标签:current alt 显示 sem void point 最优 说明 算法
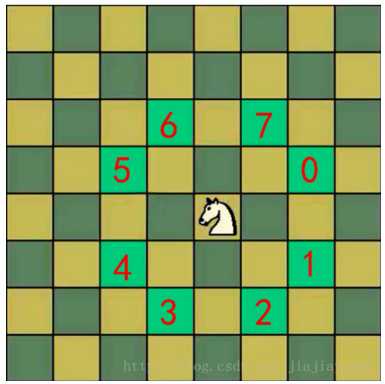
将马随机放在国际象棋的8×8棋盘的某个方格中,马按走棋规则进行移动。要求每个方格只进入一次,走遍棋盘上全部64个方格
public class TravelChessBoard {
private static int X; // 棋盘列数
private static int Y; // 棋盘行数
private static int[][] chessBoard;
// 标记整个棋盘各个位置的访问情况(一维)
private static boolean[] isVisited;
// 所有位置是否都已被访问
private static boolean finished;
public static void main(String[] args) {
X = 8;
Y = 8;
chessBoard = new int[Y][X];
isVisited = new boolean[X * Y];
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
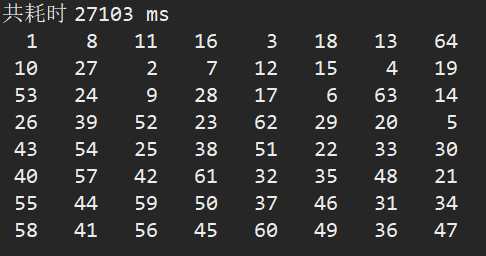
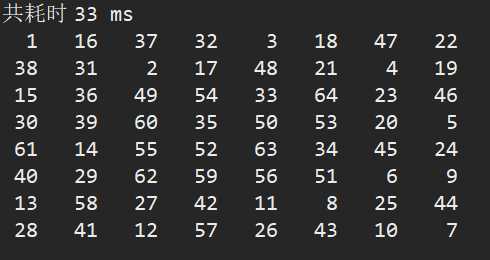
travelChessBoard(0, 0, 1); // 假定初始位置 (0,0)
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("共耗时 " + (end - start) + " ms");
// 输出棋盘
for(int[] rows : chessBoard) {
for(int step : rows)
System.out.printf("%3d ", step);
System.out.println();
}
}
/**
* 骑士周游问题
* @param row 马当前的行坐标[0...X-1]
* @param col 马当前的纵坐标[0...Y-1]
* @param step 当前这是第几步 (初始值1; 刚开始把马放到棋盘上就已经算第1步了)
*/
public static void travelChessBoard(int row, int col, int step) {
// 假定可以 (? ?_?)?
chessBoard[row][col] = step;
isVisited[row * X + col] = true;
ArrayList<Point> nextList = getNextPositions(new Point(col, row));
sortByNextSize(nextList); // 用贪心优化
while(! nextList.isEmpty()) {
Point p = nextList.remove(0);
// 判断该点是否已经访问过
if(! isVisited[p.y * X + p.x])
travelChessBoard(p.y, p.x, step + 1);
} // 说明当前这个位置没有可走的下一步了
if(step < X * Y && ! finished) {
// 实则不行 (*/ω\*)
chessBoard[row][col] = 0;
isVisited[row * X + col] = false;
} else {
// 成了 (●ˇ?ˇ●)
finished = true;
}
}
public static void sortByNextSize(ArrayList<Point> list) {
// 根据 {当前nextList中每个Point的nextList的元素数目} 对 当前nextList 进行升序排序
list.sort(new Comparator<Point>() {
@Override
public int compare(Point o1, Point o2) {
int size1 = getNextPositions(o1).size();
int size2 = getNextPositions(o2).size();
// ASC
if(size1 < size2)
return -1;
else if(size1 > size2)
return 1;
else
return 0;
}
});
}
/**
* 根据 马 的当前位置, 计算出马的下一步可以走哪些位置
* @param curPoint 封装马当前位置的Point对象
* @return 下一步可走位置组成的集合
*/
public static ArrayList<Point> getNextPositions(Point curPoint) {
ArrayList<Point> nextList = new ArrayList<>();
Point p1 = new Point();
// 能不能走 (5) 的位置
if((p1.x = curPoint.x - 2) >= 0 && (p1.y = curPoint.y - 1) >= 0)
nextList.add(new Point(p1));
// 能不能走 (6) 的位置
if((p1.x = curPoint.x - 1) >= 0 && (p1.y = curPoint.y - 2) >= 0)
nextList.add(new Point(p1));
// 能不能走 (7) 的位置
if((p1.x = curPoint.x + 1) < X && (p1.y = curPoint.y - 2) >= 0)
nextList.add(new Point(p1));
// 能不能走 (0) 的位置
if((p1.x = curPoint.x + 2) < X && (p1.y = curPoint.y - 1) >= 0)
nextList.add(new Point(p1));
// 能不能走 (1) 的位置
if((p1.x = curPoint.x + 2) < X && (p1.y = curPoint.y + 1) < Y)
nextList.add(new Point(p1));
// 能不能走 (2) 的位置
if((p1.x = curPoint.x + 1) < X && (p1.y = curPoint.y + 2) < Y)
nextList.add(new Point(p1));
// 能不能走 (3) 的位置
if((p1.x = curPoint.x - 1) >= 0 && (p1.y = curPoint.y + 2) < Y)
nextList.add(new Point(p1));
// 能不能走 (4) 的位置
if((p1.x = curPoint.x - 2) >= 0 && (p1.y = curPoint.y + 1) < Y)
nextList.add(new Point(p1));
return nextList;
}
}
标签:current alt 显示 sem void point 最优 说明 算法
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/liujiaqi1101/p/12489986.html