标签:加密 iter png cmd windows10 地址 adp pre 模型
1、网络模型7层概述
2、网络编程三要素
3、TCP 和 UDP
4、UDP 编程
5、TCP 编程
6、使用 telnet 客户端发送数据
7、BIO 模型 循环读取客户端发送的数据
1、网络模型7层概述 <--返回目录
2、网络编程三要素 <--返回目录
A:IP地址
B:端口
C:协议
3、TCP 和 UDP <--返回目录
UDP
将数据源和目的封装成数据包中,不需要建立连接;
每个数据报的大小在限制在64k;
不需要建立连接,速度快
因无连接,是不可靠协议;
TCP
建立连接,形成传输数据的通道;
在连接中进行大数据量传输;
通过三次握手完成连接,是可靠协议;
必须建立连接,效率会稍低
4、UDP 编程 <--返回目录
package com.oy; import java.net.DatagramPacket; import java.net.DatagramSocket; import java.net.InetAddress; import org.junit.Test; public class Demo1 { @Test public void server() throws Exception { // 1. 创建接收端Socket对象 DatagramSocket ds = new DatagramSocket(10086); while (true) { // 2. 创建一个数据包(接收容器) byte[] bys = new byte[1024]; DatagramPacket dp = new DatagramPacket(bys, bys.length); // 3. 调用Socket对象的接收方法接收数据 ds.receive(dp); // 阻塞式 // 3. 解析数据包,并显示在控制台 InetAddress inetAddress = dp.getAddress(); String ip = inetAddress.getHostAddress(); // 获取对方的ip byte[] bys2 = dp.getData(); // 获取数据缓冲区 int len = dp.getLength(); // 获取数据的实际长度 String s = new String(bys2, 0, len); System.out.println(ip + "传递的数据是:" + s); } // 4. 释放资源 //ds.close(); } @Test public void client() throws Exception { // 1. 创建发送端Socket对象 DatagramSocket ds = new DatagramSocket(); // 2. 创建数据,并把数据打包 // DatagramPacket(byte[] buf, int length, InetAddress address, int port) byte[] bys = "Hello, UDP...".getBytes(); // 数据 int length = bys.length; // 长度 InetAddress address = InetAddress.getByName("192.168.181.1"); // IP地址对象 int port = 10086; // 端口 DatagramPacket dp = new DatagramPacket(bys, length, address, port); // 3. 调用Socket对象的发送方法发送数据包 ds.send(dp); // 4. 释放资源 ds.close(); } }
多线程实现聊天程序
public class ChatRoom { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { DatagramSocket dsSend = new DatagramSocket(); DatagramSocket dsReceive = new DatagramSocket(12306); SendThread st = new SendThread(dsSend); ReceiveThread rt = new ReceiveThread(dsReceive); Thread t1 = new Thread(st); Thread t2 = new Thread(rt); t1.start(); t2.start(); } } public class ReceiveThread implements Runnable { private DatagramSocket ds; public ReceiveThread(DatagramSocket ds) { this.ds = ds; } @Override public void run() { try { while (true) { // 创建一个包裹 byte[] bys = new byte[1024]; DatagramPacket dp = new DatagramPacket(bys, bys.length); // 接收数据 ds.receive(dp); // 解析数据 String ip = dp.getAddress().getHostAddress(); String s = new String(dp.getData(), 0, dp.getLength()); System.out.println("from " + ip + " data is : " + s); } } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } public class SendThread implements Runnable { private DatagramSocket ds; public SendThread(DatagramSocket ds) { this.ds = ds; } @Override public void run() { try { // 封装键盘录入数据 BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in)); String line = null; while ((line = br.readLine()) != null) { if ("886".equals(line)) { break; } // 创建数据并打包 byte[] bys = line.getBytes(); DatagramPacket dp = new DatagramPacket(bys, bys.length, InetAddress.getByName("192.168.12.255"), 12306); // 发送数据 ds.send(dp); } // 释放资源 ds.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }
5、TCP 编程 <--返回目录
package com.oy; import java.io.InputStream; import java.io.OutputStream; import java.net.ServerSocket; import java.net.Socket; import org.junit.Test; public class Demo2 { @Test public void server() throws Exception { // 创建接收端的Socket对象 ServerSocket ss = new ServerSocket(8888); while (true) { // 监听客户端连接。返回一个对应的Socket对象 Socket s = ss.accept(); // 侦听并接受到此套接字的连接。此方法在连接传入之前一直阻塞。 // 获取输入流,读取数据显示在控制台 InputStream is = s.getInputStream(); byte[] bys = new byte[1024]; int len = is.read(bys); // 阻塞式方法 String str = new String(bys, 0, len); String ip = s.getInetAddress().getHostAddress(); System.out.println("from " + ip + ", " + str); // 释放资源 s.close(); // ss.close(); //这个不应该关闭 } } @Test public void client() throws Exception { // 创建发送端的Socket对象 // Socket(InetAddress address, int port) // Socket(String host, int port) // Socket s = new Socket(InetAddress.getByName("192.168.181.1"), 8888); Socket s = new Socket("192.168.181.1", 8888); // 获取输出流,写数据 OutputStream os = s.getOutputStream(); os.write("Hello TCP...".getBytes()); // 释放资源 s.close(); } }
