标签:迷宫问题 and stack 一个 解决 line bre 回溯法 def

python实现迷宫问题的栈和队列的解决方法:
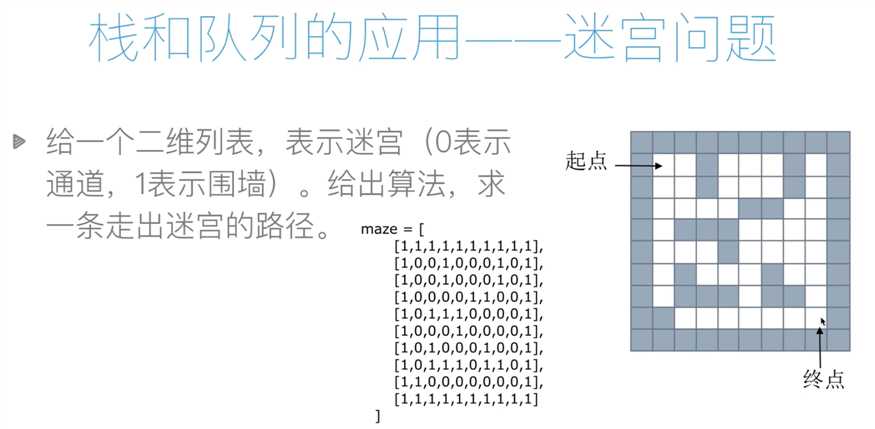
#迷宫问题
#表示迷宫的颜色,0表示路通,1表示围墙
maze=[
[1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1],
[1,0,0,1,0,0,0,1,0,1],
[1,0,0,1,0,0,0,1,0,1],
[1,0,0,0,0,1,1,0,0,1],
[1,0,1,1,1,0,0,0,0,1],
[1,0,0,0,1,0,0,0,0,1],
[1,0,1,0,0,0,1,0,0,1],
[1,0,1,1,1,0,1,1,0,1],
[1,1,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,1],
[1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1]
]
d=[
lambda x,y:(x+1,y),
lambda x,y:(x-1,y),
lambda x,y:(x,y+1),
lambda x,y:(x,y-1)
]
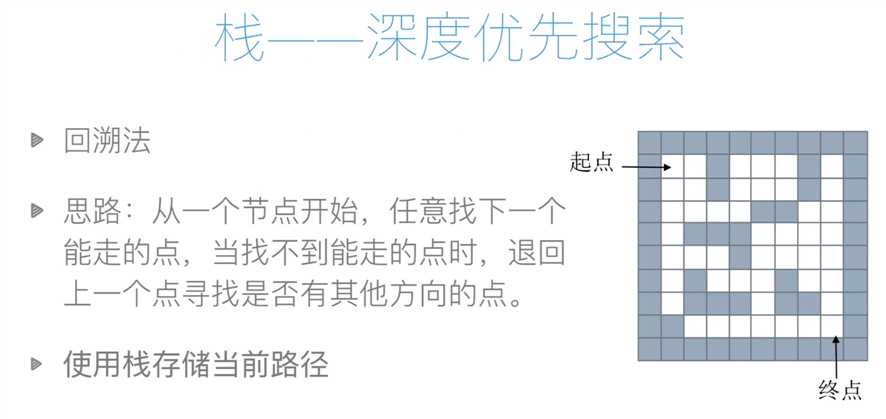
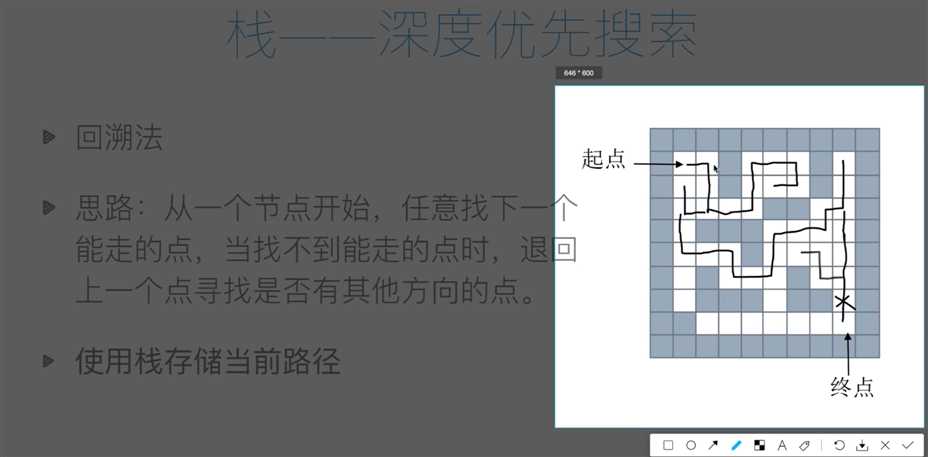
#方法1:使用栈来进行解决,方法是回溯法,即深度优先搜索,但是并非是最佳最短的路线
def maze_path(x1,y1,x2,y2):
stack=[]
stack.append((x1,y1))
while(len(stack)>0):
curnode=stack[-1]
if curnode[0]==x2 and curnode[1]==y2:
for path in stack:
print(path)
return True
for i in d:
nextnode=i(curnode[0],curnode[1])
#如果下一个位置可以走
if maze[nextnode[0]][nextnode[1]]==0:
stack.append(nextnode)
maze[nextnode[0]][nextnode[1]]= 2 #2表示走过了
break
else:
maze[nextnode[0]][nextnode[1]] =2
stack.pop()
else:
print("没路")
return False
maze_path(1,1,8,8)
maze=[
