标签:override function err eth 就是 cti nbsp turn 抽象方法
* 方法引用的使用 * * 1.使用情境:当要传递给Lambda体的操作,已经有实现的方法了,可以使用方法引用! * * 2.方法引用,本质上就是Lambda表达式,而Lambda表达式作为函数式接口的实例。所以 * 方法引用,也是函数式接口的实例。 * * 3. 使用格式: 类(或对象) :: 方法名 * * 4. 具体分为如下的三种情况: * 情况1 对象 :: 非静态方法 * 情况2 类 :: 静态方法 * * 情况3 类 :: 非静态方法 * * 5. 方法引用使用的要求:要求接口中的抽象方法的形参列表和返回值类型与方法引用的方法的 * 形参列表和返回值类型相同!(针对于情况1和情况2)
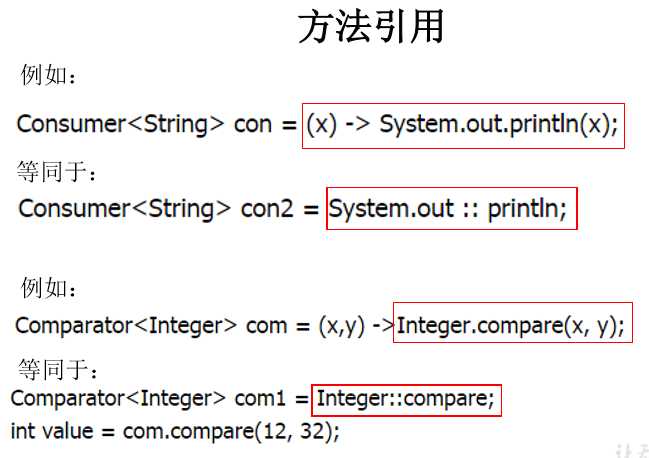
// 情况一:对象 :: 实例方法 //Consumer中的void accept(T t) //PrintStream中的void println(T t) @Test public void test1() { Consumer<String> con1 = str -> System.out.println(str); con1.accept("北京"); System.out.println("*******************"); PrintStream ps = System.out; Consumer<String> con2 = ps::println; con2.accept("beijing"); } //Supplier中的T get() //Employee中的String getName() @Test public void test2() { Employee emp = new Employee(1001,"Tom",23,5600); Supplier<String> sup1 = () -> emp.getName(); System.out.println(sup1.get()); System.out.println("*******************"); Supplier<String> sup2 = emp::getName; System.out.println(sup2.get()); } // 情况二:类 :: 静态方法 //Comparator中的int compare(T t1,T t2) //Integer中的int compare(T t1,T t2) @Test public void test3() { Comparator<Integer> com1 = (t1,t2) -> Integer.compare(t1,t2); System.out.println(com1.compare(12,21)); System.out.println("*******************"); Comparator<Integer> com2 = Integer::compare; System.out.println(com2.compare(12,3)); } //Function中的R apply(T t) //Math中的Long round(Double d) @Test public void test4() { Function<Double,Long> func = new Function<Double, Long>() { @Override public Long apply(Double d) { return Math.round(d); } }; System.out.println("*******************"); Function<Double,Long> func1 = d -> Math.round(d); System.out.println(func1.apply(12.3)); System.out.println("*******************"); Function<Double,Long> func2 = Math::round; System.out.println(func2.apply(12.6)); } // 情况三:类 :: 实例方法 (有难度) // Comparator中的int comapre(T t1,T t2) // String中的int t1.compareTo(t2) @Test public void test5() { Comparator<String> com1 = (s1,s2) -> s1.compareTo(s2); System.out.println(com1.compare("abc","abd")); System.out.println("*******************"); Comparator<String> com2 = String :: compareTo; //String 是因为调用参数为String System.out.println(com2.compare("abd","abm")); } //BiPredicate中的boolean test(T t1, T t2); //String中的boolean t1.equals(t2) @Test public void test6() { BiPredicate<String,String> pre1 = (s1,s2) -> s1.equals(s2); System.out.println(pre1.test("abc","abc")); System.out.println("*******************"); BiPredicate<String,String> pre2 = String :: equals; System.out.println(pre2.test("abc","abd")); } // Function中的R apply(T t) // Employee中的String getName(); @Test public void test7() { Employee employee = new Employee(1001, "Jerry", 23, 6000); Function<Employee,String> func1 = e -> e.getName(); System.out.println(func1.apply(employee)); System.out.println("*******************"); Function<Employee,String> func2 = Employee::getName; System.out.println(func2.apply(employee)); }


标签:override function err eth 就是 cti nbsp turn 抽象方法
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/lemonzhang/p/12890516.html