标签:style blog class code c java
面向对象 封装的原则 要求使对象之外的部分不能随意存取对象的内部数据,从而有效避免了错误对它的“交叉感染”,使软件错误能局部化,降低排错难度
继承
所有的类都继承自java.lang.Object,一些常用的方法:
equals():比较两个对象引用时否相同。
getClass():返回对象运行时所对应的类的表示,从而得到相应的信息
toString():返回对象字符串表示
finalize():用于在垃圾收集前清除对象
notify(), notifyall(), wait(): 用于多线程处理中的同步
子类(subclass)对父类(superclass,超类)的继承
子类不能继承父类中访问权限为private的成员变量和方法。
子类可以重写父类的方法,及命名与父类同名的成员变量。
Java不支持多重继承
创建子类
class SubClass extends SuperClass {
...
}
成员的隐藏和方法的重写
子类通过隐藏父类的成员变量和重写父类的方法,可以把父类的状态和行为变为自身的状态和行为。
多态性 子类继承父类后,同一个方法有不同的表现
体现在两个方面:方法重载实现的静态多态性(编译时多态),方法重写实现的动态多态性(运行时多态)
重写方法的调用原则:子类重写父类的方法,调用子类方法;反之,调用父类的方法
一个对象可以引用子类的实例来调用子类的方法
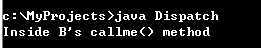
eg: B继承A,A的对象a引用B的实例,调用B的方法callme()
1 import java.io.*; 2 class A { 3 void callme() { 4 System.out.println("Inside A‘s callme()) method"); 5 } 6 } 7 8 class B extends A { 9 void callme() { 10 System.out.println("Inside B‘s callme() method"); 11 } 12 } 13 14 public class Dispatch { 15 public static void main(String args[]) { 16 A a = new B(); // 引用子类的实例17 a.callme(); 18 } 19 }
类的实现 类声明 [public][abstract|final] class className [extends superclassName] [implements interfaceNameList] {} 修饰符public, abstract, final说明类的属性 className为类的属性 superclassName为父类的名字 interfaceNameList为类所实现的接口列表
类体 class className { [public | protected | private] [static] [final] [transient] [volatile] type variableName; // 成员变量 [public | protected | private] [static] [final | abstract] [native] [synchronized] returnType methodName( [paramList]) [throws exceptionList] {statements}; //成员方法 }
成员变量 [public | protected | private] [static] [final] [transient] [volatile] type variableName; // 成员变量 static: 静态变量(类变量) final: 常量 transient:暂时性变量,用于对象存档 volatile:共享变量,用于并发线程的共享
成员方法 [public | protected | private] [static] [final | abstract] [native] [synchronized] returnType methodName( [paramList]) [throws exceptionList] {statements}; //成员方法 static: 类方法,可通过类名直接调用 abstract: 抽象方法,没有方法体 final:方法不能被重写 native:集成其他语言的代码 synchronized:控制多个并发线程的访问
Java类中的限定词:
private:类中限定为private的成员,只能被这个类本身访问。如果构造方法为private,则其他类不能实例化该类。
default:不加任何访问权限,可以被这个类本身和同一个包中的类访问。
protected:类中限定为protected的成员,可以被这个类本身、它的子类和同一个包中的其他类访问。
public:类中被限定为public的成员,可以被所有类访问。
final关键字可以修饰类、类的成员变量和成员方法,但作用不同
修饰成员变量:称为常量,须给出初始值
修饰成员方法:该方法不能被子类重写
修饰类:类不能被继承
super: 访问父类的成员
访问父类被隐藏的成员变量,如super.variable;
调用父类中被重写的方法,如super.Method([paramlist]);
调用父类的构造函数,如super([paramlist]);
eg:
1 import java.io.*; 2 class SuperClass { 3 int x; 4 5 SuperClass() { 6 x = 3; 7 System.out.println("in SuperClass: x = " + x); 8 } 9 10 void doSomething() { 11 System.out.println("in SuperClass.doSomething()"); 12 } 13 } 14 15 class SubClass extends SuperClass { 16 int x; 17 18 SubClass() { 19 super(); 20 x = 5; 21 System.out.println("in SubClass: x = " + x); 22 } 23 24 void doSomething() { 25 super.doSomething(); 26 System.out.println("in SubClass.doSomething()"); 27 System.out.println("Super.x = " + super.x + "sub.x = " + x); 28 } 29 } 30 31 public class Inhereritance { 32 33 public static void main(String chars[]) { 34 SubClass sc = new SubClass(); 35 sc.doSomething(); 36 } 37 }

