标签:false 标记 字典顺序 string children 第一个字符 字符 int ret
Trie (Prefix Tree)前缀树
使用insert,search和startsWith方法实现Trie。
Example:
Trie trie = new Trie();
trie.insert("apple");
trie.search("apple"); // returns true
trie.search("app"); // returns false
trie.startsWith("app"); // returns true
trie.insert("app");
trie.search("app"); // returns true
摘要
本文适用于中级用户。它引入了以下 idea :数据结构Trie(前缀树)和最常见的操作。
Trie(我们读作“ try”),前缀树是一种树数据结构,用于检索字符串数据集中的键。这种非常有效的数据结构有多种应用,例如:
Autocomplete
Spell checker
IP routing (Longest prefix matching)
还有其他几种数据结构,例如平衡树和哈希表,可以在字符串数据集中搜索单词。
那为什么我们需要 Trie 呢?尽管哈希表在寻找键时具有O(1)的 时间复杂度,但在以下操作中效率不高:查找具有共同前缀的所有键;按字典顺序枚举字符串数据集。
Trie 之所以胜过哈希表的另一个原因是,随着哈希表大小的增加,会有很多哈希冲突,并且搜索时间复杂度可能会恶化为O(n),其中 n 是插入的键数。
当存储许多具有相同前缀的密钥时,与哈希表相比,Trie可以使用更少的空间。在这种情况下,使用trie仅具有O(m)的时间复杂度,其中m是密钥长度。在平衡树中搜索密钥的时间复杂度为O(mlogn)。
Trie 是一棵有根树。它的节点具有以下字段:
class TrieNode { ?
// R links to node children
? ?private TrieNode[] links;
? ?private final int R = 26;
? ?private boolean isEnd;
? ?public TrieNode() {
? ? ? ?links = new TrieNode[R];
? }
? ?public boolean containsKey(char ch) {
? ? ? ?return links[ch -‘a‘] != null;
? }
? ?public TrieNode get(char ch) {
? ? ? ?return links[ch -‘a‘];
? }
