标签:应该 exp extends tab efault this 设计模式 move ===
时长:42min
定义:
迭代器模式【Iterator Pattern】,又叫游标模式【Cursor Pattern】,它提供一种顺序访问集合/容器
对象元素的方法,又无须暴露集合内部表示。
本质:
抽离集合对象迭代行为到迭代器中,提供一致访问接口。
属于行为型模式。
》寄件迭代分发
》刷脸检票进站
1.访问一个集合对象的内容而无须暴露它的内部表示【遍历集合元素】
2.为遍历不同的集合结构提供一个统一的访问接口
package com.wf.iterator.general; /** * @ClassName IAggregate * @Description 顶层聚合接口 * @Author wf * @Date 2020/6/19 9:55 * @Version 1.0 */ public interface IAggregate<E> { boolean add(E e); boolean remove(E e); Iterator<E> iterator(); }
package com.wf.iterator.general; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.List; /** * @ClassName ConcreteAggregate * @Description 聚合对象子类实现 * @Author wf * @Date 2020/6/19 9:58 * @Version 1.0 */ public class ConcreteAggregate<E> implements IAggregate<E> { private List<E> list = new ArrayList<E>(); @Override public boolean add(E ele) { return this.list.add(ele); } @Override public boolean remove(E ele) { return this.list.remove(ele); } @Override public Iterator<E> iterator() { return new ConcreteIterator<E>(this.list); } }
package com.wf.iterator.general; /** * @ClassName Iterator * @Description 顶层迭代器接口 * @Author wf * @Date 2020/6/19 10:31 * @Version 1.0 */ public interface Iterator<E> { boolean hasNext(); E next(); }
package com.wf.iterator.general; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.List; /** * @ClassName ConcreteIterator * @Description 实现迭代器功能 * @Author wf * @Date 2020/6/19 9:57 * @Version 1.0 */ public class ConcreteIterator<E> implements Iterator<E> { private List<E> list = new ArrayList<E>(); int cursor; public ConcreteIterator(List<E> list) { this.list = list; } @Override public boolean hasNext() { return cursor != list.size(); } @Override public E next() { return list.get(cursor++); } }
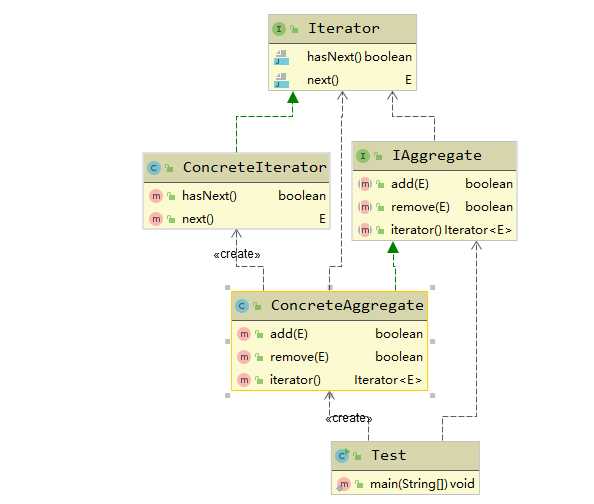
package com.wf.iterator.general; /** * @ClassName Test * @Description 测试类 * @Author wf * @Date 2020/6/19 10:01 * @Version 1.0 */ public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) { //创建一个聚合容器 IAggregate<String> aggregate = new ConcreteAggregate<String>(); //存储元素 aggregate.add("one"); aggregate.add("two"); aggregate.add("three"); //获取容器对象迭代器 Iterator<String> iterator = aggregate.iterator(); //遍历迭代器 while (iterator.hasNext()){ String ele = iterator.next(); System.out.println(ele); } } }
测试结果如下:
package com.wf.iterator.demo.course; /** * @ClassName ICourseAggregate * @Description 课程类聚合容器 * @Author wf * @Date 2020/6/19 10:42 * @Version 1.0 */ public interface ICourseAggregate { boolean add(Course course); boolean remove(Course course); Iterator<Course> iterator(); }
package com.wf.iterator.demo.course; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.List; /** * @ClassName CourseAggregateImpl * @Description 课程类聚合容器子类实现 * @Author wf * @Date 2020/6/19 10:48 * @Version 1.0 */ public class CourseAggregateImpl implements ICourseAggregate { private List<Course> courseList; public CourseAggregateImpl() { this.courseList = new ArrayList<>(); } @Override public boolean add(Course course) { return this.courseList.add(course); } @Override public boolean remove(Course course) { return this.courseList.remove(course); } @Override public Iterator<Course> iterator() { return new IteratorImpl<Course>(courseList); } }
package com.wf.iterator.demo.course; /** * @ClassName Iterator * @Description 顶层迭代器接口 * @Author wf * @Date 2020/6/19 10:31 * @Version 1.0 */ public interface Iterator<E> { boolean hasNext(); E next(); }
package com.wf.iterator.demo.course; import java.util.List; /** * @ClassName IteratorImpl * @Description 迭代器具体实现 * @Author wf * @Date 2020/6/19 10:44 * @Version 1.0 */ public class IteratorImpl<E> implements Iterator { private List<E> list; private int cursor; private E element; public IteratorImpl(List<E> list) { this.list = list; } @Override public boolean hasNext() { return cursor != list.size(); } @Override public Object next() { System.out.print("当前位置:"+cursor+ ":"); element = list.get(cursor++); return element; } }
package com.wf.iterator.demo.course; /** * @ClassName Course * @Description 课程类,业务bean * @Author wf * @Date 2020/6/19 10:40 * @Version 1.0 */ public class Course { private String name; public Course(String name) { this.name = name; } public String getName() { return name; } }
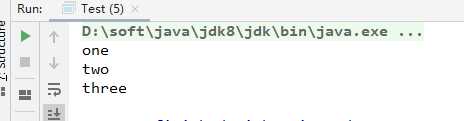
package com.wf.iterator.demo.course; /** * @ClassName Test * @Description 测试类 * @Author wf * @Date 2020/6/19 10:51 * @Version 1.0 */ public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) { Course java = new Course("Java架构"); Course javaBase = new Course("Java基础"); Course design = new Course("设计模式"); Course ai = new Course("人工智能"); ICourseAggregate aggregate = new CourseAggregateImpl(); aggregate.add(java); aggregate.add(javaBase); aggregate.add(design); aggregate.add(ai); System.out.println("===========课程列表=============="); printCourse(aggregate); aggregate.remove(ai); System.out.println("===========执行删除操作后的课程列表=============="); printCourse(aggregate); } private static void printCourse(ICourseAggregate aggregate) { Iterator<Course> it = aggregate.iterator(); while(it.hasNext()){ Course course = it.next(); System.out.println("《"+course.getName()+"》"); } } }
