标签:管理 pass got val 查询 process 约束 loop action
INSTALLED_APPS = [
‘django.contrib.admin‘,
‘django.contrib.auth‘,
‘django.contrib.contenttypes‘,
‘django.contrib.sessions‘,
‘django.contrib.messages‘,
‘django.contrib.staticfiles‘,
‘appDB‘, # 添加子项目名称,注意以逗号结尾
]
TEMPLATES = [
{
‘BACKEND‘: ‘django.template.backends.django.DjangoTemplates‘,
‘DIRS‘: [os.path.join(BASE_DIR, ‘templates‘)], # 新建项目后,此处默认为空列表,将模板渲染目录添加到此处
‘APP_DIRS‘: True,
‘OPTIONS‘: {
‘context_processors‘: [
‘django.template.context_processors.debug‘,
‘django.template.context_processors.request‘,
‘django.contrib.auth.context_processors.auth‘,
‘django.contrib.messages.context_processors.messages‘,
],
},
},
]
# 修改数据库连接信息
DATABASES = {
‘default‘: {
‘ENGINE‘: ‘django.db.backends.mysql‘,
‘NAME‘: ‘wulin‘, # 上文中新建的库名称
‘USER‘: ‘root‘, # 用户
‘PASSWORD‘: ‘2048‘, # 用户密码
‘HOST‘: ‘127.0.0.1‘, #数据库IP地址
‘PORT‘: 3306 # 数据库端口
}
}
STATIC_URL = ‘/static/‘ # 指定了静态文件别名,后期引用静态文件可以使用该别名
STATICFILES_DIRS = [
os.path.join(BASE_DIR, ‘statics‘), # 指定静态文件目录名称,主要用户存放css和js文件
]
C:\WINDOWS\system32> mysql -u root -p
