标签:dep add pytho convert line images img height without
1 import math 2 import numpy as np 3 import h5py 4 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt 5 import tensorflow as tf 6 from tensorflow.python.framework import ops 7 from tf_utils import load_dataset, random_mini_batches, convert_to_one_hot, predict 8 9 np.random.seed(1) 10 11 y_hat = tf.constant(36, name=‘y_hat‘) # Define y_hat constant. Set to 36. 12 y = tf.constant(39, name=‘y‘) # Define y. Set to 39 13 loss = tf.Variable((y - y_hat)**2, name=‘loss‘) # Create a variable for the loss 14 init = tf.global_variables_initializer() # When init is run later (session.run(init)), 15 # the loss variable will be initialized and ready to be computed 16 with tf.Session() as session: # Create a session and print the output 17 session.run(init) # Initializes the variables 18 print(session.run(loss)) # Prints the loss 19 20 21 a = tf.constant(2) 22 b = tf.constant(10) 23 c = tf.multiply(a,b) 24 print(c) #Tensor("Mul_1:0", shape=(), dtype=int32) 25 26 27 sess = tf.Session() 28 print(sess.run(c)) #20 29 30 31 # Change the value of x in the feed_dict 32 x = tf.placeholder(tf.int64, name = ‘x‘) 33 print(sess.run(2 * x, feed_dict = {x: 3})) #6 34 sess.close()
Y=W*X+b
1 def linear_function(): 2 """ 3 Implements a linear function: 4 Initializes W to be a random tensor of shape (4,3) 5 Initializes X to be a random tensor of shape (3,1) 6 Initializes b to be a random tensor of shape (4,1) 7 Returns: 8 result -- runs the session for Y = WX + b 9 """ 10 11 np.random.seed(1) 12 13 ### START CODE HERE ### (4 lines of code) 14 X=tf.constant(np.random.randn(3,1), name = "X") 15 W=tf.constant(np.random.randn(4,3), name = "W") 16 b=tf.constant(np.random.randn(4,1), name = "b") 17 Y=tf.matmul(W,X)+b 18 ### END CODE HERE ### 19 20 # Create the session using tf.Session() and run it with sess.run(...) on the variable you want to calculate 21 ### START CODE HERE ### 22 session=tf.Session() 23 result=session.run(Y) 24 ### END CODE HERE ### 25 26 sess.close() # close the session 27 return result
1 def sigmoid(z): 2 """ 3 Computes the sigmoid of z 4 5 Arguments: 6 z -- input value, scalar or vector 7 8 Returns: 9 results -- the sigmoid of z 10 """ 11 ### START CODE HERE ### ( approx. 4 lines of code) 12 # Create a placeholder for x. Name it ‘x‘. 13 x=tf.placeholder(tf.float32,name=‘x‘) 14 15 # compute sigmoid(x) 16 val=tf.sigmoid(x) 17 18 # Create a session, and run it. Please use the method 2 explained above. 19 # You should use a feed_dict to pass z‘s value to x. 20 with tf.Session() as sess: 21 # Run session and call the output "result" 22 result=sess.run(val,feed_dict={x:z}) #把z赋值到x位置 23 ### END CODE HERE ### 24 25 return result
