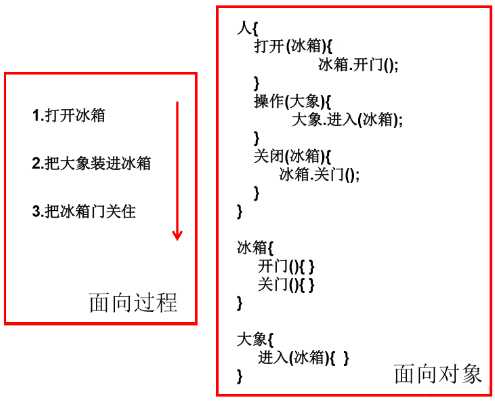
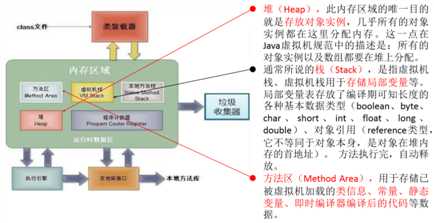
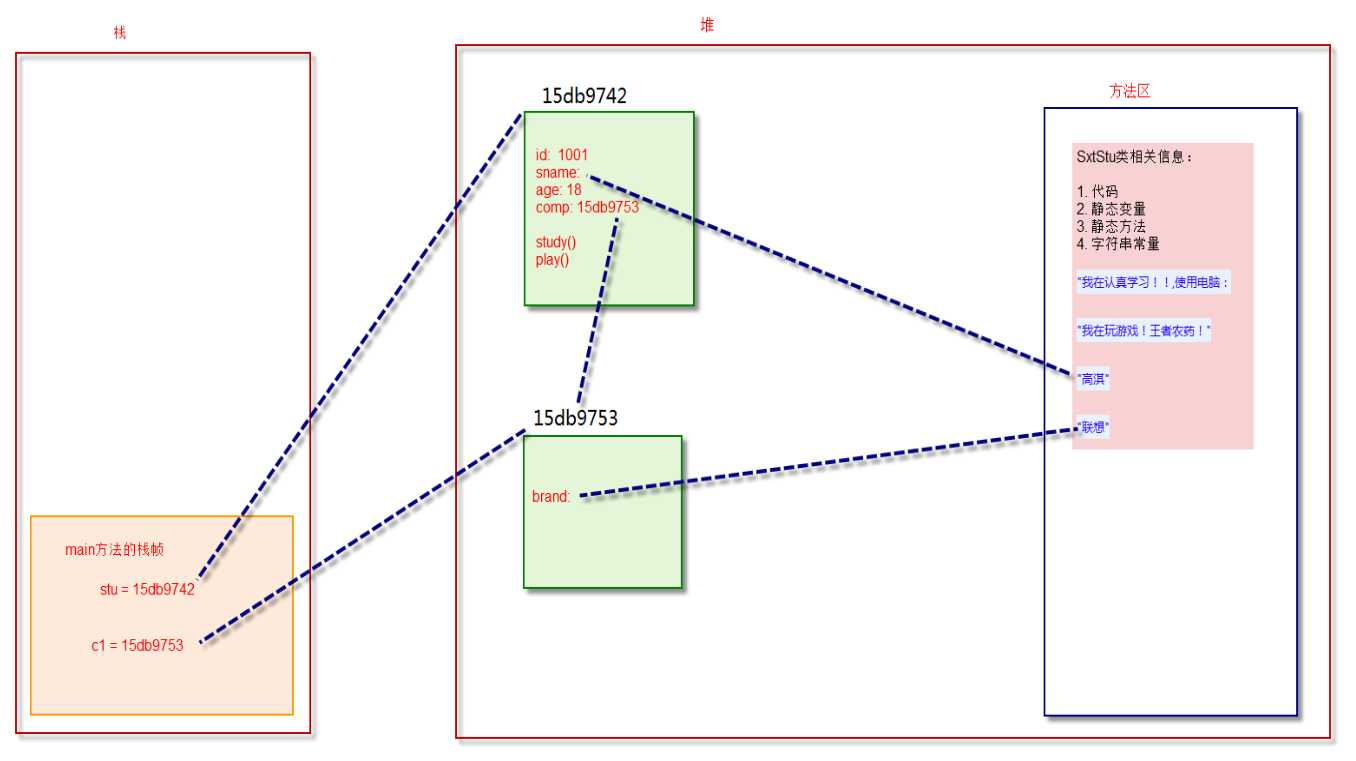
标签:实例 htm null name 属性 实例化 get 种类 结构





