标签:ict his reg required assign api 映射 实体类 ansi
在以前的文章里面,我们介绍了 ABP vNext 在 DDD 模块定义了仓储的接口定义和基本实现。本章将会介绍,ABP vNext 是如何将 EntityFramework Core 框架跟仓储进行深度集成。
ABP vNext 在集成 EF Core 的时候,不只是简单地实现了仓储模式,除开仓储以外,还提供了一系列的基础设施,如领域事件的发布,数据过滤器的实现。
EntityFrameworkCore 相关的模块基本就下面几个,除了第一个是核心 EntityFrameworkCore 模块以外,其他几个都是封装的 EntityFrameworkCore Provider,方便各种数据库进行集成。

首先从 Volo.Abp.EntityFrameworkCore 的 AbpEntityFrameworkCoreModule 开始分析,该模块只重写了 ConfigureServices() 方法,在内部也只有两句代码。
public override void ConfigureServices(ServiceConfigurationContext context)
{
// 调用 AbpDbContextOptions 的预配置方法,为了解决下面的问题。
// https://stackoverflow.com/questions/55369146/eager-loading-include-with-using-uselazyloadingproxies
Configure<AbpDbContextOptions>(options =>
{
options.PreConfigure(abpDbContextConfigurationContext =>
{
abpDbContextConfigurationContext.DbContextOptions
.ConfigureWarnings(warnings =>
{
warnings.Ignore(CoreEventId.LazyLoadOnDisposedContextWarning);
});
});
});
// 注册 IDbContextProvider 组件。
context.Services.TryAddTransient(typeof(IDbContextProvider<>), typeof(UnitOfWorkDbContextProvider<>));
}
首先看第一句代码,它在内部会调用 AbpDbContextOptions 提供的 PreConfigure() 方法。这个方法逻辑很简单,会将传入的 Action<AbpDbContextConfigurationContext> 委托添加到一个 List<Action<AbpDbContextConfigurationContext>> 集合,并且在 DbContextOptionsFactory 工厂中使用。
第二局代码则比较简单,为 IDbContextProvider<> 类型注入默认实现 UnitOfWorkDbContextProvider<>。
public class AbpDbContextOptions
{
internal List<Action<AbpDbContextConfigurationContext>> DefaultPreConfigureActions { get; set; }
// ...
public void PreConfigure([NotNull] Action<AbpDbContextConfigurationContext> action)
{
Check.NotNull(action, nameof(action));
DefaultPreConfigureActions.Add(action);
}
// ...
}
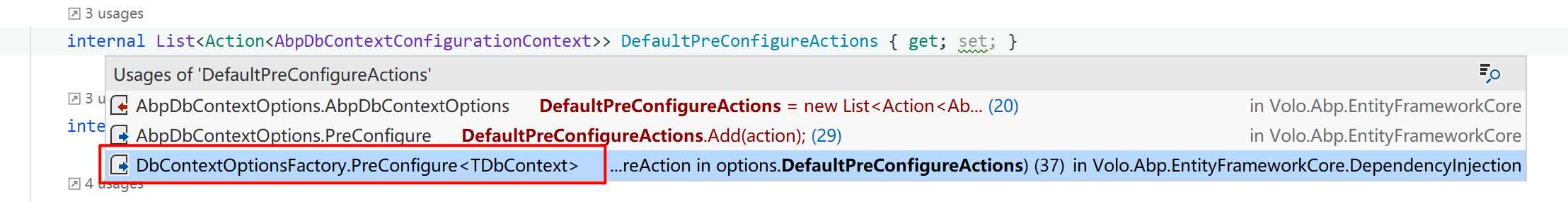
从上面的代码可以看出来,这个 AbpDbContextConfigurationContext 就是一个配置上下文,用于 ABP vNext 框架在初始化的时候进行各种配置。
在翻阅 AbpDbContextOptions 代码的时候,我发现除了预配置方法,它还提供了一个 Configure([NotNull] Action<AbpDbContextConfigurationContext> action) 方法,以及它的泛型重载 Configure<TDbContext>([NotNull] Action<AbpDbContextConfigurationContext<TDbContext>> action),它们的内部实现与预配置类似。
这两个方法在 ABP vNext 框架内部的应用,主要在各个 EF Provider 模块当中有体现。
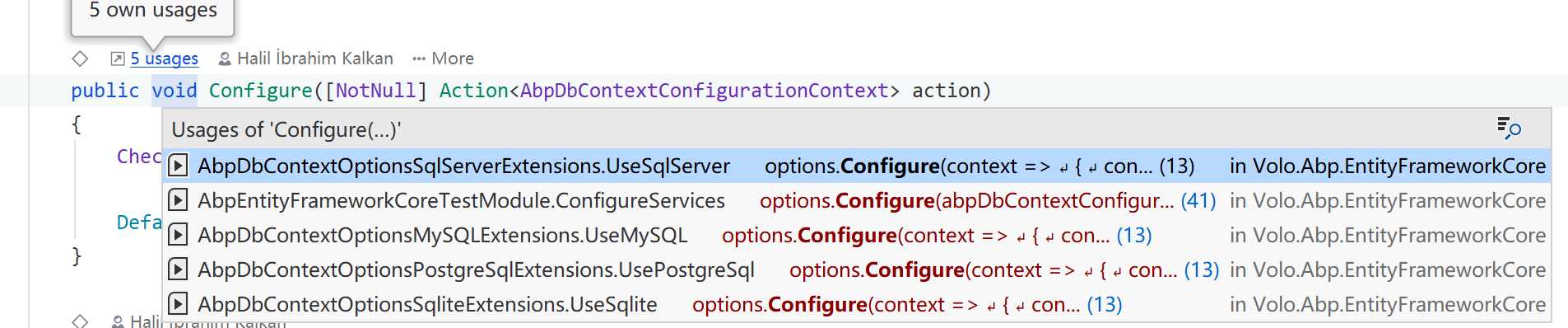
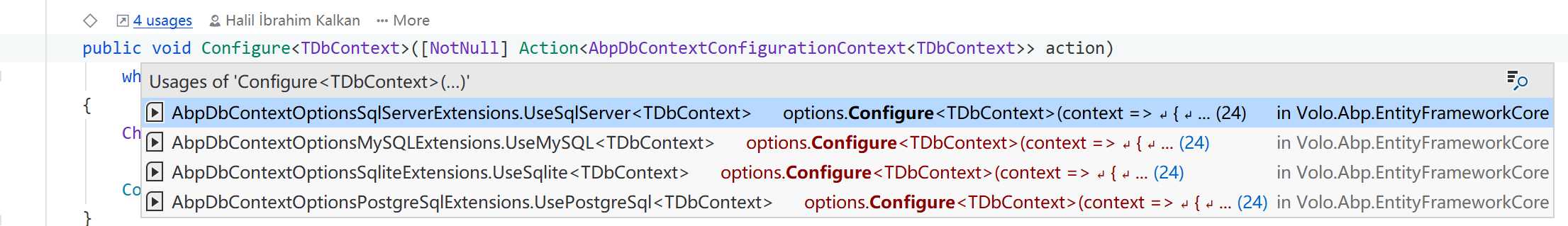
这里我以 Volo.Abp.EntityFrameworkCore.PostgreSql 模块作为例子,在项目内部只有两个扩展方法的定义类。在 AbpDbContextOptionsPostgreSqlExtensions 当中,就使用到了 Configure() 方法。
public static void UsePostgreSql(
[NotNull] this AbpDbContextOptions options,
[CanBeNull] Action<NpgsqlDbContextOptionsBuilder> postgreSqlOptionsAction = null)
{
options.Configure(context =>
{
// 这里的 context 类型是 AbpDbContextConfigurationContext。
context.UsePostgreSql(postgreSqlOptionsAction);
});
}
上面代码中的 UsePostgreSql() 方法很明显不是 EF Core Provider 所定义的扩展方法,跳转到具体实现,发现就是一层简单的封装。由于 AbpDbContextConfigurationContext 内部提供了 DbContextOptionsBuilder ,所以直接使用这个 DbContextOptionsBuilder 调用提供的扩展方法即可。
public static class AbpDbContextConfigurationContextPostgreSqlExtensions
{
public static DbContextOptionsBuilder UsePostgreSql(
[NotNull] this AbpDbContextConfigurationContext context,
[CanBeNull] Action<NpgsqlDbContextOptionsBuilder> postgreSqlOptionsAction = null)
{
if (context.ExistingConnection != null)
{
return context.DbContextOptions.UseNpgsql(context.ExistingConnection, postgreSqlOptionsAction);
}
else
{
return context.DbContextOptions.UseNpgsql(context.ConnectionString, postgreSqlOptionsAction);
}
}
}
无论是 PreConfigure() 的委托集合,还是 Configure() 配置的委托,都会在 DbContextOptionsFactory 提供的 Create<TDbContext>(IServiceProvider serviceProvider) 方法中被使用。该方法的作用只有一个,执行框架的配置方法,然后生成数据库上下文的配置对象。
internal static class DbContextOptionsFactory
{
public static DbContextOptions<TDbContext> Create<TDbContext>(IServiceProvider serviceProvider)