mysql> create database wulin; # 建库
mysql> \q;
通过Django主项目中的__init__.py指定连接数据库的客户端,前提是已经按照了pymysql,若未安装请通过pip install pymysql安装
import pymysql
pymysql.install_as_MySQLdb()
将建表语句写在appDB目录中的models.py文件中
from django.db import models
class wlmj(models.Model): # 新建wlmj表,以下是表结构和约束条件
id = models.AutoField(primary_key=True)
title = models.CharField(max_length=32)
pub_date = models.DateField()
price = models.DecimalField(max_digits=8, decimal_places=2)
publish = models.CharField(max_length=32)
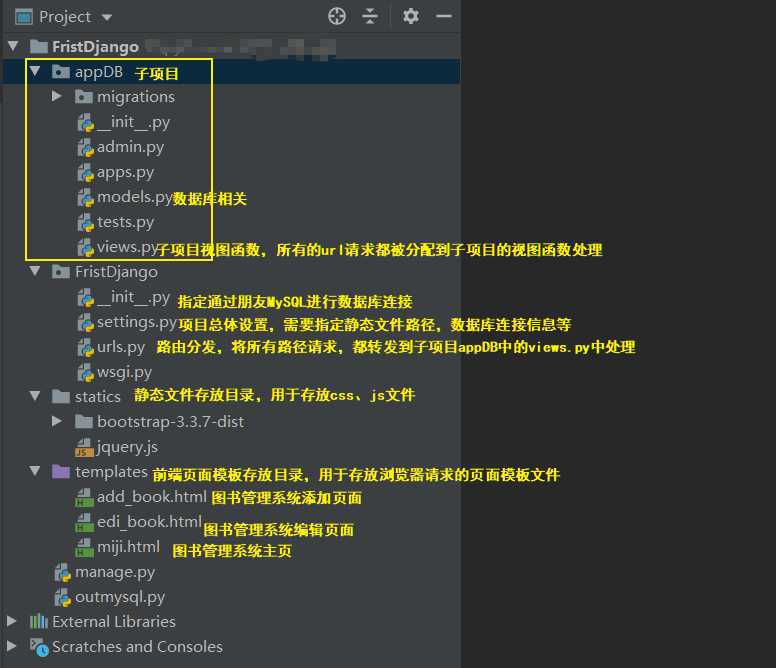
E:\python-412\FristDjango> python manage.py makemigrations
生成记录,每次修改了models里面的内容或者添加了新的app,新的app里面写了models里面的内容,都要执行这两条
E:\python-412\FristDjango> python manage.py migrate
执行上面这个语句的记录来创建表,生成的表名字前面会自带应用的名字,例如:你的book表在mysql里面叫做app01_book表
执行成功如下:
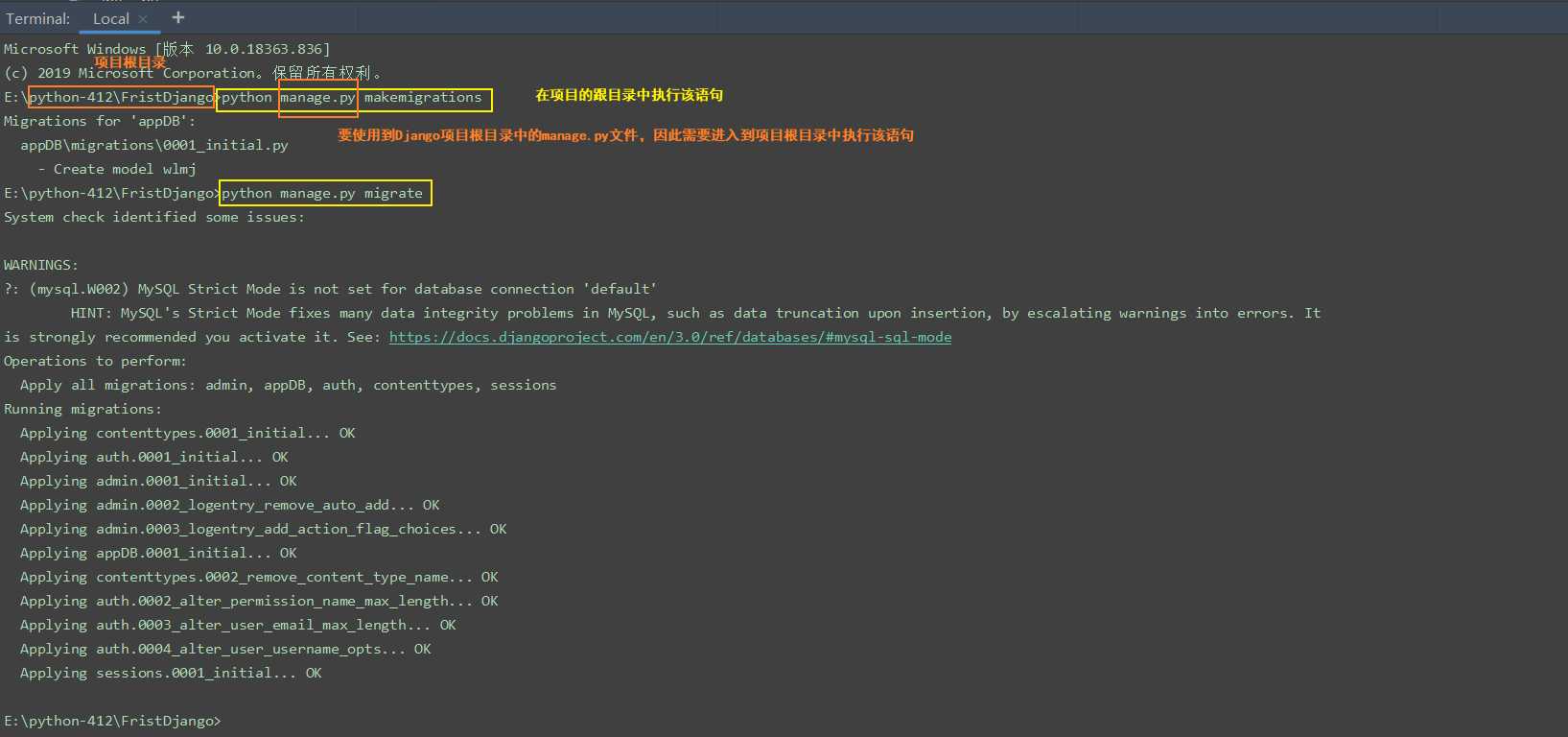
如果执行上述命令的过程中出错,若报错如下:
raise ImproperlyConfigured(‘mysqlclient 1.3.13 or newer is required; you have %s.‘ % Database.__version__)
django.core.exceptions.ImproperlyConfigured: mysqlclient 1.3.13 or newer is required; you have 0.9.3.
