标签:component 不同 注意事项 tin 另一个 func 阶段 change 全局
var v1 = new Vue({
el: "#app1",
data: {title:”hello vuw!”}
});
var v2 = new Vue({
el: "#app1",
methods:{
changev1title:function () {
v1.title = "hello python!"
},
}
});
这些属性是data或computed里定义的
var v2 = new Vue({
el: "#app1",
methods:{
changev1title:function () {
v1.title = "hello python!"
},
v1upper: function () {
v1.toUpperCase()
}
}
});
直接通过对象的方式定义的属性,是来自于data或computed中的属性,但是vue对象中的el、data等等这些键也称为属性,这些属性是vue对象的实例属性!
注意:
1)ref的使用
在vue里面,往往使用ref属性来代替id属性的使用,那么就可以快速的通过的调用ref的值来获取页面中的某个元素。
<button type="button" ref="mybtn1" @click="showVueObject">点我</button>
showVueObject:function () {
this.$refs.mybtn1.innerHTML = "hello"
}
2)mount的使用
实现了页面元素与vue对象的动态绑定,之前都是通过el的方式绑定。
<div id="app"></div>
<script src="https://cdn.bootcss.com/vue/2.6.11/vue.js"></script>
<script>
var v1 = new Vue({
template:"<h1>hello template</h1",
});
v1.$mount(‘#app‘);
</script>
Vue的一大特性:组件化。可以将vue对象作为一个组件,被反复的使用。
注册组件的方式有两种,全局注册和局部注册。
Vue.component(“组件名”,{vue对象})
在被vue对象绑定了的html元素中才可以使用组件,如果一个div没有被vue绑定,那么这个div中不能使用之前注册的组件。
<div id="app">
<model1></model1>
<model1></model1>
<model1></model1>
</div>
<script src="https://cdn.bootcss.com/vue/2.6.11/vue.js"></script>
<script>
Vue.component("model1",{
template:"<div>{{title}}<button type=‘button‘ @click=‘mybtn‘>点我</button> </div>",
data:function(){
return {
title: "hello vue",
}
},
methods: {
mybtn: function () {
alert(‘hello vue!!!‘);
}
}
});
new Vue({
el: "#app",
})
特点1:
Vue.component(“组件名”,{vue对象}),这个vue对象和之前的vue对象的data属性的写法是由区别的
new Vue({
el: "#app",
data: {
name: “xx”,
age: 23,
});
Vue.component("model1",{
data: function(){
return {
name: “xx”,
age: 23,
}
},
});
特点2:
组建中template的值是一个字符串,其有且仅有一个根元素
错误:
template:"<div>{{title}}</div><button type=‘button‘ @click=‘mybtn‘>点我</button>",
正确:
template:"<div>{{title}}<button type=‘button‘ @click=‘mybtn‘>点我</button> </div>",
