标签:存在 item 开启线程池 except bre 请求 key switch move
互斥锁
acquire递归锁
acquire多次,acquire多少次就release多少次。死锁现象
acquire避免死锁
acquire之后都要release。线程中导致数据不安全的情况
+= 、-= 、*= 、/= 相关的赋值运算队列
创建池
from concurrent.futures import ProcessPoolExecutorfrom concurrent.futrues import ThreadPoolExecutor方法
obj = tp.submit(需要在子线程执行的函数名,参数)
obj.result()是一个阻塞方法obj.add_done_callback(子线程任务结束后需要继续执行的函数)ret = tp.map(需要在子线程执行的函数名,iterable)
tp.shutdown()
什么情况使用池
锁
回调函数
import time
from concurrent.futures import ThreadPoolExecutor
def son():
print(666)
time.sleep(3)
return 888
def func(obj):
print(obj) # obj.result() = 888
t = ThreadPoolExecutor(20)
obj = t.submit(son)
print(‘main:‘, obj)
obj.add_done_callback(func)
# def my_add_done_callback(obj , fn):
# ret = obj.result()
# fn(obj)
from multiprocessing import Process
from threading import Thread
def pfunc():
print(‘启动子进程执行任务‘)
Thread(target=tfunc).start()
def tfunc():
print(‘子进程中启动子线程执行任务‘)
if __name__ == ‘__main__‘:
Process(target=pfunc).start()
print(‘主进程‘)
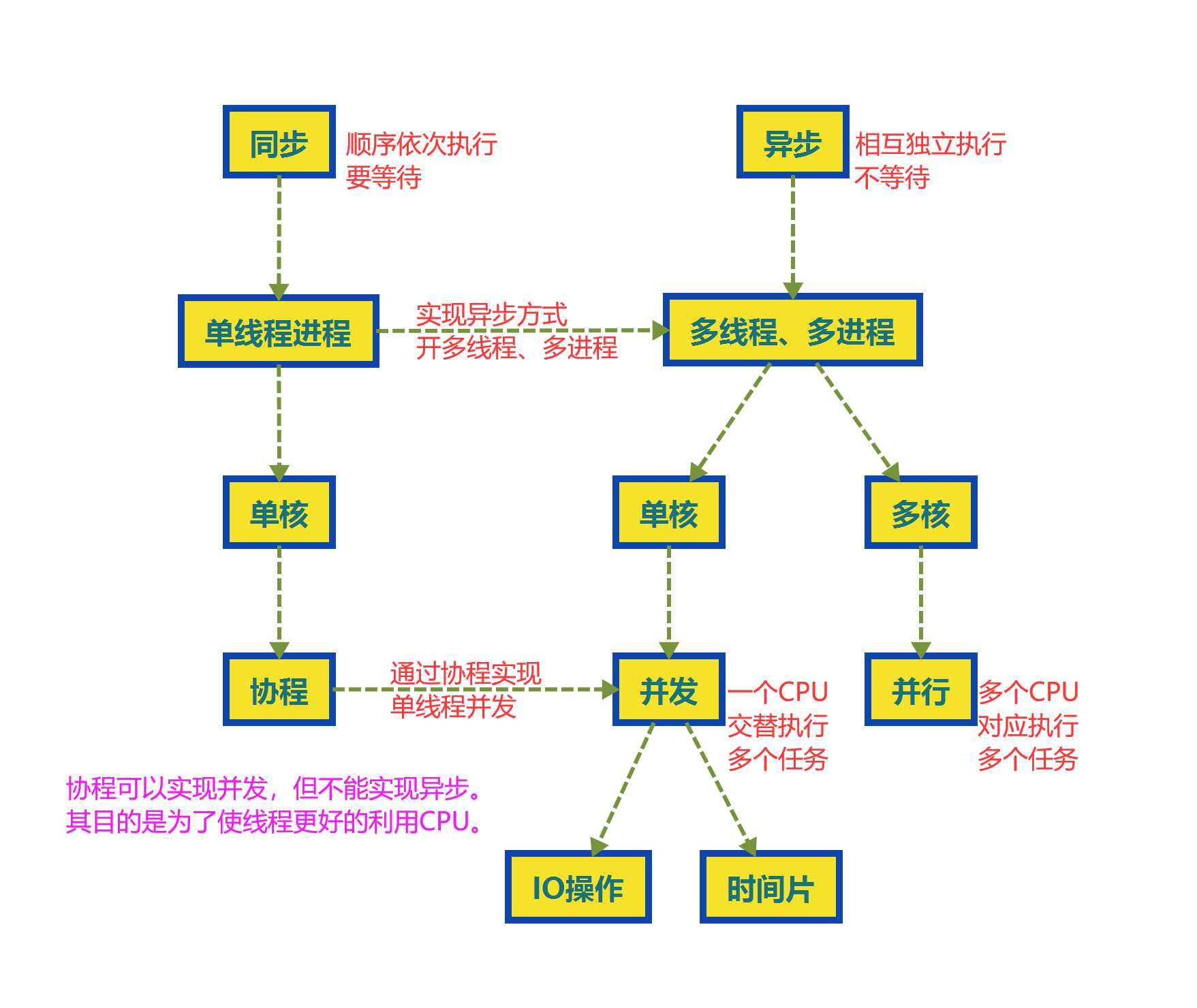
协程的本质就是在单线程下,当一个任务遇到IO阻塞后通过用户控制切换到另一个任务去执行,以此来提升效率。
进程、线程、协程的区别:
进程线程:系统级别,通过操作系统控制切换
协程:用户级别,通过Python代码控制切换
Cpython解释器下,线程和协程都不能利用多核
协程的切换方式:
协程:在一个线程中的多个任务能够相互切换,那么每一个任务就是一个协程。
原生python完成
asyncio模块基于yield实现切换
def eat():
print(‘alex is eating‘)
yield 1
print(‘alex finished eat‘)
yield 2
def sleep():
g = eat()
next(g)
print(‘yuan is sleeping‘)
print(‘yuan finished sleep‘)
next(g)
sleep()
C语言完成
gevent模块基于greenlet模块实现切换
from greenlet import greenlet
def eat():
print(‘alex is eating‘)
g2.switch()
print(‘alex finished eat‘)
def sleep():
print(‘yuan is sleeping‘)
print(‘yuan finished sleep‘)
g1.switch()
g1 = greenlet(eat)
g2 = greenlet(sleep)
g1.switch()
import gevent
def eat():
print(‘alex is eating‘)
time.sleep(1)
print(‘alex finished eat‘)
g = gevent.spawn(eat) # 创建一个协程任务,遇到阻塞才会执行。
print(‘没有阻塞则永远不会执行协程任务‘)
import time
import gevent
def eat():
print(‘alex is eating‘)
time.sleep(1)
print(‘alex finished eat‘)
g = gevent.spawn(eat) # 创建协程任务,遇到阻塞执行。
time.sleep(1)
print(‘无法识别sleep是阻塞方法。‘)
import time
import gevent
from gevent import monkey
monkey.patch_all() # 识别所有阻塞
def eat():
print(‘alex is eating‘)
time.sleep(1)
print(‘alex finished eat‘)