where TDbContext : AbpDbContext<TDbContext>
{
// 获取一个 DbContextCreationContext 对象。
var creationContext = GetCreationContext<TDbContext>(serviceProvider);
// 依据 creationContext 信息构造一个配置上下文。
var context = new AbpDbContextConfigurationContext<TDbContext>(
creationContext.ConnectionString,
serviceProvider,
creationContext.ConnectionStringName,
creationContext.ExistingConnection
);
// 获取 AbpDbOptions 配置。
var options = GetDbContextOptions<TDbContext>(serviceProvider);
// 从 Options 当中获取添加的 PreConfigure 与 Configure 委托,并执行。
PreConfigure(options, context);
Configure(options, context);
//
return context.DbContextOptions.Options;
}
// ...
}
首先我们来看看 GetCreationContext<TDbContext>() 方法是如何构造一个 DbContextCreationContext 对象的,它会优先从 Current 取得一个上下文对象,如果存在则直接返回,不存在则使用连接字符串等信息构建一个新的上下文对象。
private static DbContextCreationContext GetCreationContext<TDbContext>(IServiceProvider serviceProvider)
where TDbContext : AbpDbContext<TDbContext>
{
// 优先从一个 AsyncLocal 当中获取。
var context = DbContextCreationContext.Current;
if (context != null)
{
return context;
}
// 从 TDbContext 的 ConnectionStringName 特性获取连接字符串名称。
var connectionStringName = ConnectionStringNameAttribute.GetConnStringName<TDbContext>();
// 使用 IConnectionStringResolver 根据指定的名称获得连接字符串。
var connectionString = serviceProvider.GetRequiredService<IConnectionStringResolver>().Resolve(connectionStringName);
// 构造一个新的 DbContextCreationContext 对象。
return new DbContextCreationContext(
connectionStringName,
connectionString
);
}
与老版本的 ABP 一样,ABP vNext 将连接字符串解析的工作,抽象了一个解析器。连接字符串解析器默认有两种实现,适用于普通系统和多租户系统。
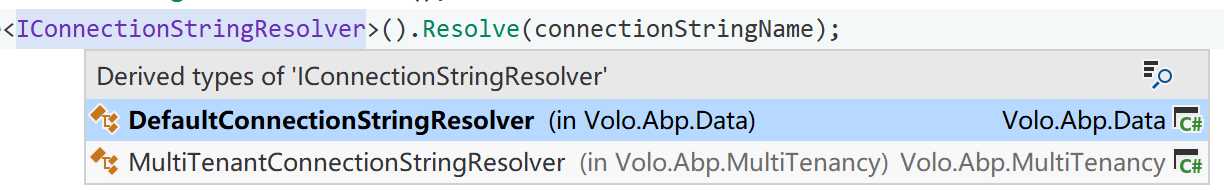
普通的解析器,名字叫做 DefaultConnectionStringResolver,它的连接字符串都是从 AbpDbConnectionOptions 当中获取的,而这个 Option 最终是从 IConfiguration 映射过来的,一般来说就是你 appsetting.json 文件当中的连接字符串配置。
多租户解析器 的实现叫做 MultiTenantConnectionStringResolver,它的内部核心逻辑就是获得到当前的租户,并查询租户所对应的连接字符串,这样就可以实现每个租户都拥有不同的数据库实例。
回到最开始的地方,方法 Create<TDbContext>(IServiceProvider serviceProvider) 在什么地方会被使用呢?跳转到唯一的调用点是在 AbpEfCoreServiceCollectionExtensions 静态类的内部,它提供的 AddAbpDbContext<TDbContext>() 方法内部,就使用了 Create<TDbContext>() 作为 DbContextOptions<TDbContext> 的工厂方法。
public static class AbpEfCoreServiceCollectionExtensions
{
public static IServiceCollection AddAbpDbContext<TDbContext>(
this IServiceCollection services,
Action<IAbpDbContextRegistrationOptionsBuilder> optionsBuilder = null)
where TDbContext : AbpDbContext<TDbContext>
{
services.AddMemoryCache();
// 构造一个数据库注册配置对象。
var options = new AbpDbContextRegistrationOptions(typeof(TDbContext), services);
// 回调传入的委托。
optionsBuilder?.Invoke(options);
// 注入指定 TDbContext 的 DbOptions<TDbContext> ,将会使用 Create<TDbContext> 方法进行瞬时对象构造。
services.TryAddTransient(DbContextOptionsFactory.Create<TDbContext>);
// 替换指定类型的 DbContext 为当前 TDbContext。
foreach (var dbContextType in options.ReplacedDbContextTypes)
{
services.Replace(ServiceDescriptor.Transient(dbContextType, typeof(TDbContext)));
}
// 构造 EF Core 仓储注册器,并添加仓储。
new EfCoreRepositoryRegistrar(options).AddRepositories();
return services;
}
}
关于仓储的注入,其实在之前的文章就有讲过,这里我就大概说一下情况。
在上述代码当中,调用了 AddAbpDbContext<TDbContext>() 方法之后,就会通过 Repository Registrar 进行仓储注入。
public virtual void AddRepositories()
{
// 遍历用户添加的自定义仓储。
foreach (var customRepository in Options.CustomRepositories)
{
// 调用 AddDefaultRepository() 方法注入仓储。
Options.Services.AddDefaultRepository(customRepository.Key, customRepository.Value);
}
// 判断是否需要注册实体的默认仓储。
if (Options.RegisterDefaultRepositories)
{
RegisterDefaultRepositories();
}
}
可以看到,在注入仓储的时候,分为两种情况。第一种是用户的自定义仓储,这种仓储是通过 AddRepository() 方法添加的,添加之后将会把它的 实体类型 与 仓储类型 放在一个字典内部。在仓储注册器进行初始化的时候,就会遍历这个字典,进行注入动作。
第二种情况则是用户在设置了 RegisterDefaultRepositories=true 的情况下,ABP vNext 就会从数据库上下文的类型定义上遍历所有实体类型,然后进行默认仓储注册。
具体的仓储注册实现:
public static IServiceCollection AddDefaultRepository(this IServiceCollection services, Type entityType, Type repositoryImplementationType)
{
// 注册 IReadOnlyBasicRepository<TEntity>。
var readOnlyBasicRepositoryInterface = typeof(IReadOnlyBasicRepository<>).MakeGenericType(entityType);
// 如果具体实现类型继承了该接口,则进行注入。
if (readOnlyBasicRepositoryInterface.IsAssignableFrom(repositoryImplementationType))
{
services.TryAddTransient(readOnlyBasicRepositoryInterface, repositoryImplementationType);
// 注册 IReadOnlyRepository<TEntity>。
var readOnlyRepositoryInterface = typeof(IReadOnlyRepository<>).MakeGenericType(entityType);
if (readOnlyRepositoryInterface.IsAssignableFrom(repositoryImplementationType))
{
services.TryAddTransient(readOnlyRepositoryInterface, repositoryImplementationType);
}
// 注册 IBasicRepository<TEntity>。
var basicRepositoryInterface = typeof(IBasicRepository<>).MakeGenericType(entityType);
if (basicRepositoryInterface.IsAssignableFrom(repositoryImplementationType))
{
services.TryAddTransient(basicRepositoryInterface, repositoryImplementationType);
// 注册 IRepository<TEntity>。
var repositoryInterface = typeof(IRepository<>).MakeGenericType(entityType);
if (repositoryInterface.IsAssignableFrom(repositoryImplementationType))
{
services.TryAddTransient(repositoryInterface, repositoryImplementationType);
}
}
}
// 获得实体的主键类型,如果不存在则忽略。
var primaryKeyType = EntityHelper.FindPrimaryKeyType(entityType);
if (primaryKeyType != null)
{
// 注册 IReadOnlyBasicRepository<TEntity, TKey>。
var readOnlyBasicRepositoryInterfaceWithPk = typeof(IReadOnlyBasicRepository<,>).MakeGenericType(entityType, primaryKeyType);
if (readOnlyBasicRepositoryInterfaceWithPk.IsAssignableFrom(repositoryImplementationType))
{
services.TryAddTransient(readOnlyBasicRepositoryInterfaceWithPk, repositoryImplementationType);
// 注册 IReadOnlyRepository<TEntity, TKey>。
var readOnlyRepositoryInterfaceWithPk = typeof(IReadOnlyRepository<,>).MakeGenericType(entityType, primaryKeyType);
if (readOnlyRepositoryInterfaceWithPk.IsAssignableFrom(repositoryImplementationType))
{
services.TryAddTransient(readOnlyRepositoryInterfaceWithPk, repositoryImplementationType);
}
// 注册 IBasicRepository<TEntity, TKey>。
var basicRepositoryInterfaceWithPk = typeof(IBasicRepository<,>).MakeGenericType(entityType, primaryKeyType);
if (basicRepositoryInterfaceWithPk.IsAssignableFrom(repositoryImplementationType))
{
services.TryAddTransient(basicRepositoryInterfaceWithPk, repositoryImplementationType);
// 注册 IRepository<TEntity, TKey>。
var repositoryInterfaceWithPk = typeof(IRepository<,>).MakeGenericType(entityType, primaryKeyType);
if (repositoryInterfaceWithPk.IsAssignableFrom(repositoryImplementationType))
{
services.TryAddTransient(repositoryInterfaceWithPk, repositoryImplementationType);
}
}
}
}
return services;
}
回到仓储自动注册的地方,可以看到实现类型是由 GetDefaultRepositoryImplementationType() 方法提供的。
protected virtual void RegisterDefaultRepository(Type entityType)
{
Options.Services.AddDefaultRepository(
entityType,
GetDefaultRepositoryImplementationType(entityType)
);
}
protected virtual Type GetDefaultRepositoryImplementationType(Type entityType)
{
var primaryKeyType = EntityHelper.FindPrimaryKeyType(entityType);
if (primaryKeyType == null)
{
return Options.SpecifiedDefaultRepositoryTypes
? Options.DefaultRepositoryImplementationTypeWithoutKey.MakeGenericType(entityType)
: GetRepositoryType(Options.DefaultRepositoryDbContextType, entityType);
}
return Options.SpecifiedDefaultRepositoryTypes
? Options.DefaultRepositoryImplementationType.MakeGenericType(entityType, primaryKeyType)
: GetRepositoryType(Options.DefaultRepositoryDbContextType, entityType, primaryKeyType);
}
