标签:结果 eof 运行 inf 输出 clu 报告 开头 stdout
fifo_read.c
1 #include<stdio.h> 2 #include <sys/stat.h> 3 #include <sys/types.h> 4 #include <stdlib.h> 5 #include <fcntl.h> 6 #include <unistd.h> 7 int main(){ 8 unlink("FIFO"); 9 if(mkfifo("FIFO",0777)<0){ //创建 10 printf("error!\n"); 11 return -1; 12 } 13 int flag=open("FIFO",O_RDONLY); //只读 14 char a[200]; 15 while(1){ 16 17 printf("等待输入\n"); 18 ssize_t size=read(flag,a,sizeof(a)-1); //读取 19 if(size<0){ 20 printf("error\n"); 21 break; 22 23 } 24 else if(size>0){
25 a[size]=0;
26 printf("%s\n",a);
27 }
28 else{ 29 printf("Exit!"); 30 break;} 31 } 32 close(flag); 33 return 0; 34 } 35
fifo.write.c
2 #include <stdio.h> 3 #include <stdlib.h> 4 #include <string.h> 5 #include <sys/stat.h> 6 #include <sys/types.h> 7 #include <fcntl.h> 8 #include <unistd.h> 9 #include"memory.h" 10 int main(){ 11 int flag=open("FIFO",O_WRONLY); //阻塞方式 12 while(1){ 13 char a[200]; 14 printf("write something:"); 15 fflush(stdout); 16 size_t size=read(0,a,sizeof(a)); 17 if(size<=0){ 18 printf("read error!\n"); 19 break; 20 } 21 else { 22 a[size]=0; 23 write(flag,a,strlen(a)); 24 } 25 } 26 close(flag); 27 return 0; 28 }
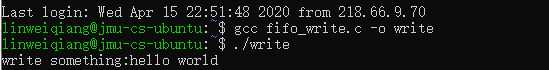
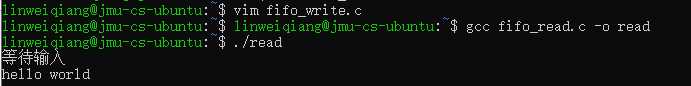
实验注意先开启read文件,因为在只读进程中创建了"FIFO"管道,并且在前面定义堵塞方式,
在write文件进入一个输入死循环,可以进行一直的写内容进管道,之后写入管道通过write函数,转
到read进程中先将开头文字打印出来并且让程序在read函数那里等待,读取有用信息后读取存在a内并且输出,注意判断a的长度,
在运行结果中机会卡在等待输入,只有在write进程中写入后才输出
open("FIFO",O_WRONLY); FIFO管道名 O_WRONLY 只写堵塞,我认为的是遇到write函数才会停下等待输入,同理read也是这样
退出时read进入了无限循环
标签:结果 eof 运行 inf 输出 clu 报告 开头 stdout
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/hxrlwq13/p/12709738.html