? ?public void put(char ch, TrieNode node) {
? ? ? ?links[ch -‘a‘] = node;
? }
? ?public void setEnd() {
? ? ? ?isEnd = true;
? }
? ?public boolean isEnd() {
? ? ? ?return isEnd;
? }
}
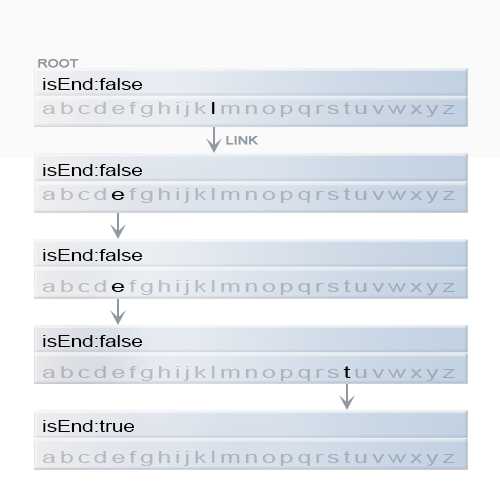
我们通过在Trie中搜索来插入 key 。我们从根开始, 搜索一个link ,该link 对应于key 的第一个字符。有两种情况:
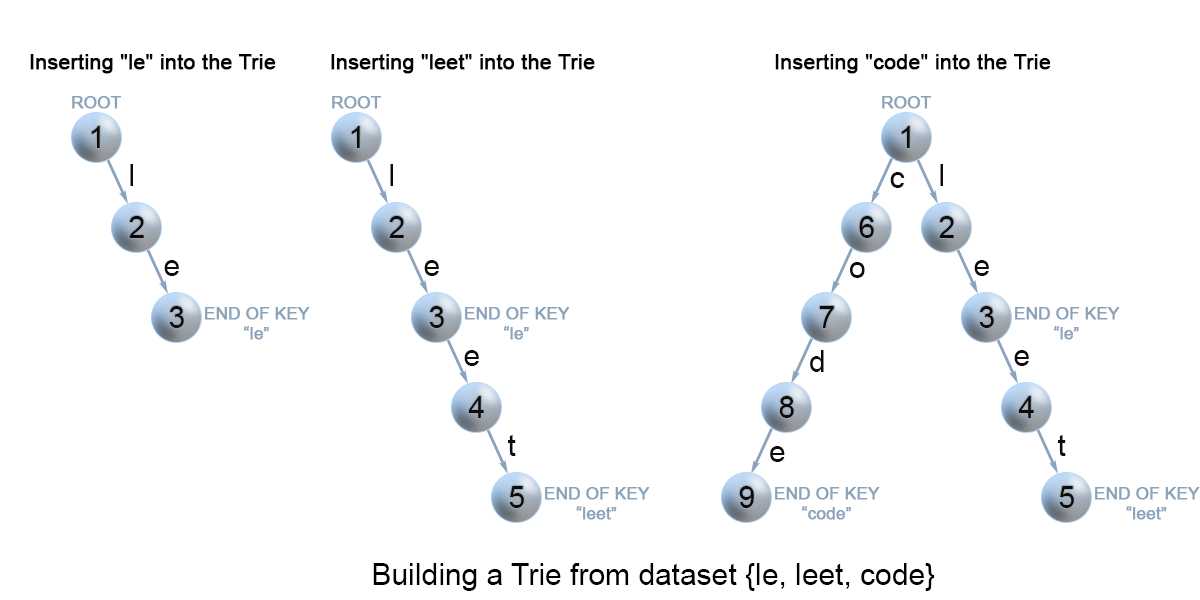
我们可以从图上看到,在逻辑上 字符的信息是存储在link上面的;
class Trie {
? ?private TrieNode root;
? ?public Trie() {
? ? ? ?root = new TrieNode();
? }
? ?// Inserts a word into the trie.
? ?public void insert(String word) {
? ? ? ?TrieNode node = root;
? ? ? ?for (int i = 0; i < word.length(); i++) {
? ? ? ? ? ?char currentChar = word.charAt(i);
? ? ? ? ? ?if (!node.containsKey(currentChar)) {
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?node.put(currentChar, new TrieNode());
? ? ? ? ? }
? ? ? ? ? ?node = node.get(currentChar);
? ? ? }
? ? ? ?node.setEnd();
? }
}
复杂度分析
时间复杂度:O(m),其中m是key长度。在算法的每次迭代中,我们都将在树中检查或创建一个节点,直到到达key的末尾。这仅需要m次的操作。
空间复杂度:O(m)。在最坏的情况下,新插入的key 没有和 已经插入到Trie中的其他key共享前缀。我们必须添加m个新节点,这需要我们O(m)的空间。
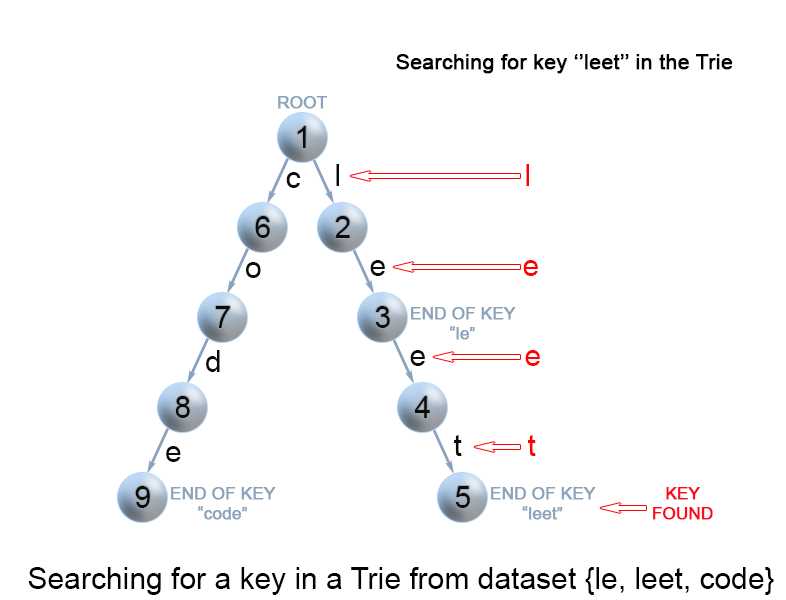
每个 key在 trie树中表示为 从根到内部节点或叶的路径。初始时我们使用key的第一个字符 从root节点 开始。我们检查当前节点是否存在与字符对应的link 。有两种情况:
class Trie {
? ...
