标签:his 隐藏 lin ima 销售 情况下 info 扩展 缓冲
装饰(Decorator)模式的定义:指在不改变现有对象结构的情况下,动态地给该对象增加一些职责(即增加其额外功能)的模式,它属于对象结构型模式。
装饰(Decorator)模式的主要优点有:
其主要缺点是:
装饰模式增加了许多子类,如果过度使用会使程序变得很复杂。
通常情况下,扩展一个类的功能会使用继承方式来实现。但继承具有静态特征,耦合度高,并且随着扩展功能的增多,子类会很膨胀。如果使用组合关系来创建一个包装对象(即装饰对象)来包裹真实对象,并在保持真实对象的类结构不变的前提下,为其提供额外的功能,这就是装饰模式的目标。下面来分析其基本结构和实现方法。
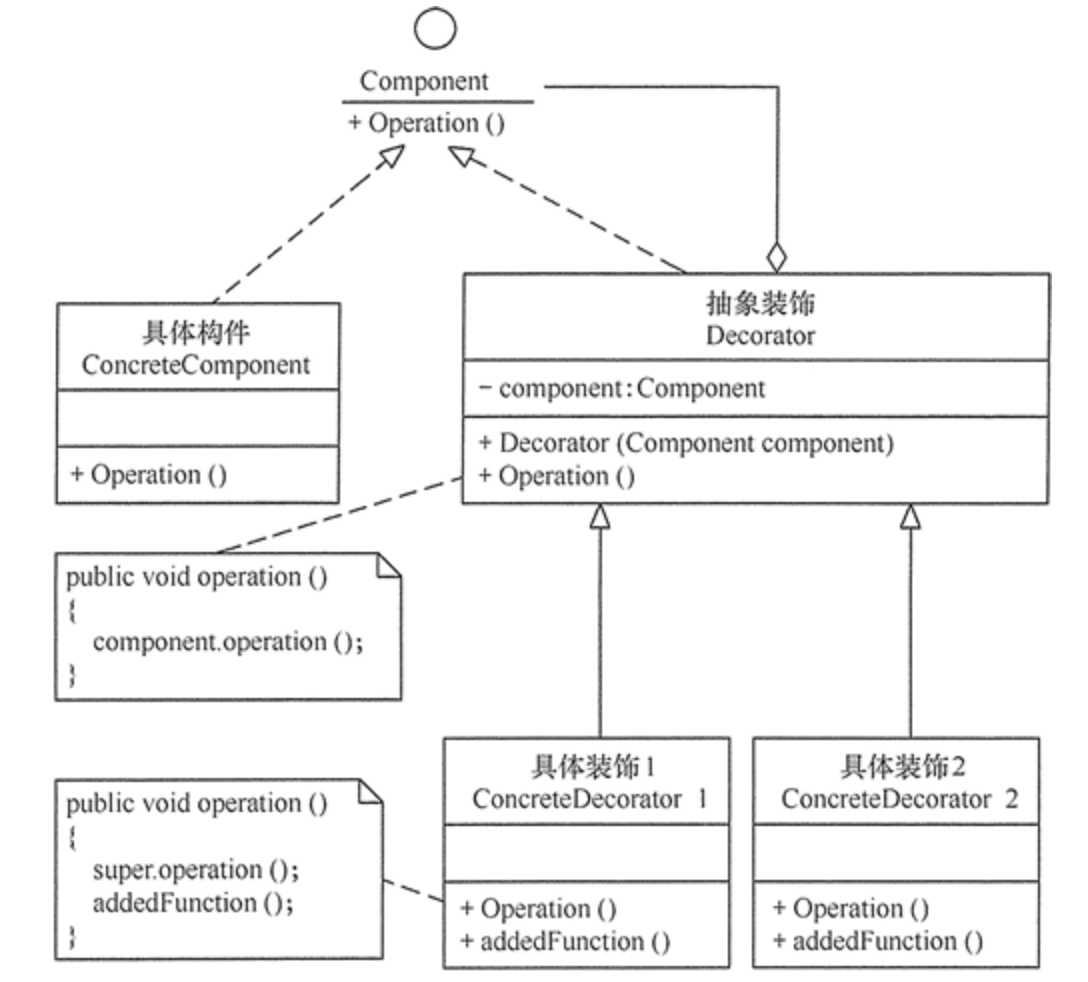
装饰模式主要包含以下角色。
装饰模式的结构图如图所示:
我们先来看看我们通过继承的方式新增特性这种实现方式,比如本例使用煎饼果子,代码如下:
/** * 煎饼 */ public class Battercake { protected String getDesc(){ return "煎饼"; } protected int cost(){ return 8; } } /** * 加蛋的煎饼 */ public class BattercakeWithEgg extends Battercake { @Override public String getDesc() { return super.getDesc()+" 加一个鸡蛋"; } @Override public int cost() { return super.cost()+1; } } /** * 加蛋加香肠的煎饼 */ public class BattercakeWithEggSausage extends BattercakeWithEgg { @Override public String getDesc() { return super.getDesc()+ " 加一根香肠"; } @Override public int cost() { return super.cost()+2; } } public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) { Battercake battercake = new