请注释掉图中指定文件中的内容,再重新执行上述的两个命令
完成上述步骤后,就能再数据库wuli中查看到新建的表信息了,值得注意的是,表名是以子项目名称+‘表名’(上文models.py文件中的表名)命名的
在项目任意目录下新建该文件--outmysql.py,并执行文件,执行完成后,可以查看到数据库中已经插入了文件中的书籍信息
import os
if __name__ == ‘__main__‘:
os.environ.setdefault("DJANGO_SETTINGS_MODULE", "FristDjango.settings")
import django
django.setup()
from appDB import models
obj_list = []
books = [‘九阳神功‘, ‘乾坤大挪移‘, ‘易筋经‘, ‘僻邪剑谱‘, ‘葵花宝典‘, ‘降龙十八掌‘, ‘六脉神剑‘, ‘北冥神功‘, ‘独孤九剑‘, ‘太极拳‘]
for i in range(10):
obj = models.wlmj(title=books[i],
pub_date=‘2000-01-11‘ if i < 3 else ‘2008-09-11‘,
price=200 + i * i,
publish=‘金庸出版社‘ if i < 5 else ‘丐帮出版社‘,
)
obj_list.append(obj)
models.wlmj.objects.bulk_create(obj_list)
from django.conf.urls import url
from appDB import views
urlpatterns = [
url(r‘^miji/‘, views.wlmj, name=‘books‘), # 图书系统主页,对应的视图函数,以及别名
url(r‘^add_book/‘, views.add_book, name=‘add_books‘), # 添加图书页面
url(r‘^del_book/(\d+)/‘, views.del_book, name="del_books"), # 删除图书页面
url(r‘^edi_book/(\d+)/‘, views.edi_book, name="edi_books"), # 编辑图书页面
from django.shortcuts import render,HttpResponse, redirect
from appDB import models
from django.urls import reverse
def wlmj(request):
# 图书主页对应的视图函数,实现从数据库中查询图书,并通过miji.html模板将内容返回给浏览器
all_objs = models.wlmj.objects.all()
return render(request, ‘miji.html‘, {‘all_objs‘: all_objs})
def add_book(request):
# 添加图书按钮url对应的视图函数,实现将用户添加的图书信息添加到数据库中
if request.method == ‘GET‘:
# 判断用户请求,如果是GET请求,就将添加图书的页面返回给用户
return render(request, ‘add_book.html‘)
else:
# 如果用户请求时POST,则捕获用户输入,并将用户输入添加进数据库,并返回添加过后的主页页面
title = request.POST.get(‘book_title‘)
