标签:add 窗口 数据 登陆方式 ethernet containe set get kth
网络嗅探与协议分析
分析的软件名称为winpcap是一款开源的抓包软件。
// 以太网协议格式的定义
typedef struct ether_header {
u_char ether_dhost[6]; // 目标MAC地址
u_char ether_shost[6]; // 源MAC地址
u_short ether_type; // 以太网类型
}ether_header;
// 用户保存4字节的IP地址
typedef struct ip_address {
u_char byte1;
u_char byte2;
u_char byte3;
u_char byte4;
}ip_address;
// 用于保存IPV4的首部
typedef struct ip_header {
u_char version_hlen; // 首部长度 版本
u_char tos; // 服务质量
u_short tlen; // 总长度
u_short identification; // 身份识别
u_short flags_offset; // 标识 分组偏移
u_char ttl; // 生命周期
u_char proto; // 协议类型
u_short checksum; // 包头测验码
u_int saddr; // 源IP地址
u_int daddr; // 目的IP地址
}ip_header;
// 用于保存TCP首部
typedef struct tcp_header {
u_short sport;
u_short dport;
u_int sequence; // 序列码
u_int ack; // 回复码
u_char hdrLen; // 首部长度保留字
u_char flags; // 标志
u_short windows; // 窗口大小
u_short checksum; // 校验和
u_short urgent_pointer; // 紧急指针
}tcp_header;
// 用于保存UDP的首部
typedef struct udp_header {
u_short sport; // 源端口
u_short dport; // 目标端口
u_short datalen; // UDP数据长度
u_short checksum; // 校验和
}udp_header;
// 用于保存ICMP的首部
typedef struct icmp_header {
u_char type; // ICMP类型
u_char code; // 代码
u_short checksum; // 校验和
u_short identification; // 标识
u_short sequence; // 序列号
u_long timestamp; // 时间戳
}icmp_header;
// 用于保存ARP的首部
typedef struct arp_header {
u_short hardware_type; // 格式化的硬件地址
u_short protocol_type; // 协议地址格式
u_char hardware_length; // 硬件地址长度
u_char protocol_length; // 协议地址长度
u_short operation_code; // 操作码
u_char source_ethernet_address[6]; // 发送者硬件地址
u_char source_ip_address[4]; // 发送者协议地址
u_char destination_ethernet_address[6]; // 目的方硬件地址
u_char destination_ip_address[4]; // 目的方协议地址
}arp_header;
ipv4报文的格式。
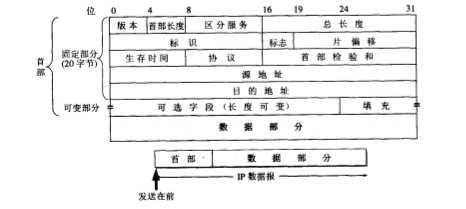