简单数据:值类型 复合数据:引用类型
1 import java.io.*; 2 public class PassTest { 3 float ptValue; 4 5 public static void main(String args[]) { 6 int val; 7 PassTest pt = new PassTest(); 8 val = 11; 9 System.out.println("Original int Value is:"+val); 10 pt.changeInt(val); 11 System.out.println("Int Value after Change is:"+val); 12 pt.ptValue = 101f; 13 System.out.println("Original ptValue is:"+pt.ptValue); 14 pt.changeObjectValue(pt); // 引用类型的参数15 System.out.println("ptValue after change is:"+pt.ptValue); 16 17 } 18 19 public void changeInt(int value) { 20 value = 55; 21 } 22 23 public void changeObjectValue(PassTest ref) { 24 ref.ptValue = 99f; 25 } 26 }
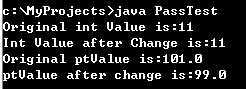
简单数据类型作为参数传递时,为值传递;复合数据类型作为参数传递时,为地址传递
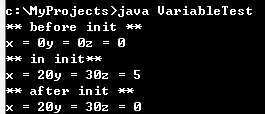
方法体 方法的实现。方法体中局部变量若与成员变量同名,局部变量将屏蔽成员变量。
1 import java.io.*; 2 class Variable { 3 int x = 0, y = 0, z = 0; // 类的成员变量 4 5 void init(int x, int y) { 6 this.x = x; 7 this.y = y; 8 int z = 5; // 局部变量 9 System.out.println("** in init**"); 10 System.out.println("x = " + x + "y = " + y + "z = " + z); 11 } 12 } 13 14 public class VariableTest { 15 public static void main(String args[]) { 16 Variable v = new Variable(); 17 System.out.println("** before init **"); 18 System.out.println("x = " + v.x + "y = " + v.y + "z = " + v.z); 19 v.init(20, 30); 20 System.out.println("** after init **"); 21 System.out.println("x = " + v.x + "y = " + v.y + "z = " + v.z); 22 } 23 }
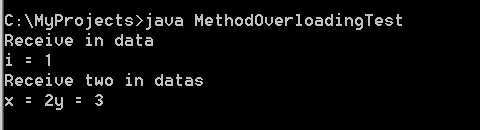
方法重载
指多个方法享有相同的名字。这些方法的参数必须不同。且参数类型区分度要足够:如不能使同一简单类型的数据:int与long
1 import java.io.*; 2 3 class MethodOverloading { 4 void receive(int i) { 5 System.out.println("Receive in data"); 6 System.out.println("i = " + i); 7 } 8 9 void receive(int x, int y) { 10 System.out.println("Receive two in datas"); 11 System.out.println("x = " + x + "y = " + y); 12 } 13 } 14 15 public class MethodOverloadingTest { 16 public static void main(String args[]) { 17 MethodOverloading mo = new MethodOverloading(); 18 mo.receive(1); 19 mo.receive(2, 3); 20 } 21 }
构造方法
一个特殊的方法。每个类都有构造方法,用来初始化该类的一个对象。
构造方法具有和类名相同的名称,不返回任何数据类型。
重载经常用于构造方法。
构造方法只能由new运算符调用
抽象类和抽象方法:
用abstract关键字修饰类:抽象类
用abstract关键字修饰方法:抽象方法
抽象类必须被继承,抽象方法必须被重写
抽象方法只需声明,无需实现
抽象类不能被实例化,抽象类不一定要包含抽象方法
若类中包含抽象方法,给类必须被定义为抽象类
接口
接口是抽象类的一种,只包含常量和方法的定义,没有变量和方法的实现,且其方法都是抽象方法。
用处体现在:
通过接口,实现不相关类的相同行为
通过接口,指明多个类需要实现的方法
通过接口,了解对象的交互界面,无需了解对象所对应的类
接口的定义:
接口声明:
[public] interface interfaceName[extends listOfSuperInterface] {...}
方法体定义:
returnType methodName([paramlist]);
接口的实现:
在类的声明中用implements子句来表示一个类使用某个接口
类体中可以使用接口中定义的常量,必须实现接口中定义的所有方法
一个类可以实现多个接口,在implements中用逗号隔开
接口类型的使用:
接口作为一种引用类型来使用
任何实现该接口的类的实例,都可以存储在该接口类型的变量中,通过这些实例,访问该类接口中的方法。
标签:style blog class code c java
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/xiaoxiaozhao/p/3733253.html