标签:style blog http io color ar os 使用 for
设计模式 组合模式
将对象合成树型结构以表示【部分-整体】的层次结构。组合模式使得用户对单个对象
和组合对象的使用具有一致性。
当发现需求中是体现部分与整体层次的结构时,以及你希望用户可以忽略组合对象与
单个对象的不同,统一地使用组合结构中的所有对象时,就应该考虑组合模式。
从编码上看,【组合模式】至少包含这几个部分:
1、一个只包含接口的类CComponent
2、一个继承自CComponent类的子类,该类实现了父类的所有接口,并且有一个父类
对象(C++里应该是指针)的集合,用来在运行时多态的调用CComponent其他子类的函数
3、若干个其他继承自CComponet的子类,实现了父类的所有接口
************************************************************************/
/* 设计模式
组合模式
将对象合成树型结构以表示【部分-整体】的层次结构。组合模式使得用户对单个对象
和组合对象的使用具有一致性。
当发现需求中是体现部分与整体层次的结构时,以及你希望用户可以忽略组合对象与
单个对象的不同,统一地使用组合结构中的所有对象时,就应该考虑组合模式。
从编码上看,【组合模式】至少包含这几个部分:
1、一个只包含接口的类CComponent
2、一个继承自CComponent类的子类,该类实现了父类的所有接口,并且有一个父类
对象(C++里应该是指针)的集合,用来在运行时多态的调用CComponent其他子类的函数
3、若干个其他继承自CComponet的子类,实现了父类的所有接口
/************************************************************************/
#include "stdafx.h"
#include <list>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
#include <iostream>
//抽象基类,只包含若干接口
class CComponent
{
public:
CComponent(string strCompanyName);
virtual ~CComponent();
virtual void Add(CComponent* pComponent) = 0;
virtual void Remove() = 0;
virtual void Work() = 0; //工作函数
protected:
string m_strCompanyName;
};
CComponent::CComponent(string strCompanyName) : m_strCompanyName(strCompanyName)
{}
CComponent::~CComponent()
{
}
//用来管理其他子类的类,实现了所有父类的接口
//有一个包含父类对象(指针)的集合
class CComposite : public CComponent
{
public:
CComposite(string strCompanyName);
virtual ~CComposite();
virtual void Add(CComponent* pComponent);
virtual void Remove();
virtual void Work(); //工作函数,运行时被不尽相同的类对象调用
protected:
list<CComponent*> m_lstComponents; //父类指针的集合,运行时多态
};
CComposite::CComposite(string strCompanyName) : CComponent(strCompanyName)
{
}
CComposite::~CComposite()
{
}
void CComposite::Add(CComponent* pComponent)
{
m_lstComponents.push_back(pComponent);
}
void CComposite::Remove()
{
}
void CComposite::Work()
{
for (list<CComponent*>::const_iterator iter = m_lstComponents.begin();
iter != m_lstComponents.end(); ++ iter)
{
if(NULL != *iter)
(*iter)->Work();
}
}
//抽象基类的一个具体子类,实现的接口中只包含跟自己业务有关的代码
//不用管其他子类
class A : public CComponent
{
public:
A(string strName);
virtual ~A();
virtual void Add(CComponent* pComponent);
virtual void Remove();
virtual void Work();
};
A::A(string strName) : CComponent(strName)
{
}
A::~A()
{
}
void A::Add(CComponent* pComponent)
{
}
void A::Remove()
{
}
void A::Work()
{
cout << m_strCompanyName << "::A::work-------" << endl;
}
//抽象基类的另一个具体子类,实现接口时也只包含跟自己业务有关的代码
//而不用管其他具体子类
class B : public CComponent
{
public:
B(string strName);
virtual ~B();
virtual void Add(CComponent* pComponent);
virtual void Remove();
virtual void Work();
};
B::B(string strName) : CComponent(strName)
{
}
B::~B()
{
}
void B::Add(CComponent* pComponent)
{
}
void B::Remove()
{
}
void B::Work()
{
cout << m_strCompanyName << "::B::work**********" << endl;
}
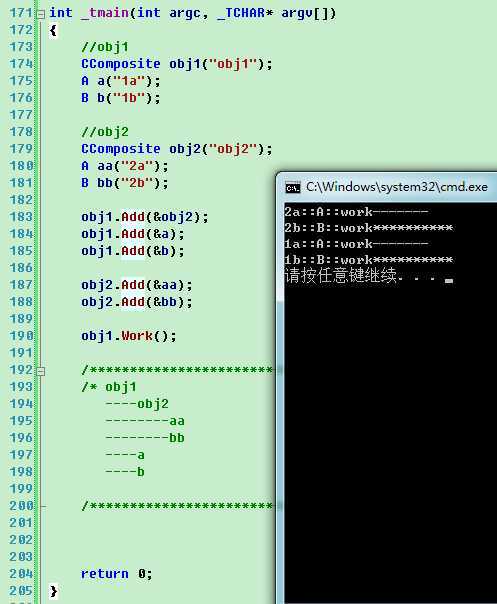
int _tmain(int argc, _TCHAR* argv[])
{
//obj1
CComposite obj1("obj1");
A a("1a");
B b("1b");
//obj2
CComposite obj2("obj2");
A aa("2a");
B bb("2b");
obj1.Add(&obj2);
obj1.Add(&a);
obj1.Add(&b);
obj2.Add(&aa);
obj2.Add(&bb);
obj1.Work();
/************************************************************************/
/* obj1
----obj2
--------aa
--------bb
----a
----b
/************************************************************************/
return 0;
}
运行结果
标签:style blog http io color ar os 使用 for
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/cuish/p/4075232.html