TCP报文首部的格式。
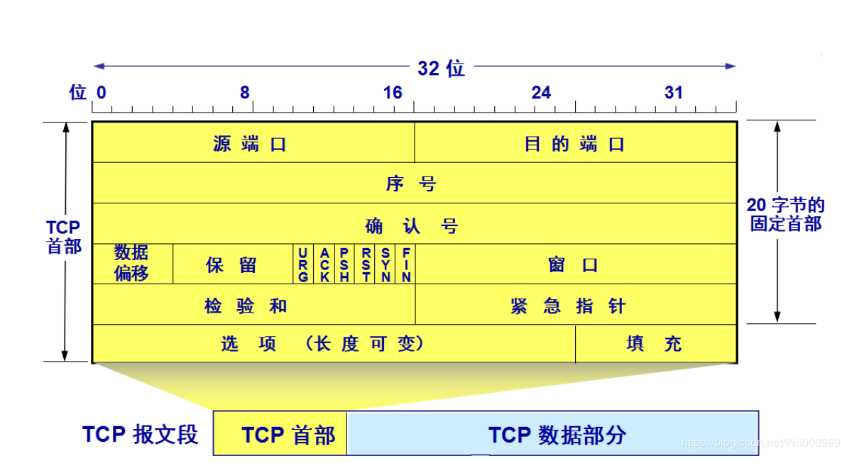
UDP报文首部的格式。
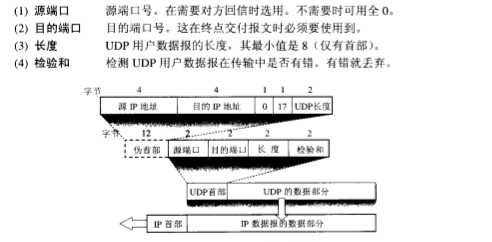
ICMP报文首部的格式。用于在IP主机、路由器之间传递控制消息。控制消息是指网络通不通、主机是否可达、路由是否可用等网络本身的消息。
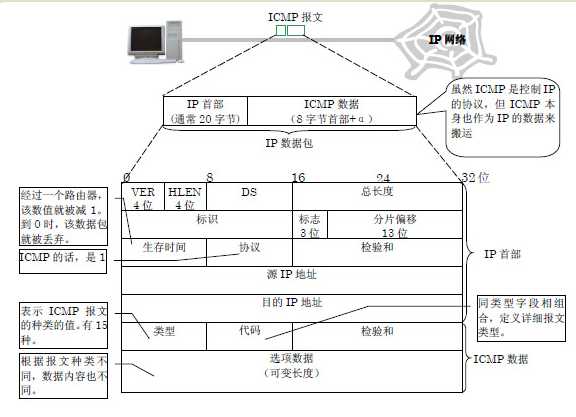
ARP报文格式。arp协议是根据IP地址获取物理地址的一个TCP/IP协议。
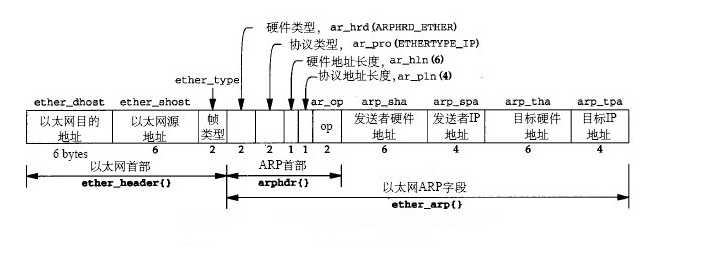
首先根据ethernet_type判断以太网类型
void ethernet_protocol_packet_handle(u_char *arg, const struct pcap_pkthdr *pkt_header, const u_char *pkt_content)
{
ether_header *ethernet_protocol;//以太网协议
u_short ethernet_type; //以太网类型
u_char *mac_string; //以太网地址
//获取以太网数据内容
ethernet_protocol = (ether_header*)pkt_content;
ethernet_type = ntohs(ethernet_protocol->ether_type);
printf("==============Ethernet Protocol=================\n");
//以太网目标地址
mac_string = ethernet_protocol->ether_dhost;
printf("Destination Mac Address: %02x:%02x:%02x:%02x:%02x:%02x\n",
*mac_string,
*(mac_string + 1),
*(mac_string + 2),
*(mac_string + 3),
*(mac_string + 4),
*(mac_string + 5));
//以太网源地址
mac_string = ethernet_protocol->ether_shost;
printf("Source Mac Address: %02x:%02x:%02x:%02x:%02x:%02x\n",
*mac_string,
*(mac_string + 1),
*(mac_string + 2),
*(mac_string + 3),
*(mac_string + 4),
*(mac_string + 5));
printf("Ethernet type: ");
switch (ethernet_type)
{
case 0x0800:
printf("%s", "IP");
break;
case 0x0806:
printf("%s", "ARP");
break;
case 0x0835:
printf("%s", "RARP");
break;
default:
printf("%s", "Unknown Protocol");
break;
}
printf(" (0x%04x)\n", ethernet_type);
switch (ethernet_type)
{
case 0x0800:
ip_protocol_packet_handle(arg, pkt_header, pkt_content);
break;
case 0x0806:
arp_protocol_packet_handle(arg, pkt_header, pkt_content);
break;
case 0x0835:
printf("==============RARP Protocol=================\n");
printf("RARP\n");
break;
default:
