标签:集合 nbsp 重复判断 无法 创建 pre table instance img
ConcurrentHashMap性能高于HashTable,都能够完成线程安全操作,
Hashtable中线程安全使用synchronized同步方法进行加锁操作,如果当前一个线程正在访问该集合,其他线程是无法进行访问的,需要进行等待
反之ConcurrentHashMap当中采用分段锁机制
JDK1.7和JDK1.8底层实现的区别
JDK1.8版本之前,ConcurrentHashMap使用分段锁技术,将数据分成一段一段的进行村粗,每一个数据段配置一把锁Segment(继承ReentrantLock)
底层采用:Segment+HashEntry
当数据添加时,根据key值找到Segment对应的数据段,然后匹配数据块,采用链表方式进行存储
1.1JDK1.7底层实现
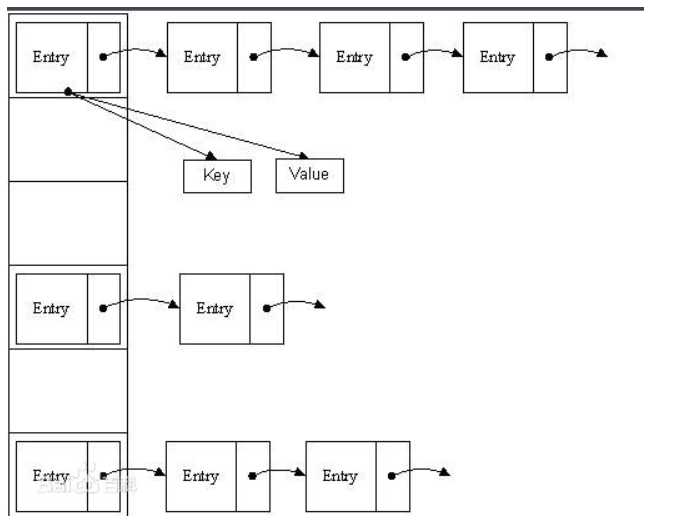
在JDK1.7版本中,ConcurrentHashMap的数据结构是由一个Segment数组和多个HashEntry组成:
Segment数组的意义就是将一个大的table分割成多个小的table来进行加锁,也就是上面的提到的锁分离技术,而每一个Segment元素存储的是HashEntry数组+链表,这个和HashMap的数据存储结构一样
1.2JDK1.8底层实现
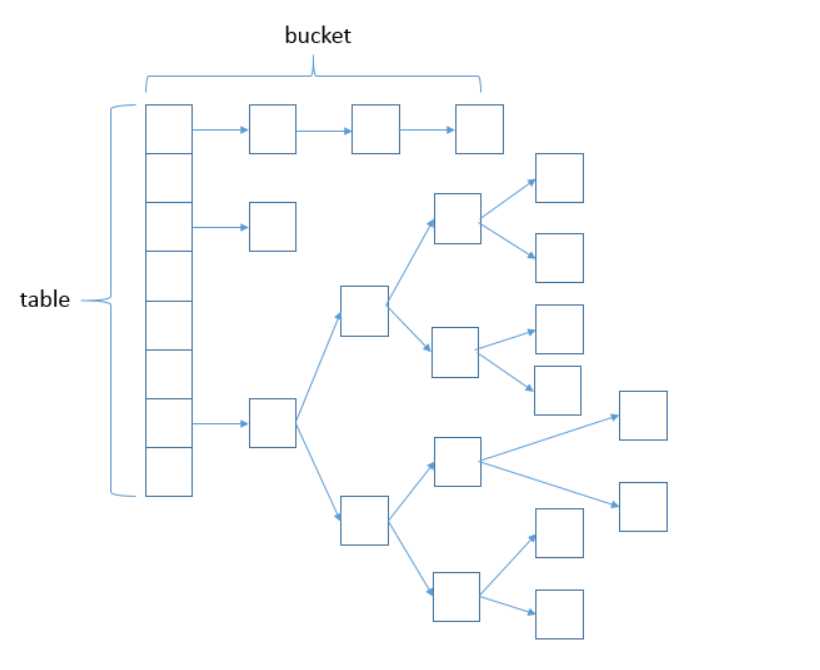
JDK1.8的实现已经摒弃了Segment的概念,而是直接用Node数组+链表+红黑树的数据结构来实现,并发控制使用Synchronized和CAS来操作,整个看起来就像是优化过且线程安全的HashMap,虽然在JDK1.8中还能看到Segment的数据结构,但是已经简化了属性,只是为了兼容旧版本
ConcurrentHashMap底层put方法实现的核心逻辑
public V put(K key, V value) {
return putVal(key, value, false);
}
/** Implementation for put and putIfAbsent */
final V putVal(K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent) {
if (key == null || value == null) throw new NullPointerException(); //判断key和value是否为空,如果为空则报异常
int hash = spread(key.hashCode()); //重新计算key的hash值,有效减少Hash值冲突
int binCount = 0;
for (Node<K,V>[] tab = table;;) { //遍历当前数组当中所有的数据
Node<K,V> f; int n, i, fh;
if (tab == null || (n = tab.length) == 0) //判断数组是否为空
tab = initTable(); //如果为空要进行数组的初始化操作
else if ((f = tabAt(tab, i = (n - 1) & hash)) == null) { //根据key的Hash值找到位置,如果该位置没有元素
if (casTabAt(tab, i, null,
new Node<K,V>(hash, key, value, null))) //获取到空的元素,然后重新创建一个新的Node放进去
break; // no lock when adding to empty bin
}
else if ((fh = f.hash) == MOVED) //判断当前数组元素状态是否需要扩容
tab = helpTransfer(tab, f);
else {
V oldVal = null;
synchronized (f) { //加锁
if (tabAt(tab, i) == f) {
if (fh >= 0) {
binCount = 1;
for (Node<K,V> e = f;; ++binCount) {
K ek;
if (e.hash == hash && //判断添加的key和原有key进行Hash值判断以及key值判断,如果相等则覆盖
((ek = e.key) == key ||
(ek != null && key.equals(ek)))) {
oldVal = e.val;
if (!onlyIfAbsent)
e.val = value;
break;
}
Node<K,V> pred = e;
if ((e = e.next) == null) { //判断当前节点的下一个节点是否为空,如果为空则添加到下一个节点当中
pred.next = new Node<K,V>(hash, key,
value, null);
break;
}
}
}
else if (f instanceof TreeBin) { //判断当前节点是否为红黑树
Node<K,V> p;
binCount = 2;
if ((p = ((TreeBin<K,V>)f).putTreeVal(hash, key,
value)) != null) { //如果为红黑树则创建一个树节点
oldVal = p.val;
if (!onlyIfAbsent)
p.val = value;
}
}
}
}
if (binCount != 0) {
if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD) //根据当前循环次数判断链表中存在多少个数据,如果数据阀值大于等于8
//则进行红黑树转换
treeifyBin(tab, i);
if (oldVal != null)
return oldVal;
break;
}
}
}
addCount(1L, binCount); //判断是否需要扩容
return null;
}
put方法核心
public V put(K key, V value) {