price = request.POST.get(‘book_price‘)
date = request.POST.get(‘book_date‘)
publish = request.POST.get(‘book_publish‘)
models.wlmj.objects.create(
title=title,
price=price,
pub_date=date,
publish=publish
)
return redirect(reverse(‘books‘))
def del_book(request, book_id):
# 删除按钮url对应的视图函数,捕获到用户将要删除书籍的ID信息,通过filter过滤,直接删除书籍
models.wlmj.objects.filter(id=book_id).delete()
return redirect(reverse(‘books‘)) # 此处用到反向地址解析,books是在urls.py中定义的别名
def edi_book(request, book_id):
# 编辑按钮url对应的视图函数,也要进行GET和POST方法的判断,然后分别进行处理
if request.method == ‘GET‘:
edi_obj = models.wlmj.objects.filter(id=book_id)
# 如果请求是GET,将编辑界面返回给用户,并且编辑界面中对应的数据应该一并返回给用户
return render(request, ‘edi_book.html‘, {‘edi_obj‘: edi_obj})
else:
# 如果请求为POST,则先捕获用户输入,然后通过数据ID进行数据更新操作
title = request.POST.get(‘book_title‘)
price = request.POST.get(‘book_price‘)
date = request.POST.get(‘book_date‘)
publish = request.POST.get(‘book_publish‘)
models.wlmj.objects.filter(id=book_id).update(
title=title,
price=price,
pub_date=date,
publish=publish
)
return redirect(reverse(‘books‘))
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
{% load static %}
<link rel="stylesheet" href="{% static ‘bootstrap-3.3.7-dist/css/bootstrap.min.css‘ %}">
</head>
<body>
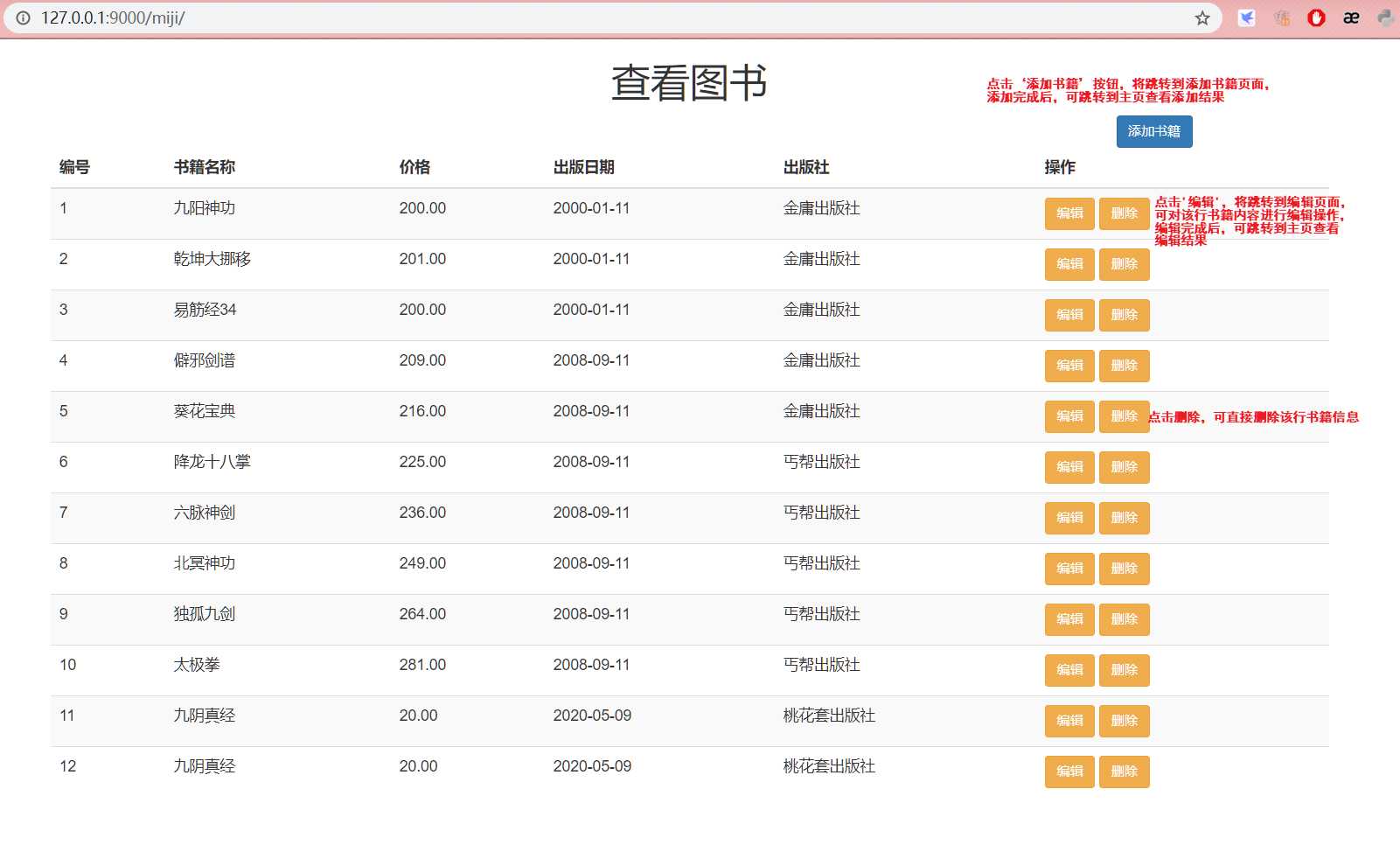
<h1 class="text-center">查看图书</h1>
<div class="container">
<div class="row">
<div class="col-md-8 col-md-offset-2"></div>
<div>
<a href="{% url ‘add_books‘ %}" class="btn btn-primary btn-sm">添加书籍</a>
</div>
<table class="table table-hover table-striped">
<thead>
<tr>
<th>编号</th>
