标签:height ras resize nbsp 去掉 停止 添加节点 out str
1. 基本概念
max_heap,min_heap是一颗堆树。其定义如下:
(1) 堆树是一颗完全二叉树;
(2) 根节点的值大于子节点(max_heap);对于·min_heap,根节点的值小于子节点;
(3) 左右子树也是一颗堆树。
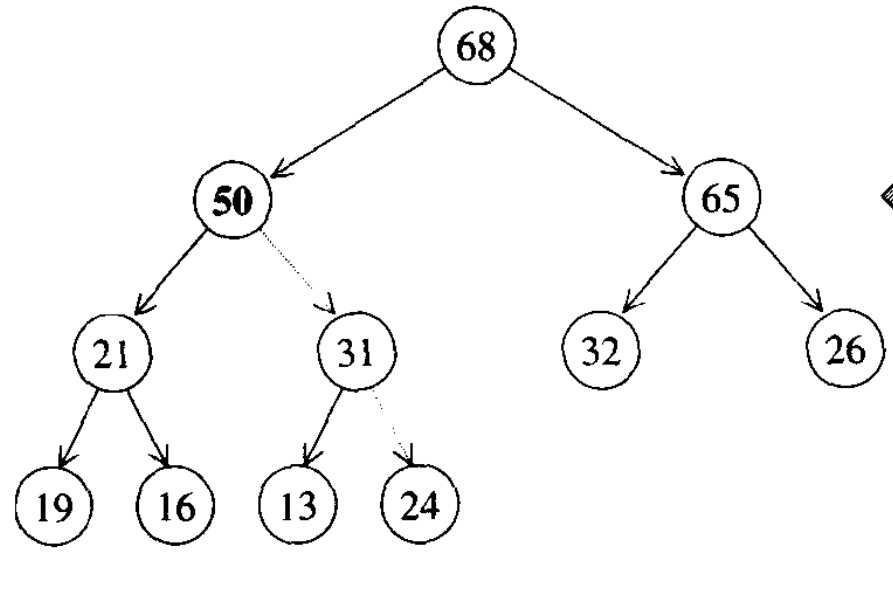
比如下面的完全二叉树,就是一个max_heap:
回想完全二叉树的性质(一个节点编号为i,如果其左右子树和父节点存在,那么左子树编号2i,右子树编号2i+1,父节点编号i/2),可以用数组来存储完全二叉树。令数组a[0]为空,从a[1]开始存储,那么就是一个完全二叉树。因此,max_heap或min_heap的底层存储结构就是一个数组(数组从编号1开始存储),下面的讲解都将以max_heap为例。对于一个max_heap,主要的操作有四个:make_heap(构造一个max_heap),
push_heap(向二叉树添加节点),pop_heap(取最大值,即根节点),sort_heap(对一个max_heap排序)。
2. 基本操作
2.1 push_heap
将一个数放入max_heap采用一种上溯(percolate up)的方法。首先将数存到max_heap数组末尾,然后与其父节点比较,如果大于父节点则与其交换,此时完成一层上溯;然后继续与父节点比较,继续上溯,直到小于父节点的值。以下图的max_heap为例:
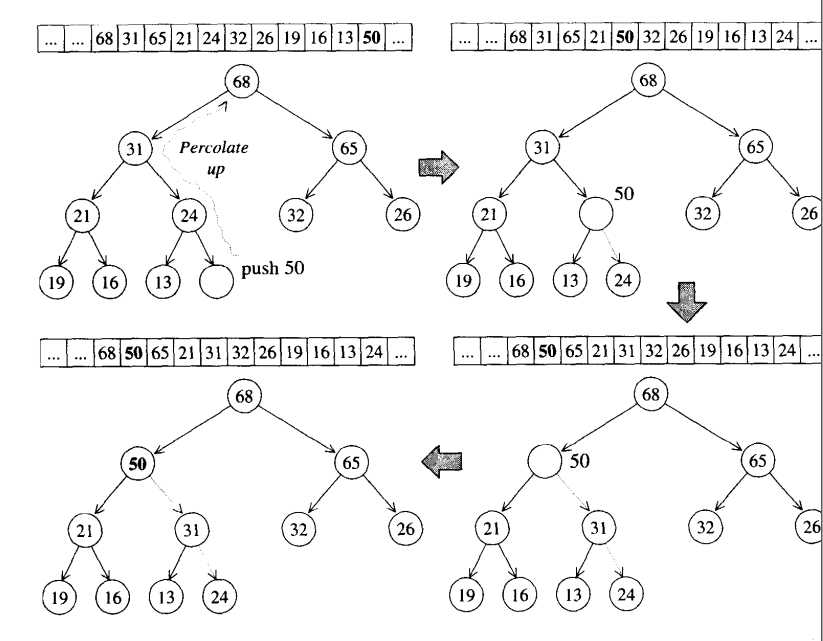
设存储max_heap数组的名字为max_heap
(a) 在原max_heap[11]中插入50;
(b) max_heap[11]与max_heap[11/2]比较,大于父节点,交换;
(c) max_heap[11/2]即max_heap[5]继续与max_heap[5/2]比较,大于父节点,交换;
(d) max_heap[2]与max_heap[2/2]比较,小于父节点,停止,push_heap成功 。
2.2 pop_heap
将最大元素即max_heap首元素删除,采用下溯(percolate down)的方法。首先将数组首元素与尾元素交换,相当于尾元素变成了根节点。然后根节点与其左右子节点比较,将其与大于它的最大子节点交换位置,下溯一层;然后重复以上操作。以下图的max_heap为例:
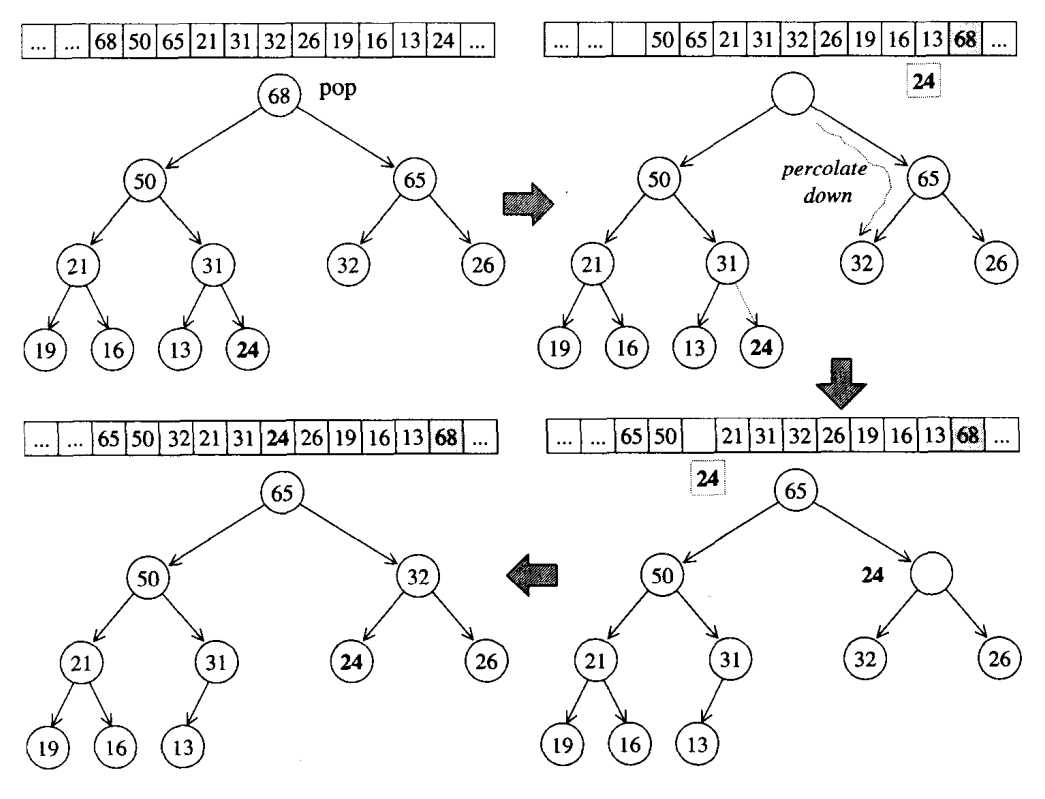
设存储max_heap数组的名字为max_heap
(a) 将根节点max_heap[1]与max_heap[max_heap.size()-1]交换,即68和24交换;
(b) 此时24在根节点,与其子节点比较,与较大的子节点交换位置,即24(max_heap[1])和65(max_heap[1*2+1])交换;
