标签:过程 throw main list() 变量 cal als 两个栈 length
? 中缀表达式是一个通用的算术或逻辑公式表示方法。中缀表达式(或中缀记法)是一个通用的算术或逻辑公式表示方法, 操作符是以中缀形式处于操作数的中间(例:3 + 4),中缀表达式是人们常用的算术表示方法。
? 与前缀表达式(例:+ 3 4)或后缀表达式(例:3 4 +)相比,中缀表达式不容易被计算机解析,但仍被许多程序语言使用,因为它符合人们的普遍用法。
? 与前缀或后缀记法不同的是,中缀记法中括号是必需的。计算过程中必须用括号将操作符和对应的操作数括起来,用于指示运算的次序。
例:
(1)8+4-6*2用后缀表达式表示为:
? 8 4+6 2*-
(2)2*(3+5)+7/1-4用后缀表达式表示为:
? 235+*71/+4-
? 逆波兰式(Reverse Polish notation,RPN,或逆波兰记法),也叫后缀表达式(将运算符写在操作数之后)
定义
一个表达式E的后缀形式可以如下定义:
(2)如果E是E1 op E2形式的表达式,这里op是任何二元操作符,则E的后缀式为E1‘E2‘ op,这里E1‘和E2‘分别为E1和E2的后缀式。
(3)如果E是(E1)形式的表达式,则E1的后缀式就是E的后缀式。
? 用逆波兰式计算表达式结果的方法为:
- 初始化两个栈:运算符栈s1和储存中间结果的栈s2;
- 从左至右扫描中缀表达式;
- 遇到操作数时,将其压s2
- 遇到运算符时,比较其与s1栈顶运算符的优先级
- (1)如果s1为空,或栈顶运算符为左括号“(”,则直接将此运算符入栈;
- (2)否则,若优先级比栈顶运算符的高,也将运算符压入s1;
- (3)否则,将s1栈顶的运算符弹出并压入到s2中,再次转到(4-1)与s1中新的栈顶运算符相比较;
- 遇到括号时:
- (1)如果是左括号“(”,则直接压入s1
- (2)如果是右括号“)”,则依次弹出s1栈顶的运算符,并压入s2,直到遇到左括号为止,此时将这一对括号丢弃
- .重复步骤2至5,直到表达式的最右边
- 将s1中剩余的运算符依次弹出并压入s2
- 依次弹出s2中的元素并输出,结果的逆序即为中缀表达式对应的后缀表达式
- 从左到右扫描表达式的字符。
- 对当前字符进行判断
- (1)如果当前字符为运算符,则直接从将栈顶元素和次栈顶元素弹出,与当前运算符进行运算,将结果压入栈中。
- (2)若当前字符为数字,直接压入栈中。
- 循环2.1,2.2直到表达式扫描完毕,最后栈中的数字就是所要的结果。
/**
* @author ymy
* @date 2020/5/12
*/
public class PolandNotation {
public static void main(String[] args) {
PolandNotation calculate = new PolandNotation();
// System.out.println(calculate.calculateSuffixExpression("30 4 + 5 * 6 -"));
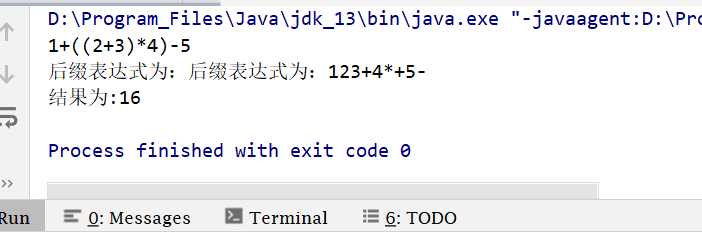
String infix ="1+((2+3)*4)-5";
List<String> list = calculate.toInfixExpressionList(infix);
List<String> suffix= calculate.toSuffixExpression(list);
System.out.print("后缀表达式为:");
String str ="";
for (String s : suffix) {
str+=s;
}
System.out.println("后缀表达式为:"+str);
System.out.printf("结果为:%d\n",calculate.calculateSuffixExpression(suffix));
}
/**
* @param expressionStr 3 4 + 5 × 6 -
* @return 计算结果
*/
public int calculateSuffixExpression(List<String> expression) {
int res = 0;
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack();
int num1;
int num2;
String operator = "";
for (int i = 0; i < expression.size(); i++) {
if (isOperaor(expression.get(i))) {
num1 = stack.pop();
num2 = stack.pop();
operator = expression.get(i);
res = calculate(num1, num2, operator);
stack.push(res);
} else {
stack.push(Integer.parseInt(expression.get(i)));
}
}
return res;
}
public int calculate(int num1, int num2, String operator) {
int res = 0;
switch (operator) {
case "+":
res = num1 + num2;
break;
case "-":
res = num2 - num1;
break;
case "*":
res = num1 * num2;
break;
case "/":
res = num2 / num1;
break;
}
return res;
}
public boolean isOperaor(String str) {
return str.equals("+") || str.equals("-") || str.equals("*") || str.equals("/");
}
public int getPriority(String oper){