? ?// search a prefix or whole key in trie and
? ?// returns the node where search ends
? ?private TrieNode searchPrefix(String word) {
? ? ? ?TrieNode node = root;
? ? ? ?for (int i = 0; i < word.length(); i++) {
? ? ? ? ? char curLetter = word.charAt(i);
? ? ? ? ? if (node.containsKey(curLetter)) {
? ? ? ? ? ? ? node = node.get(curLetter);
? ? ? ? ? } else {
? ? ? ? ? ? ? return null;
? ? ? ? ? }
? ? ? }
? ? ? ?return node;
? }
? ?// Returns if the word is in the trie.
? ?public boolean search(String word) {
? ? ? TrieNode node = searchPrefix(word);
? ? ? return node != null && node.isEnd();
? }
}
复杂度分析
时间复杂度:O(m)在算法的每个步骤中,我们要搜索key的下一个字符。在最坏的情况下,该算法执行m次运算。
空间复杂度:O(1)
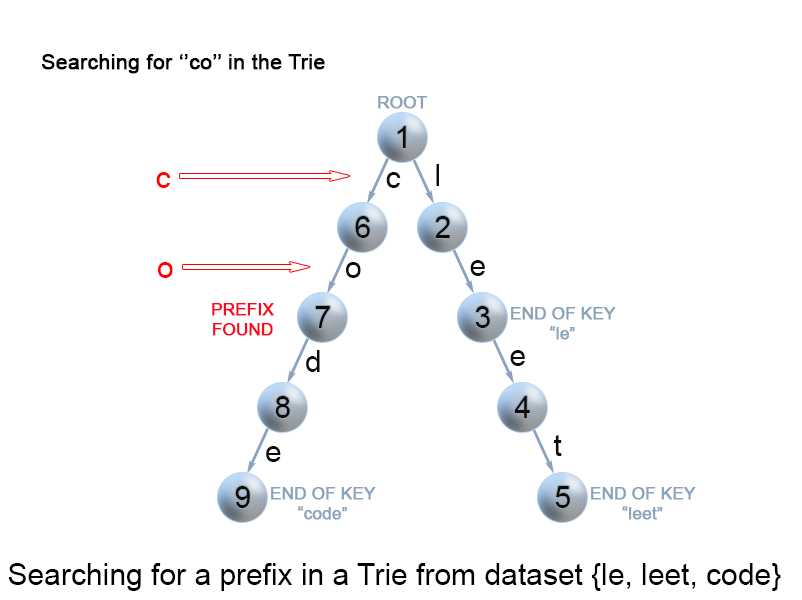
该方法与我们 在Trie 中搜索key 的方法非常相似。我们从根开始遍历Trie,直到key前缀中没有剩余字符,或者不能使用当前的字符继续在Trie中的路径遍历下去。
与上述搜索key 的算法的唯一区别是,当我们到达key前缀的末尾时,我们总是返回true。我们不需要考虑当前trie节点的isEnd标记,因为我们正在搜索键的前缀,而不是整个键。
class Trie {
? ...
? ?// Returns if there is any word in the trie
? ?// that starts with the given prefix.
? ?public boolean startsWith(String prefix) {
? ? ? ?TrieNode node = searchPrefix(prefix);
? ? ? ?return node != null;
? }
}
复杂度分析
时间复杂度:O(m)
空间复杂度:O(1)
--
参考 :?https://leetcode.com/articles/implement-trie-prefix-tree/
标签:false 标记 字典顺序 string children 第一个字符 字符 int ret
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/billxxx/p/13121972.html