(c) 24接着与其子节点比较并与大于它的最大子节点交换,即24与32交换;
(d) 此时24没有子节点,交换完成。
注:通过pop_heap之后,最大根节点到了数组末尾,此时删除或取值都行。
2.3 sort_heap
由于pop_heap可以将最大节点放置到数组末尾,所以对一个max_heap一直执行pop_heap操作,就能得到一个递增的排序后的数组。
2.4 make_heap
make_heap给定一个数组,构造max_heap,主要步骤如下:
假设给定数组元素个数为n
(1) 构造完全二叉树,即从max_heap[1]开始存储数组元素;
(2) 从第一个有子节点的数组出发(序号为n/2),将其构在为max_heap(将其与最大子节点交换位置);
(3) 从n/2开始往前遍历(for i=n/2;i>0;i++),对每个节点,都进行max_heap的构造(即对当前节点采用percolate down的方法)。
以数组a=[ 20,12,35,15,10,80,30,17,2,1 ]为例,其完全二叉树构造如下图:
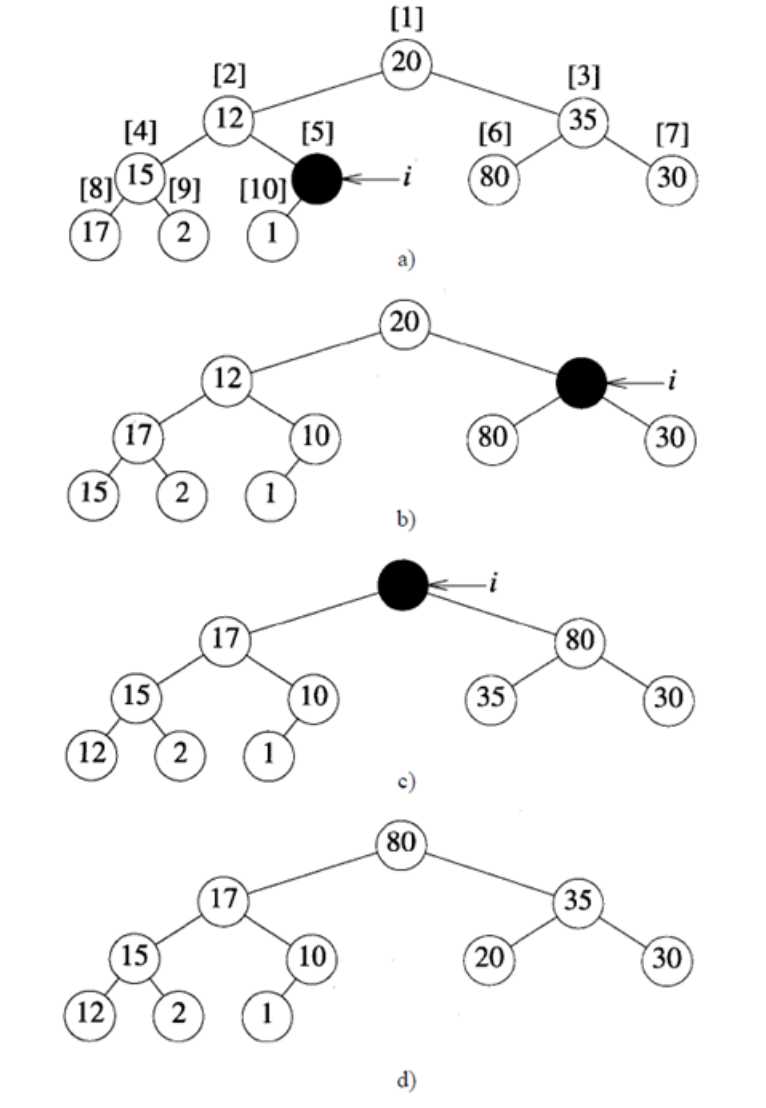
(a) 从5开始,由于a[5]>a[10]已经是max_heap; 再看a[4],由于a[4]<a[8],交换a[4],a[8],此时以a[4]为根节点的子树已经是max_heap。经过以上两步,新的树如图b)。
(b) 再看a[3],由于a[3]<a[6],交换a[3],a[6]; 再看a[2],由于a[2]<a[4],交换a[2],a[4]。经过以上两步,新的树如图c)。
(c) 再看a[1],由于a[1]<a[3],交换a[1],a[3],此时遍历完成,最终的max_heap如图d)所示。
3. 算法实现
根据2中的算法思想,编写代码实现以上四个函数。C++实现如下:
1 template<class T> 2 3 //首先调用makeHeap,将数据成员heap变成最大堆,才能接着使用popHeap,pushHeap 4 //sortHeap将输入的最大堆变成递增输出 5 class MaxHeap 6 { 7 public: 8 MaxHeap(); 9 vector<T>& getMaxHeap() 10 { 11 return heap; 12 } 13 void printHeap() //访问heap数据成员 14 { 15 if (heap.size() < 1) return; 16 for (int i = 1; i < heap.size(); i++) 17 cout << heap[i] << " "; 18 cout << endl; 19 } 20 21 void pushHeap(T value); 22 T popHeap(); //返回最大元素,并删除最大元素 23 void sortHeap(vector<T>& oldHeap); 24 void