13 pre =pre.next 14 pre = l1 if l1 is not None else l2 15 return head.next
标签:有序 有序链表 地址 nlogn 时间 temp img 递归 技术
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/shawn-young/p/12427255.html