<th>书籍名称</th>
<th>价格</th>
<th>出版日期</th>
<th>出版社</th>
<th>操作</th>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
{% for book in all_objs %}
<tr>
<td>{{ forloop.counter }}</td>
<td>{{ book.title }}</td>
<td>{{ book.price }}</td>
<td>{{ book.pub_date|date:‘Y-m-d‘ }}</td>
<td>{{ book.publish }}</td>
<td>
<a href="{% url ‘edi_books‘ book.id %}" class="btn btn-warning btn-sm">编辑</a>
<a href="{% url ‘del_books‘ book.id %}" class="btn btn-warning btn-sm">删除</a>
</td>
</tr>
{% endfor %}
</tbody>
</table>
</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
{% load static %}
<link rel="stylesheet" href="{% static ‘bootstrap-3.3.7-dist/css/bootstrap.min.css‘ %}">
</head>
<body>
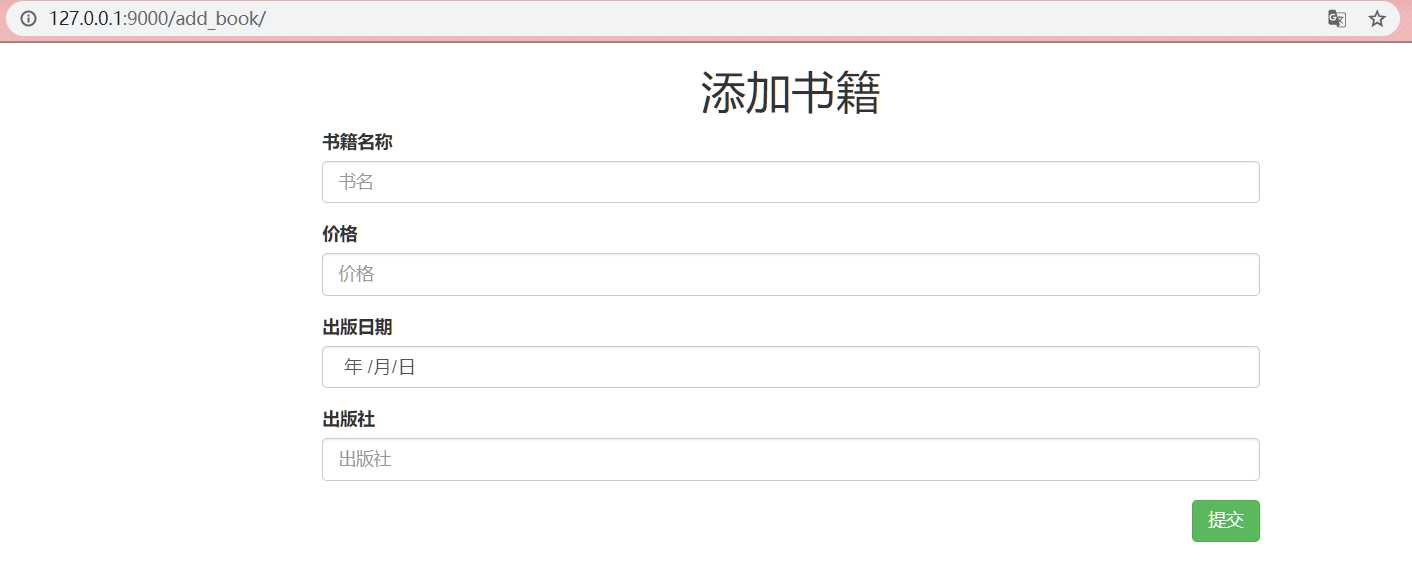
<h1 class="text-center">添加书籍</h1>
<div class="container">
<div class="row">
<div class="col-md-8 col-md-offset-2">
<form action="" method="post" novalidate>
{% csrf_token %}
<div class="form-group">
<label for="title">书籍名称</label>
<input type="text" class="form-control" id="title" placeholder="书名" name="book_title">
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label for="price">价格</label>
<input type="number" class="form-control" id="price" placeholder="价格" name="book_price">
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label for="date">出版日期</label>
<input type="date" class="form-control" id="date" placeholder="日期" name="book_date">
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label for="publish">出版社</label>
<input type="text" class="form-control" id="publish" placeholder="出版社" name="book_publish">