//计算key的Hash值,然后将Hash值以及key值本身和Value传递到putval方法当中
return putVal(hash(key), key, value, false, true);
}
final V putVal(int hash, K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent,
boolean evict) {
Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> p; int n, i;
if ((tab = table) == null || (n = tab.length) == 0) //判断当前数组是否为空,如果为空要进行第一次扩容
n = (tab = resize()).length; //扩容后将扩容大小交给N
if ((p = tab[i = (n - 1) & hash]) == null) //判断获取当前数组位置是否存在数据,如果为空则直接插入,否则需要代表当前位置不是空的,不是空的需要判断
tab[i] = newNode(hash, key, value, null); //如果为空则创建一个新的节点添加到该位置
else {
Node<K,V> e; K k;
if (p.hash == hash && ((k = p.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k)))) //判断Hash值和Key值是否相同,如果相同则需要Value覆盖
e = p;
else if (p instanceof TreeNode) //判断当前数组中存放的节点是否是树节点
e = ((TreeNode<K,V>)p).putTreeVal(this, tab, hash, key, value); //则添加树节点即可
else {
for (int binCount = 0; ; ++binCount) { //循环遍历链表
if ((e = p.next) == null) { //判断当前数组该位置的值得下一个元素是否为空,如果为空则追加到当前元素后边
p.next = newNode(hash, key, value, null);
if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD - 1) // -1 for 1st //添加完毕后判断当前链表节点有多少个,如果节点大于等于8则转换为红黑树
treeifyBin(tab, hash); //treeifyBin判断当前数组是否为空,或者长度是否小于64,如果为空或者小于64
//则先扩容
break;
}
if (e.hash == hash &&
((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k)))) //再次进行Key的重复判断
break;
p = e;
}
}
if (e != null) { // existing mapping for key
V oldValue = e.value;
if (!onlyIfAbsent || oldValue == null)
e.value = value;
afterNodeAccess(e);
return oldValue;
}
}
++modCount;
if (++size > threshold) //判断当前数组元素个数和阀值进行比较,如果数量大于阀值则需要扩容
resize(); //默认情况下,第一次添加数据的时候,先会进行一次扩容后再添加数据
afterNodeInsertion(evict); //后续都是先添加数据再扩容
return null;
}
扩容: 默认情况下,数组大小为16,当数组元素 超过大小*负载因子(0.75),如果超过12个元素,则调用resize进行扩容,扩容原来大小的2倍并且重新计算数组中元素的位置,所以比较耗费性能,一般创建集合尽量预知大小,避免多次扩容
get方法核心逻辑:
final Node<K,V> getNode(int hash, Object key) {
Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> first, e; int n; K k;
if ((tab = table) != null && (n = tab.length) > 0 &&
(first = tab[(n - 1) & hash]) != null) { //判断数组以及数组对应位置数组元素是否为空
if (first.hash == hash && // always check first node
((k = first.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k)))) //用get传递过来的Key值和对应位置第一个元素进行比较,如果相等直接返回,如果不等则进行查找
return first;
if ((e = first.next) != null) { //判断第一个元素的下一个元素是否为空,如果不为空
if (first instanceof TreeNode) //如果不为空判断当前节点是否为树节点
return ((TreeNode<K,V>)first).getTreeNode(hash, key); //如果是树节点,直接通过getTreeNode拿到该节点返回
do {
if (e.hash == hash &&
((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k)))) //循环一一对比
return e;
} while ((e = e.next) != null);
}
}
return null;
}
标签:集合 nbsp 重复判断 无法 创建 pre table instance img
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/danxun/p/12512646.html