protected abstract Type GetRepositoryType(Type dbContextType, Type entityType);
protected abstract Type GetRepositoryType(Type dbContextType, Type entityType, Type primaryKeyType);
这里的两个 GetRepositoryType() 都是抽象方法,具体的实现分别在 EfCoreRepositoryRegistrar、MemoryDbRepositoryRegistrar、MongoDbRepositoryRegistrar 的内部,这里我们只讲 EF Core 相关的。
protected override Type GetRepositoryType(Type dbContextType, Type entityType)
{
return typeof(EfCoreRepository<,>).MakeGenericType(dbContextType, entityType);
}
可以看到,在方法内部是构造了一个 EfCoreRepository 类型作为默认仓储的实现。
在 Ef Core 仓储的内部,需要操作数据库时,必须要获得一个数据库上下文。在仓储内部的数据库上下文都是由 IDbContextProvider<TDbContext> 提供了,这个东西在 EF Core 模块初始化的时候就已经被注册,它的默认实现是 UnitOfWorkDbContextProvider<TDbContext>。
public class EfCoreRepository<TDbContext, TEntity> : RepositoryBase<TEntity>, IEfCoreRepository<TEntity>
where TDbContext : IEfCoreDbContext
where TEntity : class, IEntity
{
public virtual DbSet<TEntity> DbSet => DbContext.Set<TEntity>();
DbContext IEfCoreRepository<TEntity>.DbContext => DbContext.As<DbContext>();
protected virtual TDbContext DbContext => _dbContextProvider.GetDbContext();
// ...
private readonly IDbContextProvider<TDbContext> _dbContextProvider;
// ...
public EfCoreRepository(IDbContextProvider<TDbContext> dbContextProvider)
{
_dbContextProvider = dbContextProvider;
// ...
}
// ...
}
首先来看一下这个实现类的基本定义,比较简单,注入了两个接口,分别用于获取工作单元和构造 DbContext。需要注意的是,这里通过 where 约束来指定 TDbContext 必须实现 IEfCoreDbContext 接口。
public class UnitOfWorkDbContextProvider<TDbContext> : IDbContextProvider<TDbContext>
where TDbContext : IEfCoreDbContext
{
private readonly IUnitOfWorkManager _unitOfWorkManager;
private readonly IConnectionStringResolver _connectionStringResolver;
public UnitOfWorkDbContextProvider(
IUnitOfWorkManager unitOfWorkManager,
IConnectionStringResolver connectionStringResolver)
{
_unitOfWorkManager = unitOfWorkManager;
_connectionStringResolver = connectionStringResolver;
}
// ...
}
接着想下看,接口只定义了一个方法,就是 GetDbContext(),在这个默认实现里面,首先会从缓存里面获取数据库上下文,如果没有获取到,则创建一个新的数据库上下文。
public TDbContext GetDbContext()
{
// 获得当前的可用工作单元。
var unitOfWork = _unitOfWorkManager.Current;
if (unitOfWork == null)
{
throw new AbpException("A DbContext can only be created inside a unit of work!");
}
// 获得数据库连接上下文的连接字符串名称。
var connectionStringName = ConnectionStringNameAttribute.GetConnStringName<TDbContext>();
// 根据名称解析具体的连接字符串。
var connectionString = _connectionStringResolver.Resolve(connectionStringName);
// 构造数据库上下文缓存 Key。
var dbContextKey = $"{typeof(TDbContext).FullName}_{connectionString}";
// 从工作单元的缓存当中获取数据库上下文,不存在则调用 CreateDbContext() 创建。
var databaseApi = unitOfWork.GetOrAddDatabaseApi(
dbContextKey,
() => new EfCoreDatabaseApi<TDbContext>(
CreateDbContext(unitOfWork, connectionStringName, connectionString)
));
return ((EfCoreDatabaseApi<TDbContext>)databaseApi).DbContext;
}
回到最开始的数据库上下文配置工厂,在它的内部会优先从一个 Current 获取一个 DbContextCreationContext 实例。而在这里,就是 Current 被赋值的地方,只要调用了 Use() 方法,在释放之前都会获取到同一个实例。
private TDbContext CreateDbContext(IUnitOfWork unitOfWork, string connectionStringName, string connectionString)
{
var creationContext = new DbContextCreationContext(connectionStringName, connectionString);
using (DbContextCreationContext.Use(creationContext))
{
// 这里是重点,真正创建数据库上下文的地方。
var dbContext = CreateDbContext(unitOfWork);
if (unitOfWork.Options.Timeout.HasValue &&
dbContext.Database.IsRelational() &&
!dbContext.Database.GetCommandTimeout().HasValue)
{
dbContext.Database.SetCommandTimeout(unitOfWork.Options.Timeout.Value.TotalSeconds.To<int>());
}
return dbContext;
}
}
// 如果是事务型的工作单元,则调用 CreateDbContextWithTransaction() 进行创建,但不论如何都是通过工作单元提供的 IServiceProvider 解析出来 DbContext 的。
private TDbContext CreateDbContext(IUnitOfWork unitOfWork)