printf("==============Unknown Protocol==============\n");
printf("Unknown Protocol\n");
break;
}
}
根据ip报文中的ip_protocol->proto判断ip协议类型
void ip_protocol_packet_handle(u_char *arg, const struct pcap_pkthdr *pkt_header, const u_char *pkt_content)
{
ip_header *ip_protocol;
sockaddr_in source, dest;
char sourceIP[MAX_ADDR_LEN], destIP[MAX_ADDR_LEN];
ip_protocol = (ip_header*)(pkt_content + 14);
source.sin_addr.s_addr = ip_protocol->saddr;
dest.sin_addr.s_addr = ip_protocol->daddr;
strncpy(sourceIP, inet_ntoa(source.sin_addr), MAX_ADDR_LEN);
strncpy(destIP, inet_ntoa(dest.sin_addr), MAX_ADDR_LEN);
printf("===================IP Protocol==================\n");
printf("Version: %d\n", ip_protocol->version_hlen >> 4);
printf("Header Length: %d bytes\n", (ip_protocol->version_hlen & 0x0f) * 4);
printf("Tos: %d\n", ip_protocol->tos);
printf("Total Length: %d\n", ntohs(ip_protocol->tlen));
printf("Identification: 0x%.4x (%i)\n", ntohs(ip_protocol->identification), ntohs(ip_protocol->identification));
printf("Flags: %d\n", ntohs(ip_protocol->flags_offset) >> 13);
printf("---Reserved bit: %d\n", (ntohs(ip_protocol->flags_offset) & 0x8000) >> 15);
printf("---Don‘t fragment: %d\n", (ntohs(ip_protocol->flags_offset) & 0x4000) >> 14);
printf("---More fragment: %d\n", (ntohs(ip_protocol->flags_offset) & 0x2000) >> 13);
printf("Fragment offset: %d\n", ntohs(ip_protocol->flags_offset) & 0x1fff);
printf("Time to live: %d\n", ip_protocol->ttl);
printf("Protocol Type: ");
switch (ip_protocol->proto)
{
case 1:
printf("ICMP");
break;
case 6:
printf("TCP");
break;
case 17:
printf("UDP");
break;
default:
break;
}
printf(" (%d)\n", ip_protocol->proto);
printf("Header checkSum: 0x%.4x\n", ntohs(ip_protocol->checksum));