</div>
<input type="submit" class="btn pull-right btn-success">
</form>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
{% load static %}
<link rel="stylesheet" href="{% static ‘bootstrap-3.3.7-dist/css/bootstrap.min.css‘ %}">
</head>
<body>
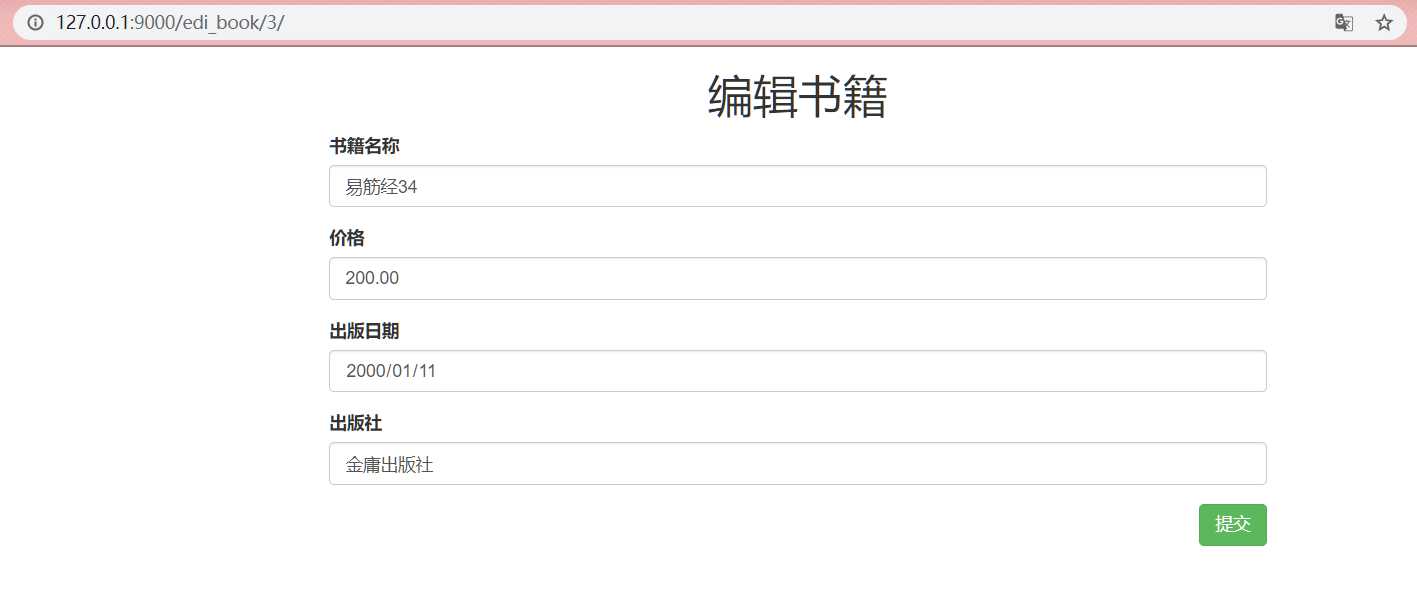
<h1 class="text-center">编辑书籍</h1>
<div class="container">
<div class="row">
<div class="col-md-8 col-md-offset-2">
<form action="" method="post" novalidate>
{% csrf_token %}
<div class="form-group">
<label for="title">书籍名称</label>
<input type="text" class="form-control" id="title" placeholder="书名" name="book_title" value="{{ edi_obj.title }}">
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label for="price">价格</label>
<input type="number" class="form-control" id="price" placeholder="价格" name="book_price" value="{{ edi_obj.price }}">
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label for="date">出版日期</label>
<input type="date" class="form-control" id="date" placeholder="日期" name="book_date" value="{{ edi_obj.pub_date|date:‘Y-m-d‘ }}">
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label for="publish">出版社</label>
<input type="text" class="form-control" id="publish" placeholder="出版社" name="book_publish" value="{{ edi_obj.publish }}">
</div>
<input type="submit" class="btn pull-right btn-success">
</form>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
标签:管理 pass got val 查询 process 约束 loop action
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/scaven-01/p/12896644.html