标签:作用 byte namespace 面积 翻转 chain int 网格 bytes
cgal文档见:https://doc.cgal.org/latest/Polygon_mesh_processing/group__pmp__namedparameters.html
本文对named parameters做些介绍,以及简单的描述下Polygon Mesh Processing中具有对应示例的named parameters。
参见:https://isocpp.org/wiki/faq/ctors
在此之前先简单的描述下什么是method chaining。
method chaining,就是一个方法返回一个对象,然后这个对象还能够继续调用别的方法,示例如:object.method1().method2()。c++中使用最多的就是cout << x << y。
c++只支持位置参数,也就是在调用函数的时候,参数的顺序是确定的。但是对于想Graph这样的实现而言,又是后一个函数需要很多的参数,那么如果像平常实现函数一样用fun(int, int, int, int)类似的形式给定参数的话,很容易忘记参数应该是什么顺序的。named parameters就在这种情况下发挥出了他的作用。具体是怎么做的呢?
它将函数的参数定义成了一个新类的方法,并且这个方法可以返回该类的引用。这样就简单的解除了对顺序的依赖。接下来看一下简单的例子。
例如“打开一个文件”。需要传入文件名,需要选择是以只读方式打开,还是以可写方式打开,还是允许在文件不存在的时候进行创建。在写入的时候,是进行追加写入,还是进行覆盖写入,创建文件的时候,块的大小,I/O是缓冲的还是非缓冲的,缓冲区大小,共享还是独占访问,等。如果我们使用带有位置参数的普通函数实现这个概念,那么调用方代码将非常难以读取:将有多达8个位置参数,调用方可能会犯很多错误。因此,我们使用命名参数习惯用法
class File;
// OpenFile
class OpenFile {
public:
OpenFile(const std::string& filename);
// sets all the default values for each data member
OpenFile& readonly(); // changes readonly_ to true
OpenFile& readwrite(); // changes readonly_ to false
OpenFile& createIfNotExist();
OpenFile& blockSize(unsigned nbytes);
// ...
private:
friend class File;
std::string filename_;
bool readonly_; // defaults to false [for example]
bool createIfNotExist_; // defaults to false [for example]
// ...
unsigned blockSize_; // defaults to 4096 [for example]
// ...
};
inline OpenFile::OpenFile(const std::string& filename)
: filename_ (filename)
, readonly_ (false)
, createIfNotExist_ (false)
, blockSize_ (4096u)
{ }
inline OpenFile& OpenFile::readonly()
{ readonly_ = true; return *this; }
inline OpenFile& OpenFile::readwrite()
{ readonly_ = false; return *this; }
inline OpenFile& OpenFile::createIfNotExist()
{ createIfNotExist_ = true; return *this; }
inline OpenFile& OpenFile::blockSize(unsigned nbytes)
{ blockSize_ = nbytes; return *this; }
class File {
public:
File(const OpenFile& params);
// ...
};
// with default parameters
File f = OpenFile("foo.txt");
// change parameters
File f = OpenFile("foo.txt")
.readonly()
.createIfNotExist()
.appendWhenWriting()
.blockSize(1024)
.unbuffered()
.exclusiveAccess();
其参数的构建方式和上面类似,如:
typedef CGAL::Extract_predicates_inexact_constructions_kernel K;
typedef CGAL::Surface_mesh<K::Point_3> Mesh;
namespace PMP = CGAL::Polygon_mesh_processing;
Mesh mesh;
PMP::parameters::vertex_point_map(get_property_map(CGAL::vertex_point, mesh))
.face_index_map(get_property_map(CGAL::face_index, mesh))
.clip_volume(true);
与mesh直接相关的参数有:vertex_point_map, vertex_index_map, face_index_map, edge_is_constrained_map。
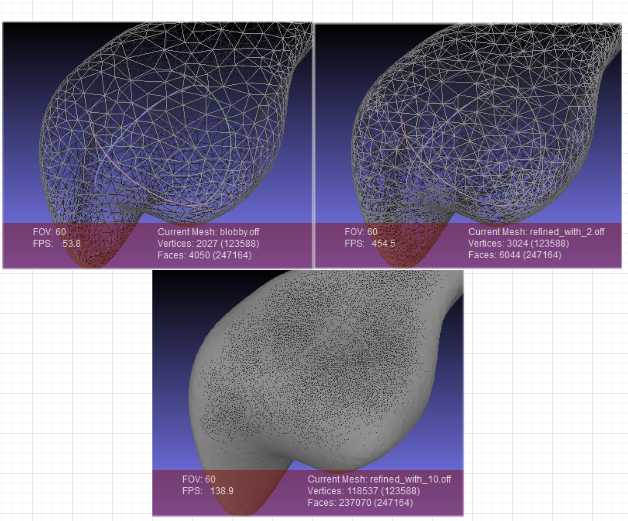
控制网格细分的程度。详细参考,仅用refine(细分网格)函数,调整density_control_factor参数:https://doc.cgal.org/latest/Polygon_mesh_processing/Polygon_mesh_processing_2refine_fair_example_8cpp-example.html#a4。
// 代码片段
PMP::refine(poly,
faces(poly),
std::back_inserter(new_facets),
