标签:== namespace names read sizeof btn open ems wrap
在一个遥远的国度,一侧是风景秀美的湖泊,另一侧则是漫无边际的沙漠。该国的行政区划十分特殊,刚好构成一个NN 行\times M×M 列的矩形,如上图所示,其中每个格子都代表一座城市,每座城市都有一个海拔高度。
为了使居民们都尽可能饮用到清澈的湖水,现在要在某些城市建造水利设施。水利设施有两种,分别为蓄水厂和输水站。蓄水厂的功能是利用水泵将湖泊中的水抽取到所在城市的蓄水池中。
因此,只有与湖泊毗邻的第11 行的城市可以建造蓄水厂。而输水站的功能则是通过输水管线利用高度落差,将湖水从高处向低处输送。故一座城市能建造输水站的前提,是存在比它海拔更高且拥有公共边的相邻城市,已经建有水利设施。由于第NN 行的城市靠近沙漠,是该国的干旱区,所以要求其中的每座城市都建有水利设施。那么,这个要求能否满足呢?如果能,请计算最少建造几个蓄水厂;如果不能,求干旱区中不可能建有水利设施的城市数目。
每行两个数,之间用一个空格隔开。输入的第一行是两个正整数N,MN,M,表示矩形的规模。接下来NN 行,每行MM 个正整数,依次代表每座城市的海拔高度。
两行。如果能满足要求,输出的第一行是整数11,第二行是一个整数,代表最少建造几个蓄水厂;如果不能满足要求,输出的第一行是整数00,第二行是一个整数,代表有几座干旱区中的城市不可能建有水利设施。
2 5 9 1 5 4 3 8 7 6 1 2
1 1
3 6 8 4 5 6 4 4 7 3 4 3 3 3 3 2 2 1 1 2
1 3
【样例1 说明】
只需要在海拔为99 的那座城市中建造蓄水厂,即可满足要求。
【样例2 说明】
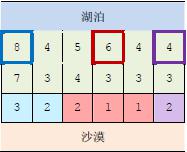
上图中,在33个粗线框出的城市中建造蓄水厂,可以满足要求。以这33个蓄水厂为源头在干旱区中建造的输水站分别用3 种颜色标出。当然,建造方法可能不唯一。
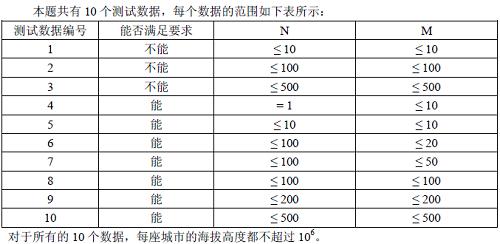
【数据范围】
思路
当有解时可知沙漠上面的城市都是可以和水边的城市形成连通块的.
通过记忆化搜索记录所有连通块在最底部的左端点和右端点, 看区间是否能覆盖沙漠上城市
CODE

1 #include <bits/stdc++.h> 2 #define dbg(x) cout << #x << "=" << x << endl 3 #define eps 1e-8 4 #define pi acos(-1.0) 5 6 using namespace std; 7 typedef long long LL; 8 9 const int inf = 0x3f3f3f3f; 10 11 template<class T>inline void read(T &res) 12 { 13 char c;T flag=1; 14 while((c=getchar())<‘0‘||c>‘9‘)if(c==‘-‘)flag=-1;res=c-‘0‘; 15 while((c=getchar())>=‘0‘&&c<=‘9‘)res=res*10+c-‘0‘;res*=flag; 16 } 17 18 namespace _buff { 19 const size_t BUFF = 1 << 19; 20 char ibuf[BUFF], *ib = ibuf, *ie = ibuf; 21 char getc() { 22 if (ib == ie) { 23 ib = ibuf; 24 ie = ibuf + fread(ibuf, 1, BUFF, stdin); 25 } 26 return ib == ie ? -1 : *ib++; 27 } 28 } 29 30 int qread() { 31 using namespace _buff; 32 int ret = 0; 33 bool pos = true; 34 char c = getc(); 35 for (; (c < ‘0‘ || c > ‘9‘) && c != ‘-‘; c = getc()) { 36 assert(~c); 37 } 38 if (c == ‘-‘) { 39 pos = false; 40 c = getc(); 41 } 42 for (; c >= ‘0‘ && c <= ‘9‘; c = getc()) { 43 ret = (ret << 3) + (ret << 1) + (c ^ 48); 44 } 45 return pos ? ret : -ret; 46 } 47 48 const int maxn = 507; 49 50 int a[maxn][maxn]; 51 bool vis[maxn][maxn]; 52 int l[maxn][maxn], r[maxn][maxn]; 53 54 int dr[4] = {1, 0, -1, 0}; 55 int dc[4] = {0, 1, 0, -1}; 56 57 int n, m; 58 59 void dfs(int x, int y) { 60 vis[x][y] = 1; 61 //printf("x:%d y:%d\n",x, y); 62 for ( int i = 0; i < 4; ++i ) { 63 int nx = x + dr[i]; 64 int ny = y + dc[i]; 65 if(nx < 1 || nx > n || ny < 1 || ny > m || a[nx][ny] >= a[x][y]) { 66 continue; 67 } 68 if(!vis[nx][ny]) { 69 dfs(nx, ny); 70 } 71 l[x][y] = min(l[x][y], l[nx][ny]); 72 r[x][y] = max(r[x][y], r[nx][ny]); 73 } 74 } 75 76 int main() 77 { 78 read(n); 79 read(m); 80 memset(r, 0, sizeof(r)); 81 memset(l, 0x3f, sizeof(l)); 82 83 for ( int i = 1; i <= n; ++i ) { 84 for ( int j = 1; j <= m; ++j ) { 85 read(a[i][j]); 86 } 87 } 88 for ( int i = 1; i <= m; ++i ) { 89 l[n][i] = r[n][i] = i; 90 } 91 int ok = 1; 92 int ans = 0; 93 for ( int i = 1; i <= m; ++i ) { 94 if(!vis[1][i]) { 95 dfs(1, i); 96 } 97 } 98 for ( int i = 1; i <= m; ++i ) { 99 if(!vis[n][i]) { 100 ok = 0; 101 ++ans; 102 } 103 } 104 if(!ok) { 105 printf("0\n%d\n",ans); 106 return 0; 107 } 108 int left = 1; 109 while(left <= m) { 110 //dbg(left); 111 int maxx = 0; 112 for ( int i = 1; i <= m; ++i ) { 113 if(l[1][i] <= left) { 114 maxx = max(maxx, r[1][i]); 115 } 116 } 117 ++ans; 118 left = maxx + 1; 119 } 120 printf("1\n%d\n",ans); 121 return 0; 122 }
标签:== namespace names read sizeof btn open ems wrap
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/orangeko/p/12514477.html