printf("Source: %s\n", sourceIP);
printf("Destination: %s\n", destIP);
if (ip_protocol->proto == htons(0x0600))
tcp_protocol_packet_handle(arg, pkt_header, pkt_content);
else if (ip_protocol->proto == htons(0x1100))
udp_protocol_packet_handle(arg, pkt_header, pkt_content);
else if (ip_protocol->proto == htons(0x0100))
icmp_protocol_packet_handle(arg, pkt_header, pkt_content);
}
ARP协议
void arp_protocol_packet_handle(u_char *arg, const struct pcap_pkthdr *pkt_header, const u_char *pkt_content)
{
arp_header *arp_protocol;
arp_protocol = (arp_header*)(pkt_content + 14);
printf("==================ARP Protocol==================\n");
printf("Hardware Type: ");
switch (ntohs(arp_protocol->hardware_type))
{
case 1:
printf("Ethernet");
break;
default:
break;
}
printf(" (%d)\n", ntohs(arp_protocol->hardware_type));
printf("Protocol Type: \n");
switch (ntohs(arp_protocol->protocol_type))
{
case 0x0800:
printf("%s", "IP");
break;
case 0x0806:
printf("%s", "ARP");
break;
case 0x0835:
printf("%s", "RARP");
break;
default:
printf("%s", "Unknown Protocol");
break;
}
printf(" (0x%04x)\n", ntohs(arp_protocol->protocol_type));
printf("Hardware Length: %d\n", arp_protocol->hardware_length);
printf("Protocol Length: %d\n", arp_protocol->protocol_length);
printf("Operation Code: ");
switch (ntohs(arp_protocol->operation_code))
{
case 1:
printf("request");
break;
case 2:
printf("reply");
break;
default:
break;
}
printf(" (%i)\n", ntohs(arp_protocol->operation_code));
}
以UDP协议为例
void udp_protocol_packet_handle(u_char *arg, const struct pcap_pkthdr *pkt_header, const u_char *pkt_content)
{
udp_header *udp_protocol;
udp_protocol = (udp_header*)(pkt_content + 14 + 20);
printf("===================UDP Protocol=================\n");