Battercake(); System.out.println(battercake.getDesc()+" 销售价格:"+battercake.cost()); Battercake battercakeWithEgg = new BattercakeWithEgg(); System.out.println(battercakeWithEgg.getDesc()+" 销售价格:"+battercakeWithEgg.cost()); Battercake battercakeWithEggSausage = new BattercakeWithEggSausage(); System.out.println(battercakeWithEggSausage.getDesc()+" 销售价格:"+battercakeWithEggSausage.cost()); } }
最后测试结果为:
煎饼 销售价格:8 煎饼 加一个鸡蛋 销售价格:9 煎饼 加一个鸡蛋 加一根香肠 销售价格:11
虽然我们也实现了扩展类的功能,但是继承的方式耦合度高,并且如果新增会无限增加类,如果修改原有类,对后面的类影响很大,因此如果使用装饰模式,代码如下:
public class DecoratorPattern { public static void main(String[] args) { Component p=new ConcreteComponent(); p.operation(); System.out.println("---------------------------------"); Component d=new ConcreteDecorator(p); d.operation(); } }
//抽象构件角色 interface Component { public void operation(); }
//具体构件角色 class ConcreteComponent implements Component { public ConcreteComponent() { System.out.println("创建具体构件角色"); } public void operation() { System.out.println("调用具体构件角色的方法operation()"); } }