{
return unitOfWork.Options.IsTransactional
? CreateDbContextWithTransaction(unitOfWork)
: unitOfWork.ServiceProvider.GetRequiredService<TDbContext>();
}
以下代码才是在真正地创建 DbContext 实例。
public TDbContext CreateDbContextWithTransaction(IUnitOfWork unitOfWork)
{
var transactionApiKey = $"EntityFrameworkCore_{DbContextCreationContext.Current.ConnectionString}";
var activeTransaction = unitOfWork.FindTransactionApi(transactionApiKey) as EfCoreTransactionApi;
// 没有取得缓存。
if (activeTransaction == null)
{
var dbContext = unitOfWork.ServiceProvider.GetRequiredService<TDbContext>();
// 判断是否指定了事务隔离级别,并开始事务。
var dbtransaction = unitOfWork.Options.IsolationLevel.HasValue
? dbContext.Database.BeginTransaction(unitOfWork.Options.IsolationLevel.Value)
: dbContext.Database.BeginTransaction();
// 跟工作单元绑定添加一个已经激活的事务。
unitOfWork.AddTransactionApi(
transactionApiKey,
new EfCoreTransactionApi(
dbtransaction,
dbContext
)
);
// 返回构造好的数据库上下文。
return dbContext;
}
else
{
DbContextCreationContext.Current.ExistingConnection = activeTransaction.DbContextTransaction.GetDbTransaction().Connection;
var dbContext = unitOfWork.ServiceProvider.GetRequiredService<TDbContext>();
if (dbContext.As<DbContext>().HasRelationalTransactionManager())
{
dbContext.Database.UseTransaction(activeTransaction.DbContextTransaction.GetDbTransaction());
}
else
{
dbContext.Database.BeginTransaction(); //TODO: Why not using the new created transaction?
}
activeTransaction.AttendedDbContexts.Add(dbContext);
return dbContext;
}
}
ABP vNext 还提供了数据过滤器机制,可以让你根据指定的标识过滤数据,例如租户 Id 和软删除标记。它的基本接口定义在 Volo.Abp.Data 项目的 IDataFilter.cs 文件中,提供了启用、禁用、检测方法。
public interface IDataFilter<TFilter>
where TFilter : class
{
IDisposable Enable();
IDisposable Disable();
bool IsEnabled { get; }
}
public interface IDataFilter
{
IDisposable Enable<TFilter>()
where TFilter : class;
IDisposable Disable<TFilter>()
where TFilter : class;
bool IsEnabled<TFilter>()
where TFilter : class;
}
默认实现也在该项目下面的 DataFilter.cs 文件,首先看以下 IDataFilter 的默认实现 DataFilter,内部有一个解析器和并发字典。这个并发字典存储了所有的过滤器,其键是真实过滤器的类型(ISoftDelete 或 IMultiTenant),值是 DataFilter<TFilter>,具体对象根据 TFilter 的不同而不同。
public class DataFilter : IDataFilter, ISingletonDependency
{
private readonly ConcurrentDictionary<Type, object> _filters;
private readonly IServiceProvider _serviceProvider;
public DataFilter(IServiceProvider serviceProvider)
{
_serviceProvider = serviceProvider;
_filters = new ConcurrentDictionary<Type, object>();
}
// ...
}
看一下其他的方法,都是对 IDataFilter<Filter> 的包装。
public class DataFilter : IDataFilter, ISingletonDependency
{
// ...
public IDisposable Enable<TFilter>()
where TFilter : class
{
return GetFilter<TFilter>().Enable();
}
public IDisposable Disable<TFilter>()
where TFilter : class
{
return GetFilter<TFilter>().Disable();
}
public bool IsEnabled<TFilter>()
where TFilter : class
{
return GetFilter<TFilter>().IsEnabled;
}
private IDataFilter<TFilter> GetFilter<TFilter>()
where TFilter : class
{
// 并发字典当中获取指定类型的过滤器,如果不存在则从 IoC 中解析。
return _filters.GetOrAdd(
typeof(TFilter),
() => _serviceProvider.GetRequiredService<IDataFilter<TFilter>>()
) as IDataFilter<TFilter>;
}
}
这么看来,IDataFilter 叫做 IDataFilterManager 更加合适一点,最开始我还没搞明白两个接口和实现的区别,真正搞事情的是 DataFilter<Filter>。
public class DataFilter<TFilter> : IDataFilter<TFilter>
where TFilter : class
{
public bool IsEnabled
{
get
{
EnsureInitialized();
return _filter.Value.IsEnabled;
}
}
// 注入数据过滤器配置类。
private readonly AbpDataFilterOptions _options;
// 用于存储过滤器的启用状态。
private readonly AsyncLocal<DataFilterState> _filter;
public DataFilter(IOptions<AbpDataFilterOptions> options)
{
_options = options.Value;
_filter = new AsyncLocal<DataFilterState>();
}
// ...