if (oper.equals("+")||oper.equals("-"))
return 0;
if (oper.equals("*")||oper.equals("/"))
return 1;
return -1;
}
/**
* 将后缀表达式用list保存
*
* @param suffixExpression
* @return
*/
public List<String> getListString(String suffixExpression) {
ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList();
String[] strings = suffixExpression.split(" ");
for (int i = 0; i < strings.length; i++) {
list.add(strings[i]);
}
return list;
}
/**
* @return 中缀表达式转化为后缀表达式
* 1.初始化两个栈:运算符栈s1和储存中间结果的栈s2;
* 2.从左至右扫描中缀表达式;
* 3.遇到操作数时,将其压s2;
* 4.遇到运算符时,比较其与s1栈顶运算符的优先级:
* (1)如果s1为空,或栈顶运算符为左括号“(”,则直接将此运算符入栈;
* (2)否则,若优先级比栈顶运算符的高,也将运算符压入s1;
* (3)否则,将s1栈顶的运算符弹出并压入到s2中,再次转到(4-1)与s1中新的栈顶运算符相比较;
* 5.遇到括号时:
* (1) 如果是左括号“(”,则直接压入s1
* (2) 如果是右括号“)”,则依次弹出s1栈顶的运算符,并压入s2,直到遇到左括号为止,此时将这一对括号丢弃
* 6.重复步骤2至5,直到表达式的最右边
* 7. 将s1中剩余的运算符依次弹出并压入s2
* 8.依次弹出s2中的元素并输出,结果的逆序即为中缀表达式对应的后缀表达式
*
*/
public List<String> toSuffixExpression(List<String> infix) {
LinkedList<String> suffix = new LinkedList<>();
Stack <String> operStack= new Stack();
Stack <String> resStack= new Stack();
String currentCh = "";
for (int i = 0; i <infix.size() ; i++) {
currentCh=infix.get(i);
if(!isOperaor(currentCh)&&!currentCh.equals("(")&&!currentCh.equals(")")){//如果是数字
resStack.push(currentCh);
}else if (isOperaor(currentCh)){//如果是运算符
//若此时运算符栈为空或者栈顶为(,则直接将运算符入栈
while (true){
if (operStack.isEmpty()||operStack.peek().equals("(")){
operStack.push(currentCh);
break;
}else if(getPriority(operStack.peek())<getPriority(currentCh)){
operStack.push(currentCh);
break;
}else {
resStack.push(operStack.pop());
}
}
}else if(currentCh.equals("(")) {
operStack.push(currentCh);
}else if(currentCh.equals(")")){
while (!operStack.peek().equals("(")){
resStack.push(operStack.pop());
}
operStack.pop();
continue;
}else{
throw new RuntimeException("表达式不规范");
}
}
while (!operStack.isEmpty()){
resStack.push(operStack.pop());
}
Stack<String> temp = new Stack<>();
while (!resStack.isEmpty()){
temp.push(resStack.pop());
}
while (!temp.isEmpty()){
suffix.add(temp.pop());
}
return suffix;
}
public List<String> toInfixExpressionList(String string) {
ArrayList<String> infix = new ArrayList<>();
int i = 0;//用来做扫描指针
String str = "";//用来拼接多位数字
char[] chars = string.trim().toCharArray();
System.out.println(chars);
for (int j = 0; j < chars.length; j++) {
if (isNumber(chars[j])) {
str += chars[j];
} else {
if (!str.equals("")){
infix.add(str);
str = "";
}
infix.add(chars[j] + "");
}
}
if (!str.equals("")) {
infix.add(str);
}
return infix;
}
public boolean isNumber(char ch) {
return !("0123456789".indexOf(ch + "") == -1);
}
}
标签:过程 throw main list() 变量 cal als 两个栈 length
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/polary/p/12875349.html