Vue的全局注册,意味着在页面中任意一个被vue绑定的div中都以使用用全局注册的vue组件。但是,如果是对vue组件进行本地注册,那么在其他被vue绑定的div中,不能使用该组件。
<div id="app">
<model11></model11>
</div>
<div id="app1">
<model11></model11>
</div>
<script src="https://cdn.bootcss.com/vue/2.6.11/vue.js"></script>
<script>
var model1 = {
template:"<div><h1>{{title}}</h1><button type=‘button‘ @click=‘mybtn‘>点我</button></div>",
data:function(){
return {
title: "hello vue",
}
},
methods: {
mybtn: function () {
alert(‘hello vue!!!‘);
}
}
};
new Vue({
el: "#app", // 只有这个组件可以使用model11组件
components:{
"model11": model1,
}
});
new Vue({
el: "#app1", // 这个div对象不能使用model11组件
})
</script>
一个Vue对象会经历初始化、创建、绑定、更新、销毁等阶段,不同的阶段,都会有相应的生命周期钩子函数被调用,可以参考官方文档的生命周期示意图。
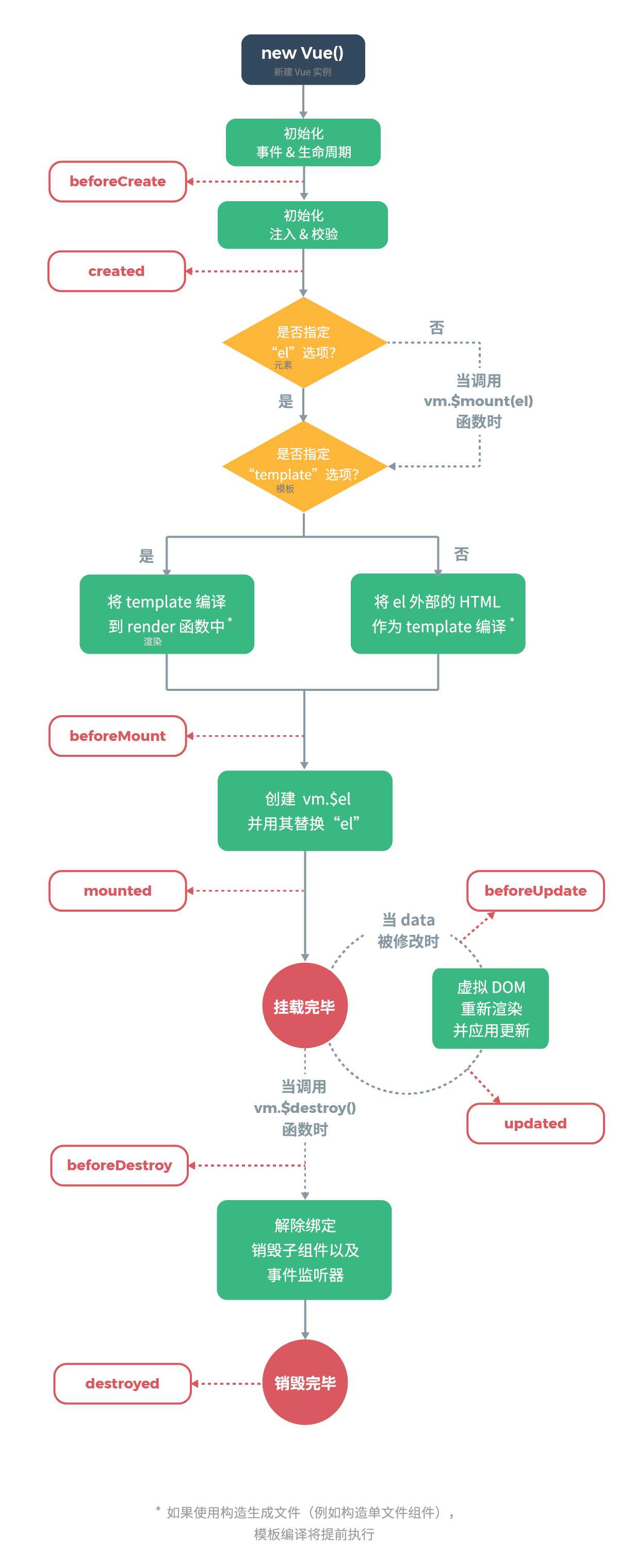
<script src="https://cdn.bootcss.com/vue/2.6.11/vue.js"></script>
<script>
new Vue({
el:"#app",
data:{
title:"this is title"
},
methods:{
changeTitle:function(){
this.title= "new title";
},
destroy:function(){
this.$destroy();
}
},
// ES5
beforeCreate:function(){
console.log("beforeCreate")
},
// ES6
created(){
console.log("created")
},
beforeMount(){
console.log("beforeMount")
// 3.一个页面中只有一个div,其他的都是vue组件
// vue组件里的data必须使用function的形式对{}对象进行封装,防止对其他数据的修改。 注意,template里必须有
// 一个根节点。
},
mounted(){
console.log("mounted")
},
beforeUpdate(){
console.log("beforeUpdate")
},
updated(){
console.log("updated")
},
beforeDestroy(){
console.log("beforeDestory")
},
destroyed(){
console.log("destory")
}
})
</script>
执行顺序:
ProductInfo.vue?ca1b:17 beforeCreate
ProductInfo.vue?ca1b:21 created
ProductInfo.vue?ca1b:24 beforeMount
ProductInfo.vue?ca1b:30 mounted
ProductInfo.vue?ca1b:30 beforeUpdate
ProductInfo.vue?ca1b:30 Update
ProductInfo.vue?ca1b:39 beforeDestory
ProductInfo.vue?ca1b:42 destory
标签:component 不同 注意事项 tin 另一个 func 阶段 change 全局
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/zhangyafei/p/12859204.html