g = gevent.spawn(eat) # 创建一个协程任务
time.sleep(1)
print(‘识别所有阻塞‘)
import time
import gevent
from gevent import monkey
monkey.patch_all()
def eat():
print(‘alex is eating‘)
time.sleep(1)
print(‘alex finished eat‘)
def sleep():
print(‘yuan is sleeping‘)
time.sleep(1)
print(‘yuan finished sleep‘)
g1 = gevent.spawn(eat)
g2 = gevent.spawn(sleep)
g1.join() # 阻塞直到g1任务完成
g2.join() # 阻塞直到g2任务完成
gevent.joinall([g1, g2]) # 阻塞直到列表中的所有完成
import time
import gevent
from gevent import monkey
monkey.patch_all()
def eat():
print(2)
time.sleep(0.5)
print(5)
def sleep():
print(3)
time.sleep(0.5)
print(6)
g1 = gevent.spawn(eat)
g2 = gevent.spawn(sleep)
print(1)
time.sleep(0.5)
print(4)
time.sleep(0.5)
print(7)
import time
import gevent
from gevent import monkey
monkey.patch_all()
def eat():
print(‘alex is eating‘)
time.sleep(1)
print(‘alex finished eat‘)
g_l = []
for i in range(10):
g = gevent.spawn(eat) # 循环添加协程任务
g_l.append(g)
print(1)
gevent.joinall(g_l)
import time
import gevent
from gevent import monkey
monkey.patch_all()
def eat():
print(‘alex is eating‘)
time.sleep(1)
print(‘alex finished eat‘)
return ‘alex‘
def sleep():
print(‘yuan is sleeping‘)
time.sleep(1)
print(‘yuan finished sleep‘)
return ‘yuan‘
g1 = gevent.spawn(eat)
g2 = gevent.spawn(sleep)
gevent.joinall([g1, g2])
print(g1.value) # 获取返回值
print(g2.value)
# 启动一个任务
import asyncio
async def demo():
print(‘start‘)
await asyncio.sleep(1)
print(‘end‘)
loop = asyncio.get_event_loop() # 创建一个事件循环对象
loop.run_until_complete(demo()) # 把demo任务丢到事件循环中执行
# 启动多个任务,无返回值。
import asyncio
async def demo():
print(‘start‘)
await asyncio.sleep(1)
print(‘end‘)
loop = asyncio.get_event_loop()
wait_obj = asyncio.wait([demo(), demo(), demo()])
loop.run_until_complete(wait_obj)
# 启动多个任务,有返回值。
import asyncio
async def demo():
print(‘start‘)
await asyncio.sleep(1)
print(‘end‘)
return 666
loop = asyncio.get_event_loop()
t1 = loop.create_task(demo())
t2 = loop.create_task(demo())
wait_obj = asyncio.wait([t1, t2])
loop.run_until_complete(wait_obj)
task_l = [t1, t2]
for t in task_l:
print(t.result())
# 谁先回来先取谁的结果
import asyncio
async def demo(i):
print(‘start‘)
await asyncio.sleep(1)
print(‘end‘)
return i, 666