1 def cost(logits, labels): 2 """ 3 Computes the cost using the sigmoid cross entropy 4 5 Arguments: 6 logits -- vector containing z, output of the last linear unit (before the final sigmoid activation) 7 labels -- vector of labels y (1 or 0) 8 9 Note: What we‘ve been calling "z" and "y" in this class are respectively called "logits" and "labels" 10 in the TensorFlow documentation. So logits will feed into z, and labels into y. 11 12 Returns: 13 cost -- runs the session of the cost (formula (2)) 14 """ 15 16 ### START CODE HERE ### 17 # Create the placeholders for "logits" (z) and "labels" (y) (approx. 2 lines) 18 z=tf.placeholder(tf.float32,name=‘z‘) 19 y=tf.placeholder(tf.float32,name=‘y‘) 20 21 # Use the loss function (approx. 1 line) 22 cost=tf.nn.sigmoid_cross_entropy_with_logits(logits=z, labels=y) 23 24 # Create a session (approx. 1 line). See method 1 above. 25 sess=tf.Session() 26 # Run the session (approx. 1 line). 27 cost=sess.run(cost,feed_dict={z: logits, y:labels}) 28 # Close the session (approx. 1 line). See method 1 above. 29 sess.close() 30 ### END CODE HERE ### 31 32 return cost
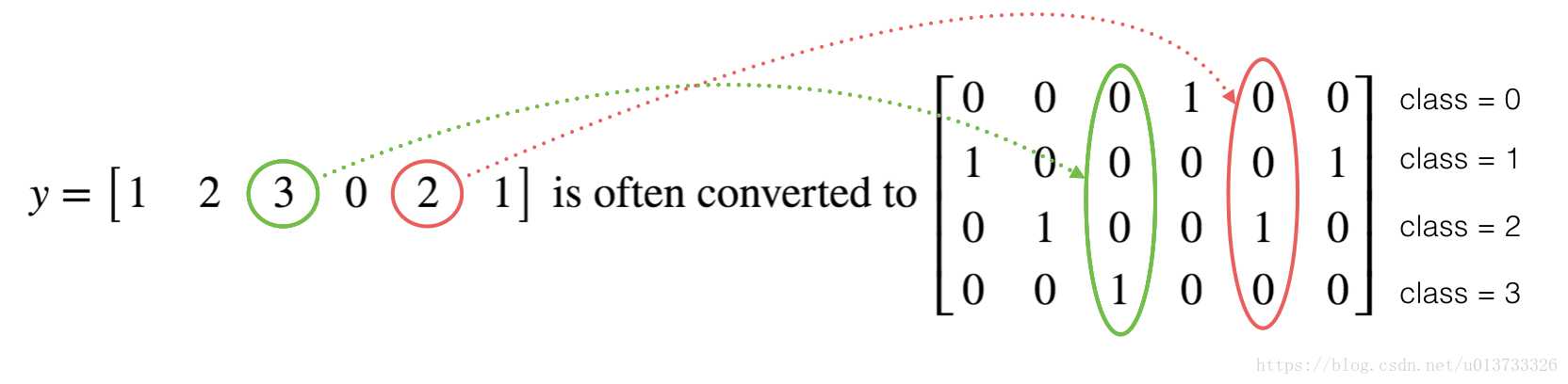
1 def one_hot_matrix(labels, C): 2 """ 3 Creates a matrix where the i-th row corresponds to the ith class number and the jth column 4 corresponds to the jth training example. So if example j had a label i. Then entry (i,j) 5 will be 1. 6 7 Arguments: 8 labels -- vector containing the labels 9 C -- number of classes, the depth of the one hot dimension 10 11 Returns: 12 one_hot -- one hot matrix 13 """ 14 15 ### START CODE HERE ### 16 # Create a tf.constant equal to C (depth), name it ‘C‘. (approx. 1 line) 17 C=tf.constant(C,name=‘C‘) 18 19 # Use tf.one_hot, be careful with the axis (approx. 1 line) 20 one_hot_matrix=tf.one_hot(indices=labels,depth=C,axis=0) 21 22 # Create a session (approx. 1 line). See method 1 above. 23 sess=tf.Session() 24 # Run the session (approx. 1 line). 25 one_hot=sess.run(one_hot_matrix) 26 # Close the session (approx. 1 line). See method 1 above. 27 sess.close() 28 ### END CODE HERE ### 29 30 return one_hot
1 def ones(shape): 2 """ 3 Creates an array of ones of dimension shape 4 5 Arguments: 6 shape -- shape of the array you want to create 7 8 Returns: 9 ones -- array containing only ones 10 """ 11 12 ### START CODE HERE ### 13 # Create "ones" tensor using tf.ones(...). (approx. 1 line) 14 ones=tf.ones(shape) 15 16 # Create a session (approx. 1 line). See method 1 above. 17 sess=tf.Session() 18 # Run the session (approx. 1 line). 19 ones=sess.run(ones) 20 # Close the session (approx. 1 line). See method 1 above. 21 sess.close() 22 ### END CODE HERE ### 23 24 return ones
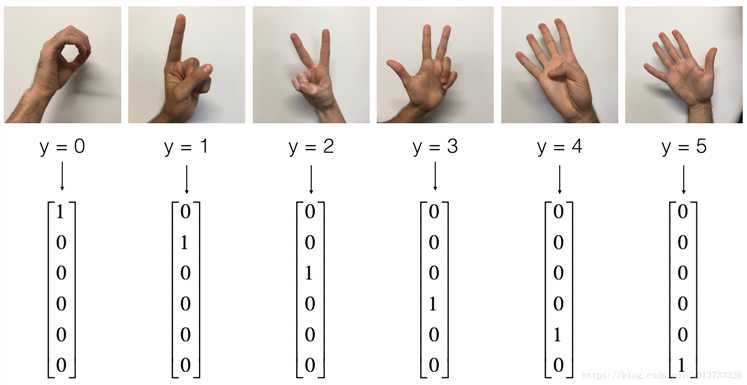
