标签:tor space const void front 宽度 方法 产生 pair
w*h的格子画了n条或垂直或水平宽度为1的直线,求出这些格子被划分成了多少个4连块(上、下、左、右连通)。
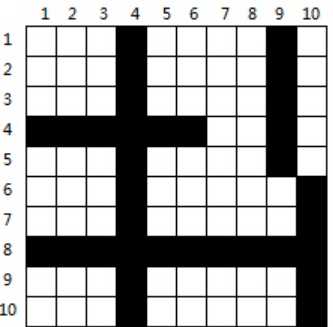
挑战程序竞赛里面的题目,很容易想到的坐标离散化。因为直接搜索的话,我们可以想到有很多的空白行会造成我们资源的浪费。所以我们会直观的产生一种压缩的思想,去离散化出来一个等价的图,这个图的搜索的代价相对而言小很多。完成图的压缩之后我们就可以使用深度优先搜索的方法去遍历图寻找空白区域了。
#include<cstdio>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cstring>
#include<cmath>
#include<queue>
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
const int maxn = 10005;
int xf[maxn], xt[maxn], yf[maxn], yt[maxn] ;
int w,h,n;
bool fld [maxn*6][maxn*6];
int dx[4]={-1,1,0,0};
int dy[4]={0,0,-1,1};
int compress (int *xf,int *xt,int w) {
vector <int> ve;
for (int i=0;i<n;i++)
for (int j=-1;j<=1;j++) {
int nx=xf[i]+j,nt=xt[i]+j;
if (nx>=1&&nx<=w) ve.push_back(nx);
if (nt>=1&&nt<=w) ve.push_back(nt);
}
sort (ve.begin(),ve.end());
ve.erase(unique(ve.begin(),ve.end()),ve.end());
for (int i=0;i<n;i++) {
xf[i]=find (ve.begin(),ve.end(),xf[i])-ve.begin();
xt[i]=find (ve.begin(),ve.end(),xt[i])-ve.begin();
}
return ve.size();
}
void solve () {
w=compress(xf,xt,w);
h=compress(yf,yt,h);
memset (fld,0,sizeof (fld));
for (int i=0;i<n;i++)
for (int y=yf[i];y<=yt[i];y++)
for (int x=xf[i];x<=xt[i];x++) {
fld[y][x]=true;
}
int ans=0;
for (int y=0;y<h;y++)
for (int x=0;x<w;x++) {
if (fld[y][x]) continue;
ans++;
queue <pair<int ,int>> q;
q.push(make_pair(x,y));
while (!q.empty()) {
int sx=q.front().first,sy=q.front().second;
q.pop();
for (int k=0;k<4;k++) {
int tx=sx+dx[k],ty=sy+dy[k];
if (tx<0||ty<0||ty>=w||tx>=h) continue;
if (fld[ty][tx]) continue;
q.push(make_pair(tx,ty));
fld[ty][tx]=true;
}
}
}
cout<<ans<<endl;
}
int main () {
cin>>w>>h>>n;
for (int i=0;i<n;i++) {
cin>>xf[i]>>xt[i]>>yf[i]>>yt[i];
}
solve ();
return 0;
}
标签:tor space const void front 宽度 方法 产生 pair
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/hhlya/p/13111148.html