[1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1],
[1,0,0,1,0,0,0,1,0,1],
[1,0,0,1,0,0,0,1,0,1],
[1,0,0,0,0,1,1,0,0,1],
[1,0,1,1,1,0,0,0,0,1],
[1,0,0,0,1,0,0,0,0,1],
[1,0,1,0,0,0,1,0,0,1],
[1,0,1,1,1,0,1,1,0,1],
[1,1,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,1],
[1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1]
]
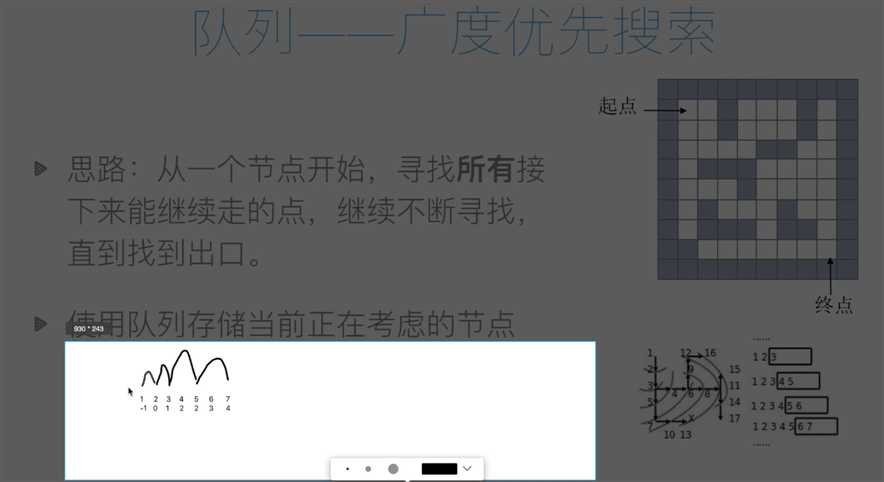
#解决方法2:使用队列来进行记录,属于广度优先搜索
from collections import deque #导入队列的内置模块
#输出路径函数
def print_r(path):
real_path=[]
i=len(path)-1
while i>=0:
real_path.append(path[i][0:2])
i=path[i][2]
real_path.reverse()
for p in real_path:
print(p)
def maze_path1(x1,y1,x2,y2):
quede=deque()
path=[]
quede.append((x1,y1,-1))
while len(quede)>0:
curnode=quede.popleft()
path.append(curnode)
if curnode[0]==x2 and curnode[1]==y2:
#到达终点
print_r(path)
for dir in d:
nextnode=dir(curnode[0],curnode[1])
if maze[nextnode[0]][nextnode[1]]==0:
quede.append((nextnode[0],nextnode[1],len(path)-1))
maze[nextnode[0]][nextnode[1]] =2 #标记已经走过
return False
maze_path1(1,1,8,8)
标签:迷宫问题 and stack 一个 解决 line bre 回溯法 def
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/Yanjy-OnlyOne/p/12433325.html