标签:使用 write shc super exce size 数据 nts ado
原型模式
原型模式(Prototype Pattern),使用原型实例复制生成新的对象。若某个类的实例化比较复杂,完全重新创建成本较大,这时可以使用原型模式。这种模式是在内存(堆)中拷贝对象,比直接new一个对象节省资源。对象拷贝的时候构造器是不会执行。
结构图:
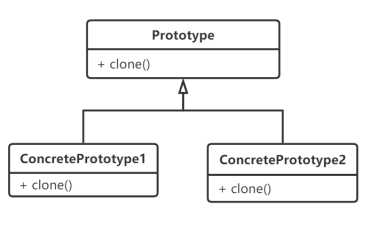
Prototype:提供拷贝方法的原型接口
ConcretePrototype:实现拷贝自身方法的类
Java中提供了实现原型模式的方式:
·实现Cloneable接口;
·重写clone方法(默认的protected改为public)
这里Cloneable即可为Prototype。
1. 浅拷贝
只拷贝对象内的基本数据类型,数组和对象仅拷贝其引用,没有真实拷贝一个新的数组/对象。
例:
public class Pen { private String name; private float cost; public Pen(String name, float cost) { this.name = name; this.cost = cost; } }
public class Student implements Cloneable{ // ConcretePrototype private String name; private int age; private Pen pen; public Student(String name, int age, Pen pen) { this.name = name; this.age = age; this.pen = pen; } @Override public Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException { return super.clone(); } // setter/getter省略 }
public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) throws CloneNotSupportedException { Student student1 = new Student("jzx",18,new Pen("真彩",3.5f)); Student student2 = (Student)student1.clone(); System.out.println("student1的hashCode:"+ student1.hashCode()); System.out.println("student2的hashCode:"+ student2.hashCode()); System.out.println("student1的pen的hashCode:"+ student1.getPen().hashCode()); System.out.println("student2的pen的hashCode:"+ student2.getPen().hashCode()); } }
输出:
student1的hashCode:1735600054 student2的hashCode:21685669 student1的pen的hashCode:2133927002 student2的pen的hashCode:2133927002
从hashCode可以看出,副本student2中的实例对象pen和student1的实例对象是同一个。
2.深拷贝
全部拷贝,真正的完全拷贝。
方式一:
让被拷贝对象中的实例对象的类也实现Cloneable接口,并重写clone方法,同时被拷贝对象的类中重写clone时对实例对象额外拷贝。
例:
public class Pen implements Cloneable{ private String name; private float cost; public Pen(String name, float cost) { this.name = name; this.cost = cost; } @Override public Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException { return super.clone(); } }
public class Student implements Cloneable{ private String name; private int age; private Pen pen; public Student(String name, int age,Pen pen) { this.name = name; this.age = age; this.pen = pen; } @Override public Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException { Student student = (Student)super.clone(); student.pen = (Pen)this.pen.clone(); return student; } // setter/getter 省略 }
public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) throws CloneNotSupportedException { Student student1 = new Student("jzx",18,new Pen("真彩",3.5f)); Student student2 = (Student)student1.clone(); System.out.println("student1的hashCode:"+ student1.hashCode()); System.out.println("student2的hashCode:"+ student2.hashCode()); System.out.println("student1的pen的hashCode:"+ student1.getPen().hashCode()); System.out.println("student2的pen的hashCode:"+ student2.getPen().hashCode()); } }
输出:
student1的hashCode:1735600054 student2的hashCode:21685669 student1的Pen的hashCode:2133927002 student2的Pen的hashCode:1836019240
这时,从hashCode可以看出,副本student2中的实例对象pen和student1的实例对象pen不再是同一个了,是完完全全的拷贝。
方式二:
被拷贝对象及其中的实例对象都实现序列化,重写clone方法时进行序列化和反序列化。
例:
public class Pen implements Serializable { private String name; private float cost; public Pen(String name, float cost) { this.name = name; this.cost = cost; } }
public class Student implements Cloneable,Serializable{ private String name; private int age; private Pen pen; public Student(String name, int age,Pen pen) { this.name = name; this.age = age; this.pen = pen; } @Override public Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException { // 序列化 ByteArrayOutputStream bos = new ByteArrayOutputStream(); ObjectOutputStream oos = null; try { oos = new ObjectOutputStream(bos); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } try { oos.writeObject(this); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } // 反序列化 ByteArrayInputStream bis = new ByteArrayInputStream(bos.toByteArray()); ObjectInputStream ois = null; try { ois = new ObjectInputStream(bis); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } Student student = null; try { student = (Student) ois.readObject(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (ClassNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } return student; } // setter/getter省略 }
public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) throws CloneNotSupportedException { Student student1 = new Student("jzx",18,new Pen("真彩",3.5f)); Student student2 = (Student)student1.clone(); System.out.println("student1的hashCode:"+ student1.hashCode()); System.out.println("student2的hashCode:"+ student2.hashCode()); System.out.println("student1的pen的hashCode:"+ student1.getPen().hashCode()); System.out.println("student2的pen的hashCode:"+ student2.getPen().hashCode()); } }
输出:
student1的hashCode:621009875 student2的hashCode:1072408673 student1的pen的hashCode:1554874502 student2的pen的hashCode:1531448569
可见,序列化实现了深拷贝。
标签:使用 write shc super exce size 数据 nts ado
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/jiazhongxin/p/12815166.html