测试结果如下:

源码如下所示:
package java.util; import java.util.function.Consumer; /* * @param <E> the type of elements returned by this iterator * * @author Josh Bloch * @see Collection * @see ListIterator * @see Iterable * @since 1.2 */ public interface Iterator<E> { boolean hasNext(); E next(); default void remove() { throw new UnsupportedOperationException("remove"); } default void forEachRemaining(Consumer<? super E> action) { Objects.requireNonNull(action); while (hasNext()) action.accept(next()); } }
定义内部迭代器实现,如下所示:
private class Itr implements Iterator<E> { int cursor; // index of next element to return int lastRet = -1; // index of last element returned; -1 if no such int expectedModCount = modCount; Itr() {} public boolean hasNext() { return cursor != size; } @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") public E next() { checkForComodification(); int i = cursor; if (i >= size) throw new NoSuchElementException(); Object[] elementData = ArrayList.this.elementData; if (i >= elementData.length) throw new ConcurrentModificationException(); cursor = i + 1; return (E) elementData[lastRet = i]; } public void remove() { if (lastRet < 0) throw new IllegalStateException(); checkForComodification(); try { ArrayList.this.remove(lastRet); cursor = lastRet; lastRet = -1; expectedModCount = modCount; } catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException ex) { throw new ConcurrentModificationException(); } } @Override @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") public void forEachRemaining(Consumer<? super E> consumer) { Objects.requireNonNull(consumer); final int size = ArrayList.this.size; int i = cursor; if (i >= size) { return; } final Object[] elementData = ArrayList.this.elementData; if (i >= elementData.length) { throw new ConcurrentModificationException(); } while (i != size && modCount == expectedModCount) { consumer.accept((E) elementData[i++]); } // update once at end of iteration to reduce heap write traffic cursor = i; lastRet = i - 1; checkForComodification(); } final void checkForComodification() { if (modCount != expectedModCount) throw new ConcurrentModificationException(); } }
public interface Collection<E> extends Iterable<E> {
abstract class HashIterator { Node<K,V> next; // next entry to return Node<K,V> current; // current entry int expectedModCount; // for fast-fail int index; // current slot HashIterator() { expectedModCount = modCount; Node<K,V>[] t = table; current = next = null; index = 0; if (t != null && size > 0) { // advance to first entry do {} while (index < t.length && (next = t[index++]) == null); } } public final boolean hasNext() { return next != null; } final Node<K,V> nextNode() { Node<K,V>[] t; Node<K,V> e = next; if (modCount != expectedModCount) throw new ConcurrentModificationException(); if (e == null) throw new NoSuchElementException(); if ((next = (current = e).next) == null && (t = table) != null) { do {} while (index < t.length && (next = t[index++]) == null); } return e; } public final void remove() { Node<K,V> p = current; if (p == null) throw new IllegalStateException(); if (modCount != expectedModCount) throw new ConcurrentModificationException(); current = null; K key = p.key; removeNode(hash(key), key, null, false, false); expectedModCount = modCount; } }
public class DefaultCursor<T> implements Cursor<T> {
内部迭代器定义:
private class CursorIterator implements Iterator<T> { /** * Holder for the next object to be returned */ T object; /** * Index of objects returned using next(), and as such, visible to users. */ int iteratorIndex = -1; @Override public boolean hasNext() { if (object == null) { object = fetchNextUsingRowBound(); } return object != null; } @Override public T next() { // Fill next with object fetched from hasNext() T next = object; if (next == null) { next = fetchNextUsingRowBound(); } if (next != null) { object = null; iteratorIndex++; return next; } throw new NoSuchElementException(); } @Override public void remove() { throw new UnsupportedOperationException("Cannot remove element from Cursor"); } }
优点:
1.多态迭代:为不同的聚合结构提供一致的遍历接口,即一个迭代接口可以访问不同的聚合容器对象。
2.简化集合对象接口:迭代器模式将集合对象本身应该提供的元素迭代接口抽取到迭代器中,使集合对象无须
关心具体迭代行为。
3.元素迭代功能多样化:每个集合对象都可以提供一个或多个不同的迭代器,使得同种元素聚合结构可以有不同的迭代行为
4.解耦迭代与集合:迭代器模式,封装了具体的迭代算法,迭代算法的变化,不会影响到集合对象的架构。
缺点:
对于比较简单的遍历【如数组或有序列表】,使用迭代器遍历反而较为繁琐。
时长:36min
11.1.1.迭代器模式的定义
11.1.1.1.迭代器模式在生活中体现
标签:应该 exp extends tab efault this 设计模式 move ===
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/wfdespace/p/13162158.html