std::back_inserter(new_vertices),
Params::density_control_factor(2.));
PMP::refine(poly,
faces(poly),
std::back_inserter(new_facets),
std::back_inserter(new_vertices),
Params::density_control_factor(10));
效果对比如下:
效果如下:
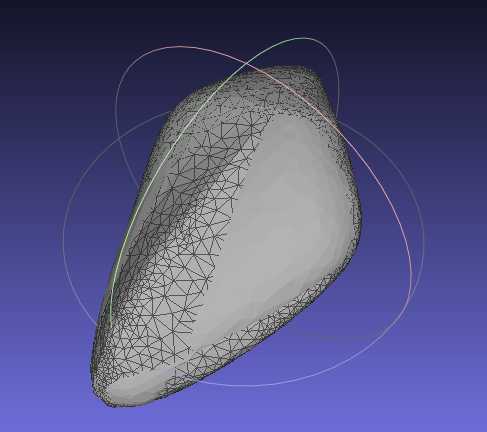
从效果中可见,函数fair是用来对一定区域的网格做平滑处理。具体要参考论文了:https://doc.cgal.org/latest/Polygon_mesh_processing/citelist.html#CITEREF_Botsch2008OnLinearVariational。
remesh 依次执行边分割、边折叠、边翻转、切线松弛和投影到初始曲面,以生成具有指定边长度的平滑网格。 参考demo见:https://doc.cgal.org/latest/Polygon_mesh_processing/Polygon_mesh_processing_2isotropic_remeshing_example_8cpp-example.html#a5
如果remesh参数种给的target_edge_length为0,那么不会执行边分割,边折叠。参数的使用方式与简单介绍如下:
PMP::isotropic_remeshing(
faces(mesh),
target_edge_length,
mesh,
Params::number_of_iterations(1) // 迭代次数
.protect_constraints(false) // 如果这个为true,那么edge_is_constrained_map中设定的edge是不会被改变的
.collapse_constraints(true) // 如果是true,那么edge_is_constrained_map中的边会进行collapse操作
.relax_constraints(true) // 如果protect_constraints为true,那么这个值被忽略;
// 该值为true,会对edge_is_constrained_map中给定的约束的边和点进行relaxation操作
.number_of_relaxation_steps(1) // isotropic_remeshing迭代过程中,relaxation迭代次数
);
默认情况下edge_is_constrained_map中设定的值为false,protect_constraints, collapse_constraints, relax_constraints对结果不会有影响。如何对edge_is_constrained_map的值进行设定了,可以参见:https://doc.cgal.org/latest/Polygon_mesh_processing/Polygon_mesh_processing_2corefinement_difference_remeshed_8cpp-example.html#a2。
number_of_points_on_faces设置的示例如下:
#include <CGAL/Exact_predicates_inexact_constructions_kernel.h>
#include <CGAL/Surface_mesh.h>
#include <CGAL/Polygon_mesh_processing/distance.h>
#include <boost/function_output_iterator.hpp>
#include <fstream>
#include <map>
typedef CGAL::Exact_predicates_inexact_constructions_kernel Kernel;
typedef CGAL::Surface_mesh<Kernel::Point_3> Mesh;
namespace PMP = CGAL::Polygon_mesh_processing;
namespace Params = PMP::parameters;
void read_mesh(Mesh& mesh, std::string filename)
{
std::ifstream input(filename);
if (!input || !(input >> mesh) || !CGAL::is_triangle_mesh(mesh)) {
std::cerr << "Not a valid input file" << std::endl;
return;
}
}
void write_points(const std::vector<Kernel::Point_3>& points, std::string filename)
{
std::ofstream out(filename);
for (int i = 0; i < points.size(); ++i)
{
out << points[i].x() << " " << points[i].y() << " " << points[i].z() << "\n";
}
out.close();
}
int main()
{
Mesh mesh;
read_mesh(mesh, "E:/stl/cube.off");
std::vector<Kernel::Point_3> outPoints;
PMP::sample_triangle_mesh(
mesh, std::back_inserter(outPoints),
Params::use_random_uniform_sampling(true)
.number_of_points_on_faces(50));
write_points(outPoints, "E:/stl/test/np_on_faces_50.xyz"); // 最终得到的点为采样的点和原始mesh中的点和合集
return 0;
}
clip_volume,如果为true,会补全clip之后的洞。default false。
CGAL Polygon mesh processing named parameters
标签:作用 byte namespace 面积 翻转 chain int 网格 bytes
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/grass-and-moon/p/13168017.html