async def main():
lst = []
for i in range(10):
task = asyncio.ensure_future(demo(i))
lst.append(task)
for ret in asyncio.as_completed(lst):
res = await ret
print(ret)
loop = asyncio.get_event_loop()
loop.run_until_complete(main())
# 方式一
import requests
key_lst = [‘alex‘, ‘wusir‘, ‘yuan‘]
for item in key_lst:
ret = requests.get(‘https://www.baidu.com/s?wd=%s‘ % item)
print(ret.text)
# 方式二
import socket
def get_data(key):
client = socket.socket()
# 创建连接:和百度创建连接,阻塞。
client.connect((‘www.baidu.com‘, 80))
# 发送请求:告诉百度你要什么。
client.sendall(b‘GET /s?wd=%s HTTP/1.0\r\nhost:www.baidu.com\r\n\r\n‘ % key)
# 接收数据:等着接收百度的回复。
chunk_list = []
while True:
chunk = client.recv(8096)
if not chunk:
break
chunk_list.append(chunk)
body = b‘‘.join(chunk_list)
print(body.decode(‘utf-8‘))
key_lst = [‘alex‘, ‘wusir‘, ‘yuan‘]
for item in key_lst:
get_data(item)
# 多线程并发
import threading
for item in key_lst:
t = threading.Thread(target=get_data, args=(item,))
t.start()
基于IO多路复用 + socket实现单线程并发请求
对象.setblocking(False)import socket
import select
client1 = socket.socket()
client1.setblocking(False) # 将原来阻塞的位置变成非阻塞
try:
client1.connect((‘www.baidu.com‘, 80))
except BlockingIOError as e:
pass
client2 = socket.socket()
client2.setblocking(False) # 将原来阻塞的位置变成非阻塞
try:
client2.connect((‘www.sogou.com‘, 80))
except BlockingIOError as e:
pass
socket_lst = [client1, client2]
conn_lst = [client1, client2]
while True:
r_lst, w_lst, e_lst = select.select(socket_lst, conn_lst, [], 0.005) # IO多路复用
# w_lst 表示已经连接成功的socket对象
for sk in w_lst:
if sk == client1:
sk.sendall(b‘GET /s?wd=alex HTTP/1.0\r\nhost:www.baidu.com\r\n\r\n‘)
else:
sk.sendall(b‘GET /web?query=wusir HTTP/1.0\r\nhost:www.sogou.com\r\n\r\n‘)
conn_lst.remove(sk)
# r_lst 表示已经返回数据的socket对象
for sk in r_lst:
chunk_lst = []
while True:
try:
chunk = sk.recv(8096)
if not chunk:
break
chunk_lst.append(chunk)
except BlockingIOError as e:
break
body = b‘‘.join(chunk_lst)
# print(‘>>>>>>>>‘, body.decode(‘utf-8‘))
print(‘>>>>>>>>‘, body)
sk.close()
socket_lst.remove(sk)
if not socket_lst:
break
协程
单线程并发方式
标签:存在 item 开启线程池 except bre 请求 key switch move
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/elliottwave/p/12656278.html