1 # Loading the dataset 2 X_train_orig, Y_train_orig, X_test_orig, Y_test_orig, classes = load_dataset() 3 4 # Example of a picture 5 index = 0 6 plt.imshow(X_train_orig[index]) 7 print ("y = " + str(np.squeeze(Y_train_orig[:, index]))) 8 9 10 # Flatten the training and test images 11 X_train_flatten = X_train_orig.reshape(X_train_orig.shape[0], -1).T 12 X_test_flatten = X_test_orig.reshape(X_test_orig.shape[0], -1).T 13 # Normalize image vectors 14 X_train = X_train_flatten / 255. 15 X_test = X_test_flatten / 255. 16 # Convert training and test labels to one hot matrices 17 Y_train = convert_to_one_hot(Y_train_orig, 6) 18 Y_test = convert_to_one_hot(Y_test_orig, 6) 19 20 print("number of training examples = " + str(X_train.shape[1])) #1080 21 print("number of test examples = " + str(X_test.shape[1])) #120 22 print("X_train shape: " + str(X_train.shape)) #(12288,1080) 23 print("Y_train shape: " + str(Y_train.shape)) #(6,1080) 24 print("X_test shape: " + str(X_test.shape)) #(12288,120) 25 print("Y_test shape: " + str(Y_test.shape)) #(6,120)
1 def create_placeholders(n_x, n_y): 2 """ 3 Creates the placeholders for the tensorflow session. 4 5 Arguments: 6 n_x -- scalar, size of an image vector (num_px * num_px = 64 * 64 * 3 = 12288) 7 n_y -- scalar, number of classes (from 0 to 5, so -> 6) 8 9 Returns: 10 X -- placeholder for the data input, of shape [n_x, None] and dtype "float" 11 Y -- placeholder for the input labels, of shape [n_y, None] and dtype "float" 12 13 Tips: 14 - You will use None because it let‘s us be flexible on the number of examples you will for the placeholders. 15 In fact, the number of examples during test/train is different. 16 """ 17 18 ### START CODE HERE ### (approx. 2 lines) 19 X=tf.placeholder(tf.float32,[n_x,None],name=‘X‘) 20 Y=tf.placeholder(tf.float32,[n_y,None],name=‘Y‘) 21 ### END CODE HERE ### 22 23 return X, Y
1 def initialize_parameters(): 2 """ 3 Initializes parameters to build a neural network with tensorflow. The shapes are: 4 W1 : [25, 12288] 5 b1 : [25, 1] 6 W2 : [12, 25] 7 b2 : [12, 1] 8 W3 : [6, 12] 9 b3 : [6, 1] 10 11 Returns: 12 parameters -- a dictionary of tensors containing W1, b1, W2, b2, W3, b3 13 """ 14 tf.set_random_seed(1) # so that your "random" numbers match ours 15 16 ### START CODE HERE ### (approx. 6 lines of code) 17 W1 = tf.get_variable("W1",[25,12288],initializer=tf.contrib.layers.xavier_initializer(seed=1)) 18 b1 = tf.get_variable("b1",[25,1],initializer=tf.zeros_initializer()) 19 W2 = tf.get_variable("W2", [12, 25], initializer = tf.contrib.layers.xavier_initializer(seed=1)) 20 b2 = tf.get_variable("b2", [12, 1], initializer = tf.zeros_initializer()) 21 W3 = tf.get_variable("W3", [6, 12], initializer = tf.contrib.layers.xavier_initializer(seed=1)) 22 b3 = tf.get_variable("b3", [6, 1], initializer = tf.zeros_initializer()) 23 ### END CODE HERE ### 24 25 parameters = {"W1": W1, 26 "b1": b1, 27 "W2": W2, 28 "b2": b2, 29 "W3": W3, 30 "b3": b3} 31 return parameters