printf("Source Port: %i\n", ntohs(udp_protocol->sport));
printf("Destination Port: %i\n", ntohs(udp_protocol->dport));
printf("Datalen: %i\n", ntohs(udp_protocol->datalen));
printf("Checksum: 0x%.4x\n", ntohs(udp_protocol->checksum));
}
icmp中包含两种一种是请求一种是回复
void icmp_protocol_packet_handle(u_char *arg, const struct pcap_pkthdr *pkt_header, const u_char *pkt_content)
{
icmp_header *icmp_protocol;
icmp_protocol = (icmp_header*)(pkt_content + 14 + 20);
printf("==================ICMP Protocol=================\n");
printf("Type: %d ", icmp_protocol->type);
switch (icmp_protocol->type)
{
case 8:
printf("(request)\n");
break;
case 0:
printf("(reply)\n");
break;
default:
printf("\n");
break;
}
printf("Code: %d\n", icmp_protocol->code);
printf("CheckSum: 0x%.4x\n", ntohs(icmp_protocol->checksum));
printf("Identification: 0x%.4x\n", ntohs(icmp_protocol->identification));
printf("Sequence: 0x%.4x\n", ntohs(icmp_protocol->sequence));
}
由于目前大多数网站都是使用的https协议,该协议对报文进行了加密,无法获取传输的账号和密码。本次测试的网站为天翼快递,步骤如下:
(1)在浏览器中登陆网址:http://www.tykd.com/User/login/
(2)网页打开成功后,运行wireshark,单机开始按钮抓包。
(3)转到网页的登陆界面,输入测试账号和密码登陆。
(4)在wireshark中单机捕获—停止按钮停止抓包,这时对捕获到的许多数据包进行过滤。在过滤器中输入http,此时会显示所有的HTTP报文。
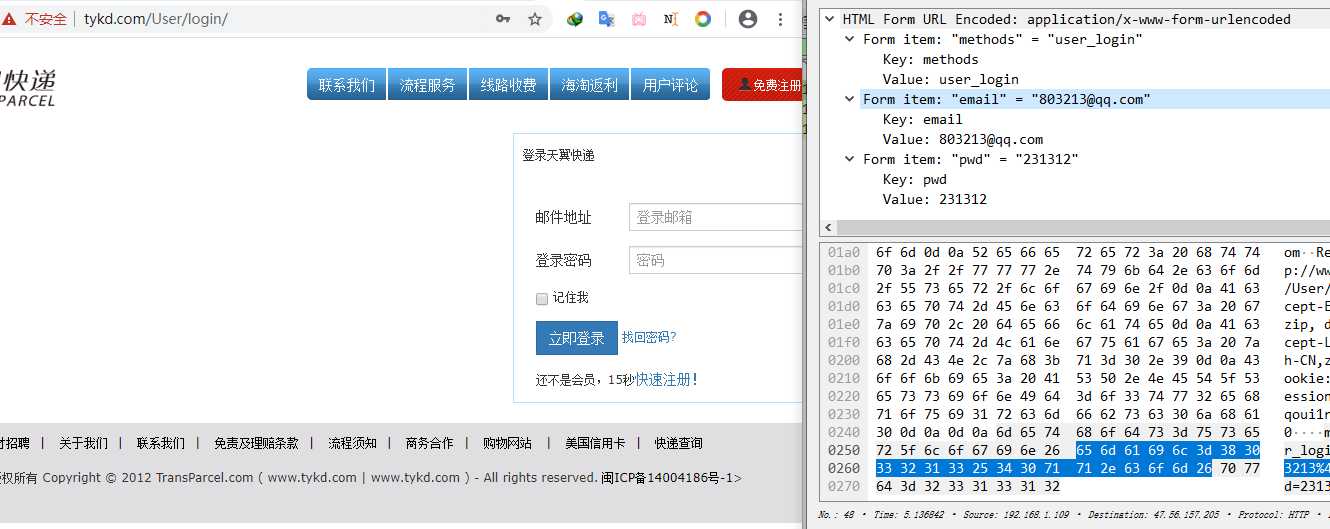
(5)在HTTP中,定义了客户端和服务器交互的不同方法,其中最基本的方法就是GET和POST。GET和POST这两种方法都能用于客户端向服务器提交数据,常用于用户向服务器提交请求的页面路径或者个人信息等,如用户登录信息。在数据包列表中选择info项有POST或者GET字样的数据包,数据详情栏如图所示
(6)在图中可以看出数据包列表中的包含POST的HTTP数据包显示了登录的账号为803213@q.com,密码为231132,说明账号和密码在网络中传输时是明文传输。
之前也尝试着抓了考研帮的网站,但是考研帮采用了特殊的登陆方式,无妨抓取账号密码
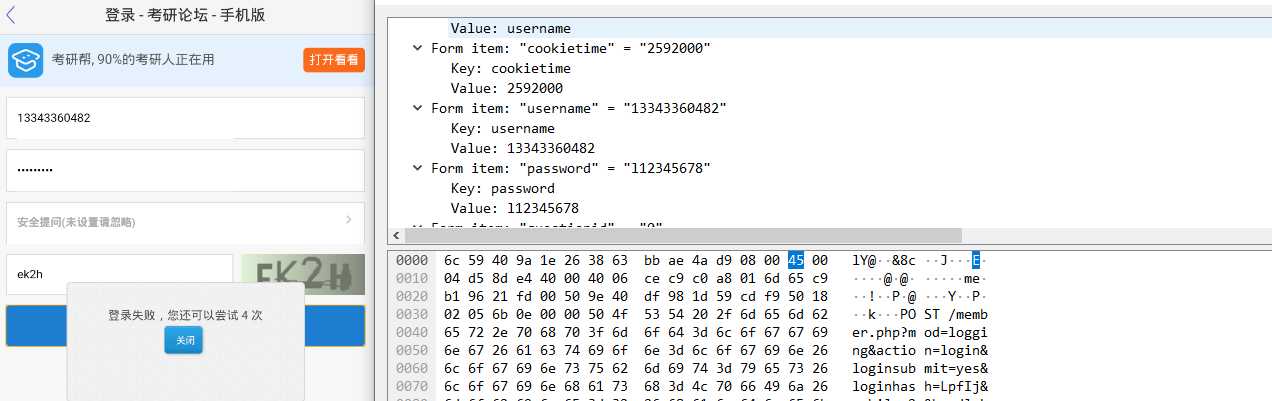
这个app实在坑爹,登陆的时候说该号码未注册,注册的时候显示该号码已经注册,最后选择了在app内使用第三方-考研帮登陆,成功抓取了账号和密码。
标签:add 窗口 数据 登陆方式 ethernet containe set get kth
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/banpingcu/p/12586088.html