标签:singleton ima ack 实践 软件 空间 int 定义 顺序
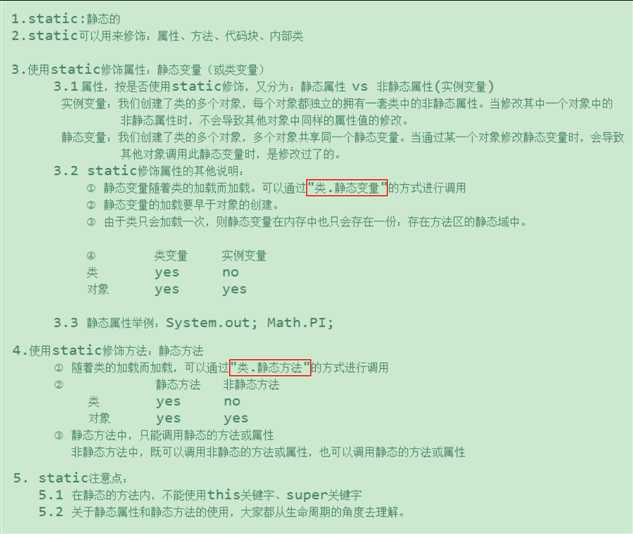
当我们编写一个类时,其实就是在描述其对象的属性和行为,而并没有产生实质上 的对象,只有通过new关键字才会产生出对象,这时系统才会分配内存空间给对象, 其(!static)方法才可以供外部调用。
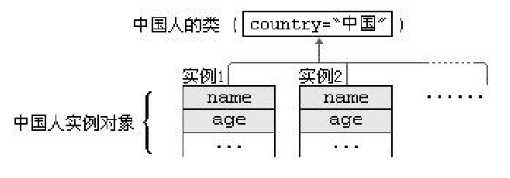
我们有时候希望无论是否产生了对象或无论产生了多少 对象的情况下,某些特定的数据在内存空间里只有一份,例如所有的中国人都有个国家名称,每一个中国人都共享这个国家名称,不必在每一个中国人的实例对象中都单独分配一个用于代表国家名称的变量。
截自《龙书》