p3 = p1,那么p3和p1都指向原本只有p1指向的那个对象// 举例
public class PersonTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建对象
Person p1 = new Person();
Person p2 = new Person();
// 将p1所引用的对象的地址赋值给p3, 此时p1和p3引用同一个对象
Person p3 = p1;
// 调用对象的属性
p1.name = "tom";
p1.isMale = true;
System.out.printf("%s, %d, %b\n", p1.name, p1.age, p1.isMale);
System.out.printf("%s, %d, %b\n", p2.name, p2.age, p2.isMale);
p3.age = 10;
System.out.printf("%s, %d, %b\n", p1.name, p1.age, p1.isMale);
// 调用对象的方法
p1.eat();
p1.talkTo("jerry");
}
}
class Person {
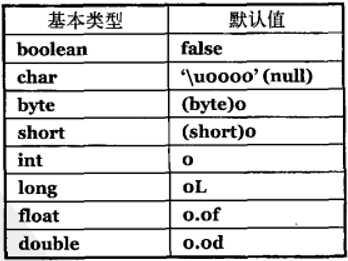
String name;
int age = 1;
boolean isMale;
public void eat() {
System.out.println("eat chips");
}
public void talkTo(String name) {
System.out.println("和" + name + "说话");
}
}

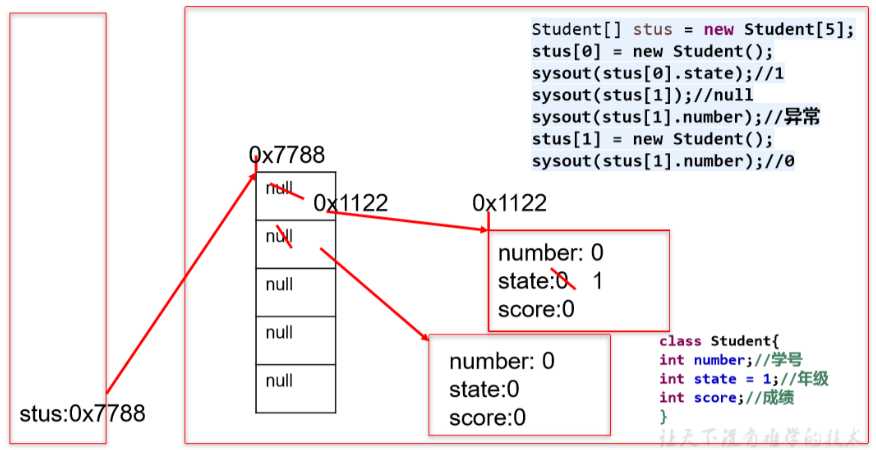

public class StudentTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 这仅仅是在堆中为10个Student类型引用!开辟了存储空间(不是对象!)
Student[] stuArr = new Student[20];
int score, state;
for(int i = 0; i < stuArr.length; i++) {
state = (int) (Math.random()*4)+1;
score = (int) (Math.random()*101);
// 给数组元素赋值
stuArr[i] = new Student();
// 给元素属性赋值
stuArr[i].number = i+1;
stuArr[i].state = state;
stuArr[i].score = score;
if(stuArr[i].state == 3)
System.out.println(stuArr[i].getInfo());
}
for(int i = stuArr.length - 1; i>0; i--)
for(int j = 0; j < i; j++)
if(stuArr[j].score > stuArr[j+1].score) {
Student stu = stuArr[j];
stuArr[j] = stuArr[j+1];
stuArr[j+1] = stu;
}
for(int i = 0; i < stuArr.length; i++)
System.out.println(stuArr[i].getInfo());
}
}
class Student {
int number;
int state;
int score;
public String getInfo() {
return "number=" + number + ", state=" + state + ", score=" + score;
}
}
new 类名(参数列表)标签:实例 htm null name 属性 实例化 get 种类 结构
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/liujiaqi1101/p/12996957.html