// 确保初始化成功。
private void EnsureInitialized()
{
if (_filter.Value != null)
{
return;
}
// 如果过滤器的默认状态为 NULL,优先从配置类中取得指定过滤器的默认启用状态,如果不存在则默认为启用。
_filter.Value = _options.DefaultStates.GetOrDefault(typeof(TFilter))?.Clone() ?? new DataFilterState(true);
}
}
数据过滤器在设计的时候,也是按照工作单元的形式进行设计的。不论是启用还是停用都是范围性的,会返回一个用 DisposeAction 包装的可释放对象,这样在离开 using 语句块的时候,就会还原为来的状态。比如调用 Enable() 方法,在离开 using 语句块之后,会调用 Disable() 禁用掉数据过滤器。
public IDisposable Enable()
{
if (IsEnabled)
{
return NullDisposable.Instance;
}
_filter.Value.IsEnabled = true;
return new DisposeAction(() => Disable());
}
public IDisposable Disable()
{
if (!IsEnabled)
{
return NullDisposable.Instance;
}
_filter.Value.IsEnabled = false;
return new DisposeAction(() => Enable());
}
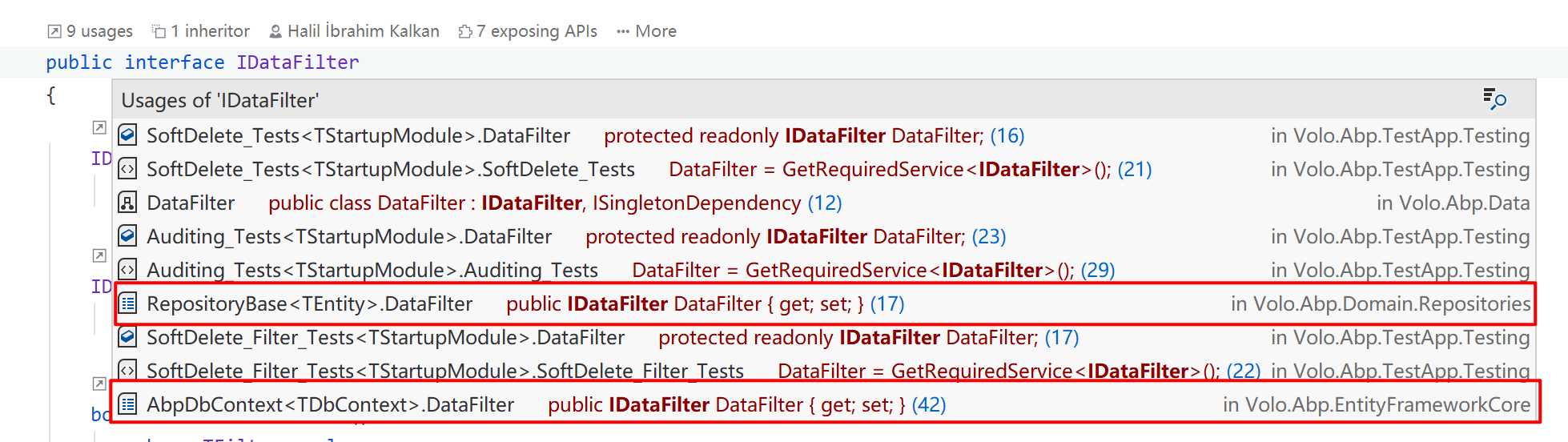
可以看到有两处使用,分别是 Volo.Abp.Domain 项目与 Volo.Abp.EntityFrameworkCore 项目。
首先看第一个项目的用法:
public abstract class RepositoryBase<TEntity> : BasicRepositoryBase<TEntity>, IRepository<TEntity>
where TEntity : class, IEntity
{
public IDataFilter DataFilter { get; set; }
// ...
// 分别在查询的时候判断实体是否实现了两个接口。
protected virtual TQueryable ApplyDataFilters<TQueryable>(TQueryable query)
where TQueryable : IQueryable<TEntity>
{
// 如果实现了软删除接口,则从 DataFilter 中获取过滤器的开启状态。
// 如果已经开启,则过滤掉被删除的数据。
if (typeof(ISoftDelete).IsAssignableFrom(typeof(TEntity)))
{
query = (TQueryable)query.WhereIf(DataFilter.IsEnabled<ISoftDelete>(), e => ((ISoftDelete)e).IsDeleted == false);
}
// 如果实现了多租户接口,则从 DataFilter 中获取过滤器的开启状态。
// 如果已经开启,则按照租户 Id 过滤数据。
if (typeof(IMultiTenant).IsAssignableFrom(typeof(TEntity)))
{
var tenantId = CurrentTenant.Id;
query = (TQueryable)query.WhereIf(DataFilter.IsEnabled<IMultiTenant>(), e => ((IMultiTenant)e).TenantId == tenantId);
}
return query;
}
// ...
}
逻辑比较简单,都是判断实体是否实现某个接口,并且结合启用状态来进行过滤,在原有 IQuerable 拼接 WhereIf() 即可。但是 EF Core 使用这种方式不行,所以上述方法只会在 Memory 和 MongoDb 有使用。
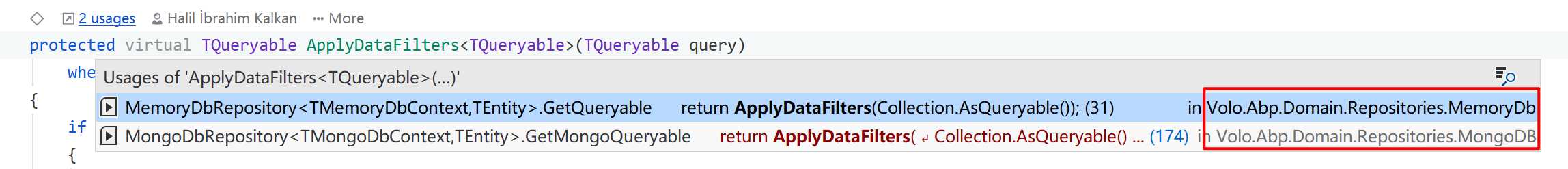
EF Core 集成数据过滤器则是放在数据库上下文基类 AbpDbContext<TDbContext> 中,在数据库上下文的 OnModelCreating() 方法内通过 ConfigureBasePropertiesMethodInfo 进行反射调用。
public abstract class AbpDbContext<TDbContext> : DbContext, IEfCoreDbContext, ITransientDependency
where TDbContext : DbContext
{
// ...
protected virtual bool IsMultiTenantFilterEnabled => DataFilter?.IsEnabled<IMultiTenant>() ?? false;
protected virtual bool IsSoftDeleteFilterEnabled => DataFilter?.IsEnabled<ISoftDelete>() ?? false;
// ...
public IDataFilter DataFilter { get; set; }
// ...
private static readonly MethodInfo ConfigureBasePropertiesMethodInfo = typeof(AbpDbContext<TDbContext>)
.GetMethod(
nameof(ConfigureBaseProperties),
BindingFlags.Instance | BindingFlags.NonPublic
);
// ...
protected override void OnModelCreating(ModelBuilder modelBuilder)
{
base.OnModelCreating(modelBuilder);
foreach (var entityType in modelBuilder.Model.GetEntityTypes())
{
ConfigureBasePropertiesMethodInfo
.MakeGenericMethod(entityType.ClrType)
.Invoke(this, new object[] { modelBuilder, entityType });
// ...