//抽象装饰角色 class Decorator implements Component { private Component component; public Decorator(Component component) { this.component=component; } public void operation() { component.operation(); } }
//具体装饰角色 class ConcreteDecorator extends Decorator { public ConcreteDecorator(Component component) { super(component); } public void operation() { super.operation(); addedFunction(); } public void addedFunction() { System.out.println("为具体构件角色增加额外的功能addedFunction()"); } }
前面讲解了关于装饰模式的结构与特点,下面介绍其适用的应用场景,装饰模式通常在以下几种情况使用。
装饰模式在 Java 语言中的最著名的应用莫过于 Java I/O 标准库的设计了。例如,InputStream 的子类 FilterInputStream,OutputStream 的子类 FilterOutputStream,Reader 的子类 BufferedReader 以及 FilterReader,还有 Writer 的子类 BufferedWriter、FilterWriter 以及 PrintWriter 等,它们都是抽象装饰类。
下面代码是为 FileReader 增加缓冲区而采用的装饰类 BufferedReader 的例子:
BufferedReader in=new BufferedReader(new FileReader("filename.txtn)); String s=in.readLine();
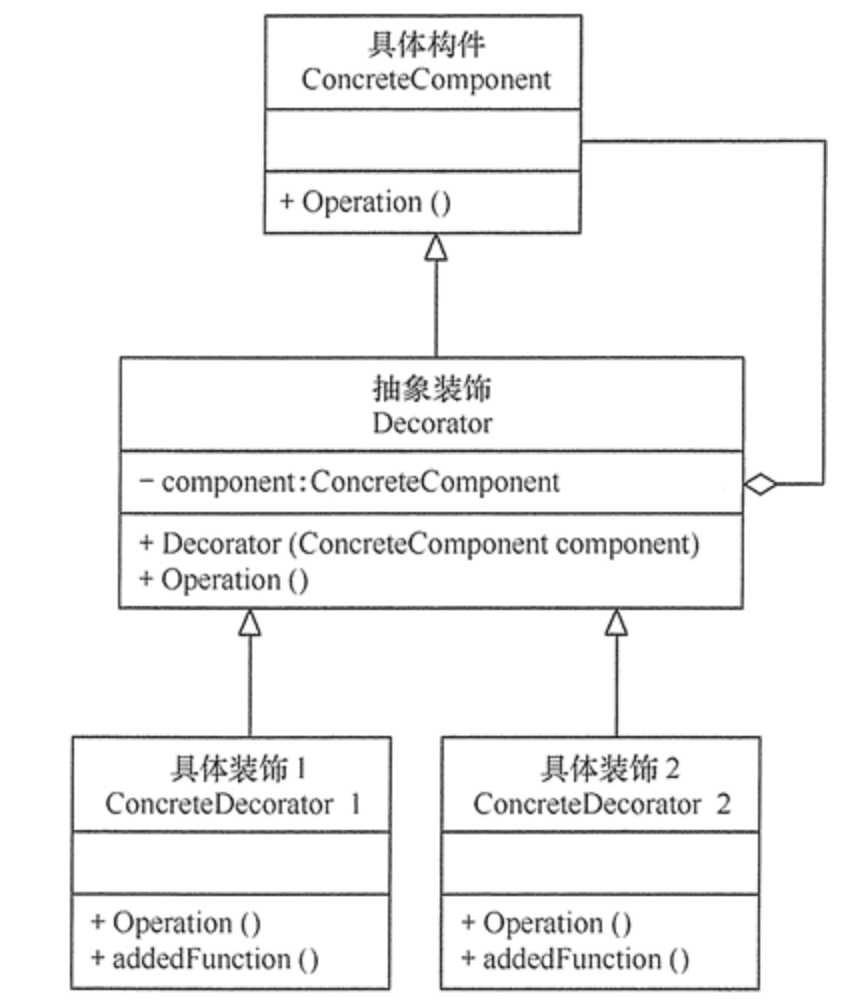
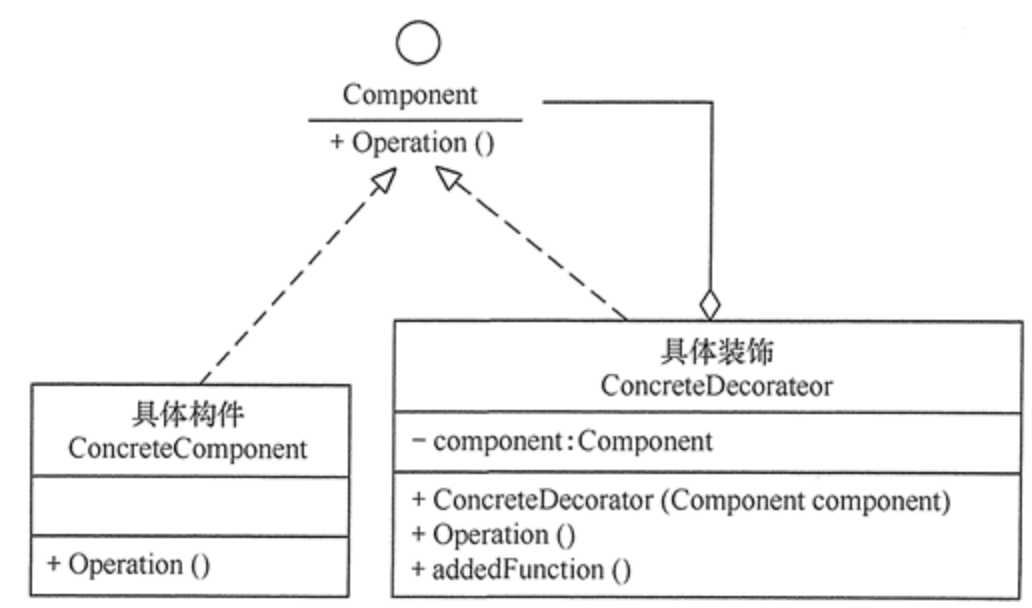
装饰模式所包含的 4 个角色不是任何时候都要存在的,在有些应用环境下模式是可以简化的,如以下两种情况。
标签:his 隐藏 lin ima 销售 情况下 info 扩展 缓冲
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/jing99/p/12602674.html