截自《Java编程思想》


// 饿汉式:对象加载时间过长; 线程安全
// 懒汉式:延迟对象的创建; 当前写法存在线程安全问题
public class SingletonTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Bank bank1 = Bank.getInstance();
Bank bank2 = Bank.getInstance();
System.out.println(bank1 == bank2);
Factory fact1 = Factory.getInstance();
Factory fact2 = Factory.getInstance();
System.out.println(fact1 == fact2);
}
}
// 饿汉式
class Bank {
// 1. 私有化类的构造器
private Bank() {}
// 2. 该类对象的变量也必须定义成静态的
private static Bank instance = new Bank();
// public static final Bank instance = new Bank(); 则无需提供get方法
// 3. 提供一个公共静态方法以返回类内部创建的对象
public static Bank getInstance() {
return instance;
}
}
// 懒汉式
class Factory {
// 1. 私有化类的构造器
private Factory() {}
// 2. 仅声明
private static Factory instance = null;
// 3. 提供一个公共静态方法以返回类内部创建的对象
public static Factory getInstance() {
if(instance == null)
instance = new Factory();
return instance;
}
}
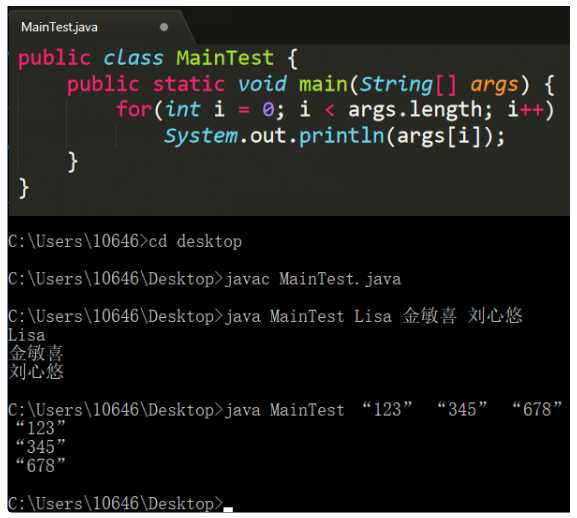
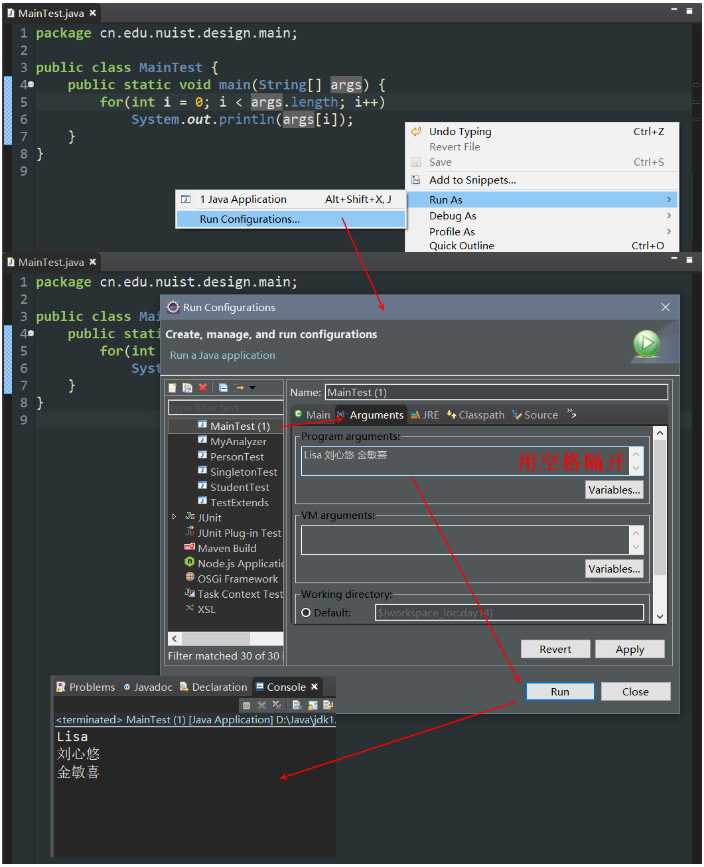
java命令时传递给所运行的类的参数(作为和控制台交互的一种方式)
// 测试代码1
public class InitBlockDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(Person.nation);
// ------------------------------
Person p1 = new Person();
System.out.println(p1.name);
Person p2 = new Person();
}
}
class Person {
String name;
int age;
static String nation = "China";
static {
System.out.println("static block 1");
nation = "CN";
}
static {
System.out.println("static block 2");
// func_1(); Cannot make a static reference to the non-static method
func_2();
}
{
System.out.println("block 1");
name = "LJQ";
}
{
System.out.println("block 2");
func_1();
func_2();
}
public void func_1() {
System.out.println("成员方法");
}
public static void func_2() {
System.out.println("静态方法");
}
}
/*
控制台:
static block 1
static block 2
静态方法
CN
block 1
block 2
成员方法
静态方法
LJQ
block 1
block 2
成员方法
静态方法
*/
// 测试代码2
class Root{
static{
System.out.println("Root的静态初始化块");
}
{
System.out.println("Root的普通初始化块");
}
public Root() {
System.out.println("Root的无参数的构造器");
}
}
class Mid extends Root{
static {
System.out.println("Mid的静态初始化块");
}
{
System.out.println("Mid的普通初始化块");
}
public Mid() {
System.out.println("Mid的无参数的构造器");
}
public Mid(String msg){
this(); // 通过this调用同一类中重载的构造器
System.out.println("Mid的带参数构造器:" + msg);
}
}
class Leaf extends Mid{
static{
System.out.println("Leaf的静态初始化块");
}
{
System.out.println("Leaf的普通初始化块");
}
public Leaf(){
super("LJQ"); // 通过super调用父类中有一个字符串参数的构造器
System.out.println("Leaf的构造器");
}
}
public class LeafTest{
public static void main(String[] args){
new Leaf();
System.out.println("------------------------");
new Leaf();
}
}
/*
控制台:
Root的静态初始化块
Mid的静态初始化块
Leaf的静态初始化块
Root的普通初始化块
Root的无参数的构造器
Mid的普通初始化块
Mid的无参数的构造器
Mid的带参数构造器:LJQ
Leaf的普通初始化块
Leaf的构造器
------------------------
Root的普通初始化块
Root的无参数的构造器
Mid的普通初始化块
Mid的无参数的构造器
Mid的带参数构造器:LJQ
Leaf的普通初始化块
Leaf的构造器
*/
// 测试代码3
public class Son extends Father {
static {
System.out.println("44444444444");
}
{
System.out.println("55555555555");
}
public Son() {
System.out.println("66666666666");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("77777777777"); // 147
System.out.println("***********");
new Son(); // 2356
System.out.println("***********");
new Son(); // 2356
System.out.println("***********");
new Father(); // 23
}
}
class Father {
static {
System.out.println("11111111111");
}
{
System.out.println("22222222222");
}
public Father() {
System.out.println("33333333333");
}
}
/*
控制台:
11111111111
44444444444
77777777777
***********
22222222222
33333333333
55555555555
66666666666
***********
22222222222
33333333333
55555555555
66666666666
***********
22222222222
33333333333
*/
// 数据库连接池
public class JDBCUtils {
private static DataSource dataSource = null;
static {
InputStream is = null;
try {
is = DBCPTest.class.getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("dbcp.properties");
Properties pros = new Properties();
pros.load(is);
//调用BasicDataSourceFactory的静态方法,获取数据源
dataSource = BasicDataSourceFactory.createDataSource(pros);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if(is != null) {
try {
is.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
// 使用DBCP数据库连接池实现数据库的连接
public static Connection getConnection2() throws SQLException {
Connection conn = dataSource.getConnection();
System.out.println(conn);
return conn;
}
}
// 针对step2, 做个测试
public class InitAttrDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(new Test1().attr); // 7
System.out.println(new Test2().attr); // 1101
}
}
class Test1 {
int attr = 6;
{
attr = 7;
}
}
class Test2 {
{
attr = 13;
}
int attr = 1101;
}

在Java中声明类、变量和方法时,可使用关键字final来修饰,表示"最终的"
public void method(final int num) {...}【例题】

标签:singleton ima ack 实践 软件 空间 int 定义 顺序
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/liujiaqi1101/p/13113506.html