makeHeap(vector<T> vec); 25 private: 26 vector<T> heap; 27 int maxIdx; //最后一个元素的下标 28 }; 29 30 template<class T> 31 MaxHeap<T>::MaxHeap() 32 { 33 } 34 35 template<class T> 36 void MaxHeap<T>::makeHeap(vector<T> vec) 37 { 38 int n = vec.size(); 39 heap.resize(n + 1); 40 maxIdx = n; 41 for (int i = 1; i < n + 1; i++) 42 heap[i] = vec[i - 1]; 43 for (int i = maxIdx / 2; i > 0; i--) 44 { 45 int parentIdx = i; //父节点下标 46 int childIdx = 2 * i; //孩子节点的下标 47 while (childIdx <= maxIdx) { 48 if (childIdx + 1 <= maxIdx && heap[childIdx + 1] >= heap[childIdx] && heap[childIdx + 1] > heap[parentIdx]) //右孩子最大 49 { 50 swap(heap[parentIdx], heap[childIdx + 1]); 51 parentIdx = childIdx + 1; 52 } 53 else if (heap[childIdx] > heap[parentIdx]) //左孩子最大 54 { 55 swap(heap[parentIdx], heap[childIdx]); 56 parentIdx = childIdx; 57 } 58 else 59 break; 60 childIdx = 2 * parentIdx; 61 } 62 } 63 } 64 65 template<class T> 66 void MaxHeap<T>::pushHeap(T value) 67 { 68 heap.push_back(value); //先构造完全二叉树 69 maxIdx++; 70 int i = maxIdx; 71 while (i!=1 && heap[i] > heap[i / 2]) { 72 swap(heap[i], heap[i / 2]); 73 i = i / 2; 74 } 75 } 76 77 template<class T> 78 T MaxHeap<T>::popHeap() 79 { 80 if (maxIdx == 0) { 81 cout << "empty MaxHeap" << endl; 82 } 83 swap(heap[1], heap[maxIdx]); 