1 def forward_propagation(X, parameters): 2 """ 3 Implements the forward propagation for the model: LINEAR -> RELU -> LINEAR -> RELU -> LINEAR -> SOFTMAX 4 5 Arguments: 6 X -- input dataset placeholder, of shape (input size, number of examples) 7 parameters -- python dictionary containing your parameters "W1", "b1", "W2", "b2", "W3", "b3" 8 the shapes are given in initialize_parameters 9 10 Returns: 11 Z3 -- the output of the last LINEAR unit 12 """ 13 # Retrieve the parameters from the dictionary "parameters" 14 W1 = parameters[‘W1‘] 15 b1 = parameters[‘b1‘] 16 W2 = parameters[‘W2‘] 17 b2 = parameters[‘b2‘] 18 W3 = parameters[‘W3‘] 19 b3 = parameters[‘b3‘] 20 21 ### START CODE HERE ### (approx. 5 lines) # Numpy Equivalents: 22 Z1=tf.matmul(W1,X)+b1 # Z1 = np.dot(W1, X) + b1 23 A1=tf.nn.relu(Z1) # A1 = relu(Z1) 24 Z2=tf.matmul(W2,A1)+b2 # Z2 = np.dot(W2, a1) + b2 25 A2=tf.nn.relu(Z2) # A2 = relu(Z2) 26 Z3=tf.matmul(W3,A2)+b3 # Z3 = np.dot(W3,Z2) + b3 27 ### END CODE HERE ### 28 29 return Z3
1 def compute_cost(Z3, Y): 2 """ 3 Computes the cost 4 5 Arguments: 6 Z3 -- output of forward propagation (output of the last LINEAR unit), of shape (6, number of examples) 7 Y -- "true" labels vector placeholder, same shape as Z3 8 9 Returns: 10 cost - Tensor of the cost function 11 """ 12 13 # to fit the tensorflow requirement for tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(...,...) 14 logits = tf.transpose(Z3) 15 labels = tf.transpose(Y) 16 17 ### START CODE HERE ### (1 line of code) 18 cost=tf.reduce_mean(tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(logits=logits, labels=labels)) 19 ### END CODE HERE ### 20 21 return cost
1 def model(X_train, Y_train, X_test, Y_test, learning_rate = 0.0001, 2 num_epochs = 1500, minibatch_size = 32, print_cost = True): 3 """ 4 Implements a three-layer tensorflow neural network: LINEAR->RELU->LINEAR->RELU->LINEAR->SOFTMAX. 5 6 Arguments: 7 X_train -- training set, of shape (input size = 12288, number of training examples = 1080) 8 Y_train -- test set, of shape (output size = 6, number of training examples = 1080) 9 X_test -- training set, of shape (input size = 12288, number of training examples = 120) 10 Y_test -- test set, of shape (output size = 6, number of test examples = 120) 11 learning_rate -- learning rate of the optimization 12 num_epochs -- number of epochs of the optimization loop 13 minibatch_size -- size of a minibatch 14 print_cost -- True to print the cost every 100 epochs 15 16 Returns: 17 parameters -- parameters learnt by the model. They can then be used to predict. 18 """ 19 20 ops.reset_default_graph() # to be able to rerun the model without overwriting tf variables 21 tf.set_random_seed(1) # to keep consistent results 22 seed = 3 # to keep consistent results 23 (n_x, m) = X_train.shape # (n_x: input size, m : number of examples in the train set) 24 n_y = Y_train.shape[0] # n_y : output size 25 costs = [] # To keep track of the cost 26 27 # Create Placeholders of shape (n_x, n_y) 28 ### START CODE HERE ### (1 line) 29 X,Y=create_placeholders(n_x,n_y) 30 ### END CODE HERE ### 31 32 # Initialize parameters 33 ### START CODE HERE ### (1 line) 34 