}
}
// ...
protected virtual void ConfigureBaseProperties<TEntity>(ModelBuilder modelBuilder, IMutableEntityType mutableEntityType)
where TEntity : class
{
if (mutableEntityType.IsOwned())
{
return;
}
ConfigureConcurrencyStampProperty<TEntity>(modelBuilder, mutableEntityType);
ConfigureExtraProperties<TEntity>(modelBuilder, mutableEntityType);
ConfigureAuditProperties<TEntity>(modelBuilder, mutableEntityType);
ConfigureTenantIdProperty<TEntity>(modelBuilder, mutableEntityType);
// 在这里,配置全局过滤器。
ConfigureGlobalFilters<TEntity>(modelBuilder, mutableEntityType);
}
// ...
protected virtual void ConfigureGlobalFilters<TEntity>(ModelBuilder modelBuilder, IMutableEntityType mutableEntityType)
where TEntity : class
{
// 符合条件则为其创建过滤表达式。
if (mutableEntityType.BaseType == null && ShouldFilterEntity<TEntity>(mutableEntityType))
{
// 创建过滤表达式。
var filterExpression = CreateFilterExpression<TEntity>();
if (filterExpression != null)
{
// 为指定的实体配置查询过滤器。
modelBuilder.Entity<TEntity>().HasQueryFilter(filterExpression);
}
}
}
// ...
// 判断实体是否拥有过滤器。
protected virtual bool ShouldFilterEntity<TEntity>(IMutableEntityType entityType) where TEntity : class
{
if (typeof(IMultiTenant).IsAssignableFrom(typeof(TEntity)))
{
return true;
}
if (typeof(ISoftDelete).IsAssignableFrom(typeof(TEntity)))
{
return true;
}
return false;
}
// 构建表达式。
protected virtual Expression<Func<TEntity, bool>> CreateFilterExpression<TEntity>()
where TEntity : class
{
Expression<Func<TEntity, bool>> expression = null;
if (typeof(ISoftDelete).IsAssignableFrom(typeof(TEntity)))
{
expression = e => !IsSoftDeleteFilterEnabled || !EF.Property<bool>(e, "IsDeleted");
}
if (typeof(IMultiTenant).IsAssignableFrom(typeof(TEntity)))
{
Expression<Func<TEntity, bool>> multiTenantFilter = e => !IsMultiTenantFilterEnabled || EF.Property<Guid>(e, "TenantId") == CurrentTenantId;
expression = expression == null ? multiTenantFilter : CombineExpressions(expression, multiTenantFilter);
}
return expression;
}
// ...
}
在讲解事件总线与 DDD 这块的时候,我有提到过 ABP vNext 有实现领域事件功能,用户可以在聚合根内部使用 AddLocalEvent(object eventData) 或 AddDistributedEvent(object eventData) 添加了领域事件。
public abstract class AggregateRoot : Entity,
IAggregateRoot,
IGeneratesDomainEvents,
IHasExtraProperties,
IHasConcurrencyStamp
{
// ...
private readonly ICollection<object> _localEvents = new Collection<object>();
private readonly ICollection<object> _distributedEvents = new Collection<object>();
// ...
// 添加本地事件。
protected virtual void AddLocalEvent(object eventData)
{
_localEvents.Add(eventData);
}
// 添加分布式事件。
protected virtual void AddDistributedEvent(object eventData)
{
_distributedEvents.Add(eventData);
}
// 获得所有本地事件。
public virtual IEnumerable<object> GetLocalEvents()
{
return _localEvents;
}
// 获得所有分布式事件。
public virtual IEnumerable<object> GetDistributedEvents()
{
return _distributedEvents;
}
// 清空聚合需要触发的所有本地事件。
public virtual void ClearLocalEvents()
{
_localEvents.Clear();
}
// 清空聚合需要触发的所有分布式事件。
public virtual void ClearDistributedEvents()
{
_distributedEvents.Clear();
}
}
可以看到,我们在聚合内部执行任何业务行为的时候,可以通过上述的方法发送领域事件。那这些事件是在什么时候被发布的呢?