服务器给客户端一个反馈
@Test public void server() throws Exception { // 创建接收端的Socket对象 ServerSocket ss = new ServerSocket(8888); while (true) { // 监听客户端连接。返回一个对应的Socket对象 Socket s = ss.accept(); // 侦听并接受到此套接字的连接。此方法在连接传入之前一直阻塞。 // 获取输入流,读取数据显示在控制台 InputStream is = s.getInputStream(); byte[] bys = new byte[1024]; int len = is.read(bys); // 阻塞式方法 String str = new String(bys, 0, len); String ip = s.getInetAddress().getHostAddress(); System.out.println("from " + ip + ", " + str); // 获取输出流 OutputStream os = s.getOutputStream(); os.write("server已经收到数据".getBytes()); // 释放资源 s.close(); // ss.close(); //这个不应该关闭 } } @Test public void client() throws Exception { // 创建发送端的Socket对象 Socket s = new Socket("192.168.181.1", 8888); // 获取输出流,写数据 OutputStream os = s.getOutputStream(); os.write("今天天气很好,适合睡觉".getBytes()); // 获取输入流 InputStream is = s.getInputStream(); byte[] bys = new byte[1024]; int len = is.read(bys);// 阻塞 String client = new String(bys, 0, len); System.out.println("client收到server反馈: " + client); // 释放资源 s.close(); }
TCP 实现文件上传
public class UploadServer { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { // 创建服务器端的Socket对象 ServerSocket ss = new ServerSocket(10086); // 监听客户端连接 Socket s = ss.accept(); // 封装通道内的流 BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(s.getInputStream())); // 封装文本文件 BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter("d:/copy.txt")); String line = null; while ((line = br.readLine()) != null) { bw.write(line); bw.newLine(); bw.flush(); } bw.close(); s.close(); } }
public class UploadClient { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { // 创建客户端Socket对象 Socket s = new Socket("192.168.181.1", 10086); // 封装文本文件 BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("d:/a.txt")); // 封装通道内流 BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(s.getOutputStream())); String line = null; while ((line = br.readLine()) != null) { bw.write(line); bw.newLine(); bw.flush(); } // 释放资源 br.close(); s.close(); } }
6、使用 telnet 客户端发送数据 <--返回目录
windows10 开启 telnet:
1) 控制面板\所有控制面板项\程序和功能
2) 启用或关闭 windows 功能
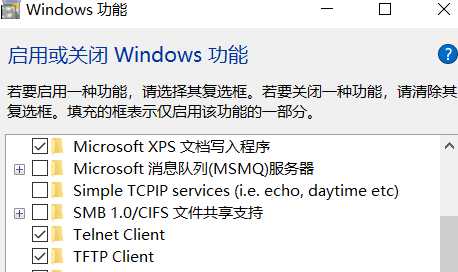
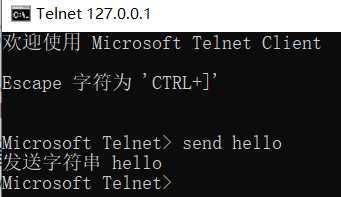
telnet 发送数据:
1) 打开 cmd, 执行 telnet 127.0.0.1 8888
2) ctrl + "]"
3) send 内容
7、BIO 模型 循环读取客户端发送的数据 <--返回目录
使用 BIO 模型编写一个服务器端,监听6666端口,当有客户端连接时,就启动一个线程与之通信;
要求使用线程池机制,可以连接多个客户端;
服务器可以接收客户端发送的数据(telnet 方式);
public class Demo3 { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { ExecutorService threadPool = Executors.newCachedThreadPool(); ServerSocket serverSocket = new ServerSocket(6666); System.out.println("服务器启动了。。。"); while (true) { final Socket socket = serverSocket.accept(); System.out.println("连接到一个客户端"); // 创建线程,与之通信 threadPool.execute(new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { handler(socket); } }); } } /** * 与客户端通信 */ public static void handler(Socket socket) { try { // 获取输入流 InputStream inputStream = socket.getInputStream(); byte[] bytes = new byte[1024]; // 循环读取客户端发送的数据 while (true) { int read = inputStream.read(bytes); if (read != -1) { System.out.println("from client: " + new String(bytes, 0, read)); } else { break; } } } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { System.out.println("关闭于 client 的连接"); try { socket.close(); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } }
telnet 客户端连接并发送数据
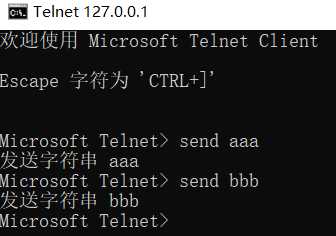
程序控制台打印:

---
标签:加密 iter png cmd windows10 地址 adp pre 模型
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/xy-ouyang/p/12810694.html