84 int i = 1; 85 int ci = 2 * i; //左孩子节点 86 while (ci<maxIdx) { 87 if (ci + 1 < maxIdx && heap[ci] < heap[ci + 1] && heap[i] < heap[ci + 1]) //右孩子最大 88 { 89 swap(heap[i], heap[ci + 1]); 90 i = ci + 1; 91 } 92 else if (heap[ci] > heap[i]) //左孩子最大 93 { 94 swap(heap[i], heap[ci]); 95 i = ci; 96 } 97 else 98 break; 99 ci = 2 * i; 100 } 101 T tmp = heap.back(); 102 heap.pop_back(); 103 maxIdx--; 104 return tmp; 105 } 106 107 template<class T> 108 void MaxHeap<T>::sortHeap(vector<T>& oldheap) //传入参数必须是maxHeap 109 { 110 oldheap.insert(oldheap.begin(), oldheap[0]); //0为填充 111 int n = size(oldheap)-1; 112 int endIdx = n; 113 for (int k = 1; k < n; k++) 114 { 115 //此段代码与pop_heap基本一致 116 swap(oldheap[1], oldheap[endIdx]); 117 int i = 1; 118 int ci = 2 * i; //左孩子节点 119 while (ci < endIdx) { 120 if (ci + 1 < endIdx && oldheap[ci] < oldheap[ci + 1] && oldheap[i] < oldheap[ci + 1]) //右孩子最大 121 { 122 swap(oldheap[i], oldheap[ci + 1]); 123 i = ci + 1; 124 } 125 else if (oldheap[ci] > oldheap[i]) //左孩子最大 126 { 127 swap(oldheap[i], oldheap[ci]); 128 i = ci; 129 } 130 else 131 break; 132 ci = 2 * i; 133 } 134 endIdx--; //每次排序后,最后一个元素就是最大,所以无序数组的下标要减少 135 } 136 oldheap.erase(oldheap.begin()); //去掉填充位 137 }
为了验证以上代码合理性,利用STL自带的make_heap,sort_heap,pop_heap,push_heap进行对照:
1 int main() 2 { 3 vector<int> heap1 = { 0,1,2,3,4,8,9,3,5 }; 4 make_heap(heap1.begin(), heap1.end()); //STL自带的 5 for (int i = 0; i < size(heap1); i++) 6 cout << heap1[i] << " "; 7 cout << endl; 8 9 vector<int> vec = { 0,1,2,3,4,8,9,3,5 }; 10 MaxHeap<int> heap2; 11 heap2.makeHeap(vec); 12 heap2.printHeap(); 13 14 15 heap1.push_back(7); 16 push_heap(heap1.begin(), heap1.end()); 17 for (int i = 0; i < size(heap1); i++) 18 cout << heap1[i] << " "; 19 cout << endl; 20 21 heap2.pushHeap(7); 22 heap2.printHeap(); 23 24 25 pop_heap(heap1.begin(), heap1.end()); 26 cout << heap1.back()<<endl; //自带的库函数不会删除最大的元素 27 heap1.pop_back(); 28 for (int i = 0; i < size(heap1); i++) 29 cout << heap1[i] << " "; 30 cout << endl; 31 32 cout << heap2.popHeap() << endl; 33 heap2.printHeap(); 34 35 36 vector<int> tmpheap = heap1; 37 sort_heap(heap1.begin(), heap1.end()); 38 for (int i = 0; i < size(heap1); i++) 39 cout << heap1[i] << " "; 40 cout << endl; 41 42 heap2.sortHeap(tmpheap); 43 for (int i = 0; i < size(tmpheap); i++) 44 cout << tmpheap[i] << " "; 45 cout << endl; 46 47 48 system("pause"); 49 }
PS: STL的最大堆函数需要包含头文件#include <algorithm>
标签:height ras resize nbsp 去掉 停止 添加节点 out str
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/yuanwebpage/p/13036879.html