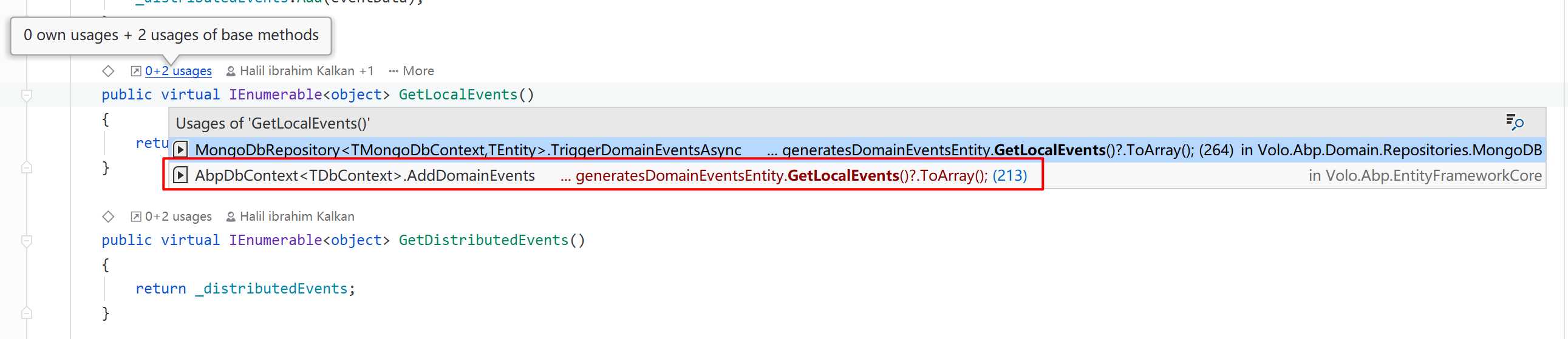
发现这几个 Get 方法有被 AbpDbContext 所调用,其实在它的内部,会在每次 SaveChangesAsync() 的时候,遍历所有实体,并获取它们的本地事件与分布式事件集合,最后由 EntityChangeEventHelper 进行触发。
public abstract class AbpDbContext<TDbContext> : DbContext, IEfCoreDbContext, ITransientDependency
where TDbContext : DbContext
{
// ...
public override async Task<int> SaveChangesAsync(bool acceptAllChangesOnSuccess, CancellationToken cancellationToken = default)
{
try
{
var auditLog = AuditingManager?.Current?.Log;
List<EntityChangeInfo> entityChangeList = null;
if (auditLog != null)
{
entityChangeList = EntityHistoryHelper.CreateChangeList(ChangeTracker.Entries().ToList());
}
var changeReport = ApplyAbpConcepts();
var result = await base.SaveChangesAsync(acceptAllChangesOnSuccess, cancellationToken).ConfigureAwait(false);
// 触发领域事件。
await EntityChangeEventHelper.TriggerEventsAsync(changeReport).ConfigureAwait(false);
if (auditLog != null)
{
EntityHistoryHelper.UpdateChangeList(entityChangeList);
auditLog.EntityChanges.AddRange(entityChangeList);
Logger.LogDebug($"Added {entityChangeList.Count} entity changes to the current audit log");
}
return result;
}
catch (DbUpdateConcurrencyException ex)
{
throw new AbpDbConcurrencyException(ex.Message, ex);
}
finally
{
ChangeTracker.AutoDetectChangesEnabled = true;
}
}
// ...
protected virtual EntityChangeReport ApplyAbpConcepts()
{
var changeReport = new EntityChangeReport();
// 遍历所有的实体变更事件。
foreach (var entry in ChangeTracker.Entries().ToList())
{
ApplyAbpConcepts(entry, changeReport);
}
return changeReport;
}
protected virtual void ApplyAbpConcepts(EntityEntry entry, EntityChangeReport changeReport)
{
// 根据不同的实体操作状态,执行不同的操作。
switch (entry.State)
{
case EntityState.Added:
ApplyAbpConceptsForAddedEntity(entry, changeReport);
break;
case EntityState.Modified:
ApplyAbpConceptsForModifiedEntity(entry, changeReport);
break;
case EntityState.Deleted:
ApplyAbpConceptsForDeletedEntity(entry, changeReport);
break;
}
// 添加领域事件。
AddDomainEvents(changeReport, entry.Entity);
}
// ...
protected virtual void AddDomainEvents(EntityChangeReport changeReport, object entityAsObj)
{
var generatesDomainEventsEntity = entityAsObj as IGeneratesDomainEvents;
if (generatesDomainEventsEntity == null)
{
return;
}
// 获取到所有的本地事件和分布式事件,将其加入到 EntityChangeReport 对象当中。
var localEvents = generatesDomainEventsEntity.GetLocalEvents()?.ToArray();
if (localEvents != null && localEvents.Any())
{
changeReport.DomainEvents.AddRange(localEvents.Select(eventData => new DomainEventEntry(entityAsObj, eventData)));
generatesDomainEventsEntity.ClearLocalEvents();
}
var distributedEvents = generatesDomainEventsEntity.GetDistributedEvents()?.ToArray();
if (distributedEvents != null && distributedEvents.Any())
{
changeReport.DistributedEvents.AddRange(distributedEvents.Select(eventData => new DomainEventEntry(entityAsObj, eventData)));
generatesDomainEventsEntity.ClearDistributedEvents();
}
}
}
转到 `` 的内部,发现有如下代码:
// ...
public async Task TriggerEventsAsync(EntityChangeReport changeReport)
{
// 触发领域事件。
await TriggerEventsInternalAsync(changeReport).ConfigureAwait(false);
if (changeReport.IsEmpty() || UnitOfWorkManager.Current == null)
{
return;
}
await UnitOfWorkManager.Current.SaveChangesAsync().ConfigureAwait(false);
}
protected virtual async Task TriggerEventsInternalAsync(EntityChangeReport changeReport)
{
// 触发默认的实体变更事件,例如某个实体被创建、修改、删除。
await TriggerEntityChangeEvents(changeReport.ChangedEntities).ConfigureAwait(false);
// 触发用户自己发送的领域事件。
await TriggerLocalEvents(changeReport.DomainEvents).ConfigureAwait(false);
await TriggerDistributedEvents(changeReport.DistributedEvents).ConfigureAwait(false);
}
// ...
protected virtual async Task TriggerLocalEvents(List<DomainEventEntry> localEvents)
{
foreach (var localEvent in localEvents)
{
await LocalEventBus.PublishAsync(localEvent.EventData.GetType(), localEvent.EventData).ConfigureAwait(false);
}
}
protected virtual async Task TriggerDistributedEvents(List<DomainEventEntry> distributedEvents)
{
foreach (var distributedEvent in distributedEvents)
{
await DistributedEventBus.PublishAsync(distributedEvent.EventData.GetType(), distributedEvent.EventData).ConfigureAwait(false);
}
}
点击我 跳转到文章总目录。
[Abp vNext 源码分析] - 14. EntityFramework Core 的集成
标签:ict his reg required assign api 映射 实体类 ansi
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/dongshenjun/p/12763287.html