parameters=initialize_parameters() 35 ### END CODE HERE ### 36 37 # Forward propagation: Build the forward propagation in the tensorflow graph 38 ### START CODE HERE ### (1 line) 39 Z3=forward_propagation(X,parameters) 40 ### END CODE HERE ### 41 42 # Cost function: Add cost function to tensorflow graph 43 ### START CODE HERE ### (1 line) 44 cost=compute_cost(Z3,Y) 45 ### END CODE HERE ### 46 47 # Backpropagation: Define the tensorflow optimizer. Use an AdamOptimizer. 48 ### START CODE HERE ### (1 line) 49 optimizer = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(learning_rate=learning_rate).minimize(cost) 50 ### END CODE HERE ### 51 52 # Initialize all the variables 53 init = tf.global_variables_initializer() 54 55 # Start the session to compute the tensorflow graph 56 with tf.Session() as sess: 57 58 # Run the initialization 59 sess.run(init) 60 61 # Do the training loop 62 for epoch in range(num_epochs): 63 64 epoch_cost = 0. # Defines a cost related to an epoch 65 num_minibatches = int(m / minibatch_size) # number of minibatches of size minibatch_size in the train set 66 seed = seed + 1 67 minibatches = random_mini_batches(X_train, Y_train, minibatch_size, seed) 68 69 for minibatch in minibatches: 70 71 # Select a minibatch 72 (minibatch_X, minibatch_Y) = minibatch 73 74 # IMPORTANT: The line that runs the graph on a minibatch. 75 # Run the session to execute the "optimizer" and the "cost", the feedict should contain a minibatch for (X,Y). 76 ### START CODE HERE ### (1 line) 77 _ , minibatch_cost = sess.run([optimizer, cost], feed_dict={X: minibatch_X, Y: minibatch_Y}) 78 ### END CODE HERE ### 79 80 epoch_cost += minibatch_cost / num_minibatches 81 82 # Print the cost every epoch 83 if print_cost == True and epoch % 100 == 0: 84 print ("Cost after epoch %i: %f" % (epoch, epoch_cost)) 85 if print_cost == True and epoch % 5 == 0: 86 costs.append(epoch_cost) 87 88 # plot the cost 89 plt.plot(np.squeeze(costs)) 90 plt.ylabel(‘cost‘) 91 plt.xlabel(‘iterations (per tens)‘) 92 plt.title("Learning rate =" + str(learning_rate)) 93 plt.show() 94 95 # lets save the parameters in a variable 96 parameters = sess.run(parameters) 97 print("Parameters have been trained!") 98 99 # Calculate the correct predictions 100 correct_prediction = tf.equal(tf.argmax(Z3), tf.argmax(Y)) 101 102 # Calculate accuracy on the test set 103 accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(correct_prediction, "float")) 104 105 print("Train Accuracy:", accuracy.eval({X: X_train, Y: Y_train})) 106 print("Test Accuracy:", accuracy.eval({X: X_test, Y: Y_test})) 107 108 return parameters
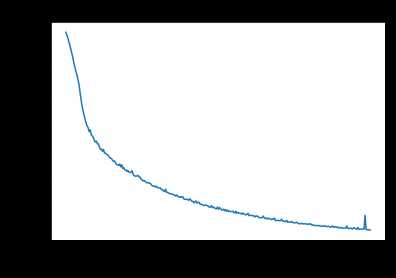
Parameters have been trained!
Train Accuracy: 0.999074
Test Accuracy: 0.725
改善深层神经网络-week3编程题(TensorFlow实现手势数字识别)
标签:dep add pytho convert line images img height without
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/cxq1126/p/13128387.html