标签:tar end 必须 class 回溯 开始 n皇后问题 lazy 坐标

#include <stdio.h>
#include <malloc.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
#define Max_Size 100
typedef char ElemType;
typedef struct
{
ElemType data[Max_Size];
int top;
}SeqStack;
//初始化栈
static void init_stack(SeqStack *&s)
{
s = (SeqStack *)malloc(sizeof(SeqStack));
s->top = -1;
}
//销毁顺序栈
static void destroy_stack(SeqStack *&s)
{
free(s);
}
//判断栈空否
static bool stack_empty(SeqStack *s)
{
return (s->top == -1);
}
//进栈
static bool push(SeqStack *&s,ElemType e)
{
if(s->top==(Max_Size-1)) //栈满的情况,栈上溢出
return false;
s->top++;
s->data[s->top]=e;
return true;
}
//出栈
static bool pop(SeqStack *&s,ElemType &e)
{
if(s->top==-1) //栈为空的情况,即栈下溢出
return false;
e=s->data[s->top];
s->top--;
return true;
}
//取栈顶元素
static bool get_top(SeqStack *s,ElemType &e)
{
if(s->top==-1)
return false;
e=s->data[s->top];
return true;
}
int main()
{
ElemType e;
SeqStack *s;
printf("顺序栈s的基本运算如下:\n");
printf(" (1)初始化栈s\n");
init_stack(s);
printf(" (2)栈为%s\n",(stack_empty(s) ? "空" : "非空"));
printf(" (3)依次进栈元素a,b,c,d,e\n");
push(s, ‘a‘);
push(s, ‘b‘);
push(s, ‘c‘);
push(s, ‘d‘);
push(s, ‘e‘);
printf(" (4)栈为%s\n",(stack_empty(s) ? "空" : "非空"));
printf(" (5)出栈序列:");
while(!stack_empty(s))
{
pop(s, e);
printf("%c ", e);
}
printf("\n");
printf(" (6)栈为%s\n",(stack_empty(s) ? "空" : "非空"));
printf(" (7)释放栈\n");
destroy_stack(s);
}


#include <stdio.h>
#include <malloc.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
typedef char ElemType;
typedef struct linknode
{
ElemType data;
struct linknode *next;
}LinkStNode;
//初始化链栈
static void init_stack(LinkStNode *&s)
{
s = (LinkStNode *)malloc(sizeof(LinkStNode));
s->next = NULL;
}
//销毁链栈
static void destroy_stack(LinkStNode *&s)
{
LinkStNode *p = s->next;
while(p != NULL)
{
free(s);
s = p;
p = p->next;
}
free(s); //s指向尾结点,释放其空间
}
//判断链栈空否
static bool stack_empty(LinkStNode *s)
{
return (s->next == NULL);
}
//进栈
static void push(LinkStNode *&s,ElemType e)
{
LinkStNode *p;
p=(LinkStNode *)malloc(sizeof(LinkStNode));
p->data=e;
p->next=s->next;
s->next=p;
}
//出栈
static bool pop(LinkStNode *&s,ElemType &e)
{
LinkStNode *p;
if(s->next==NULL)
return false;
p=s->next;
e=p->data;
s->next=p->next; //删除首节点
free(p);
return true;
}
//取栈顶元素
static bool get_top(LinkStNode *s, ElemType &e)
{
if(s->next==NULL)
return false;
e=s->next->data; //提取首节点值
return true;
}
int main()
{
ElemType e;
LinkStNode *s;
printf("链栈s的基本运算如下:\n");
printf(" (1)初始化栈s\n");
init_stack(s);
printf(" (2)栈为%s\n", (stack_empty(s) ? "空" : "非空"));
printf(" (3)依次进栈元素a,b,c,d,e\n");
push(s, ‘a‘);
push(s, ‘b‘);
push(s, ‘c‘);
push(s, ‘d‘);
push(s, ‘e‘);
printf(" (4)栈为%s\n", (stack_empty(s) ? "空" : "非空"));
printf(" (5)出栈序列:");
while(!stack_empty(s))
{
pop(s, e);
printf("%c ", e);
}
printf("\n");
printf(" (6)栈为%s\n", (stack_empty(s) ? "空" : "非空"));
printf(" (7)释放栈\n");
destroy_stack(s);
}


#include <stdio.h>
#include <malloc.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
#define MAX_SIZE 100
typedef char ElemType;
typedef struct
{
ElemType data[MAX_SIZE];
int queue_front; //队首指针
int queue_rear; //队尾指针
}SeqQueue;
//初始化队列
static void init_queue(SeqQueue *&q)
{
q = (SeqQueue *)malloc(sizeof(SeqQueue)); // 动态分配存储空间
q->queue_front = q->queue_rear = 0; //空
}
//销毁队列q
static void destroy_queue(SeqQueue *&q)
{
free(q);
}
//判断队列q是否空
static bool queue_empty(SeqQueue *q)
{
return (q->queue_front == q->queue_rear);
}
//入队
static bool en_queue(SeqQueue *&q, ElemType e)
{
if((q->queue_rear + 1) % MAX_SIZE == q->queue_front) //队满,上溢出,返回假
return false;
q->queue_rear = (q->queue_rear + 1) % MAX_SIZE; //计算队尾指针
q->data[q->queue_rear] = e; //将元素e入队
return true;
}
//出队
static bool de_queue(SeqQueue *&q, ElemType &e)
{
if(q->queue_front == q->queue_rear) //队空,下溢出,返回假
return false;
q->queue_front = (q->queue_front + 1) % MAX_SIZE; //计算队首指针
e = q->data[q->queue_front]; //提取队列中的元素
return true;
}
int main()
{
ElemType e;
SeqQueue *q;
printf("环形队列基本运算如下:\n");
printf(" (1)初始化队列q\n");
init_queue(q);
printf(" (2)依次进队元素a、b、c\n");
if(!en_queue(q, ‘a‘))
printf("\t提示:队满,不能入队\n");
if(!en_queue(q, ‘b‘))
printf("\t提示:队满,不能入队\n");
if(!en_queue(q, ‘c‘))
printf("\t提示:队满,不能入队\n");
printf(" (3)队列为%s\n", (queue_empty(q) ? "空" : "非空"));
if(!de_queue(q, e))
printf("队空,不能出队\n");
else
printf(" (4)出队一个元素%c\n", e);
printf(" (5)依次进队元素d、e、f\n");
if(!en_queue(q, ‘d‘))
printf("\t提示:队满,不能入队\n");
if(!en_queue(q, ‘e‘))
printf("\t提示:队满,不能入队\n");
if(!en_queue(q, ‘f‘))
printf("\t提示:队满,不能入队\n");
printf(" (6)出队列序列: ");
while(!queue_empty(q))
{
de_queue(q, e);
printf("%c ", e);
}
printf("\n");
printf(" (7)释放队列\n");
destroy_queue(q);
}


#include <stdio.h>
#include <malloc.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
#define MAX_SIZE 100
typedef char ElemType;
typedef struct DataNode
{
ElemType data;
struct DataNode *next;
}DataNode;
typedef struct
{
DataNode *queue_front; //队头指针
DataNode *queue_rear; //队尾指针
}LinkQuNode;
//初始化队列
static void init_queue(LinkQuNode *&q)
{
q = (LinkQuNode *)malloc(sizeof(LinkQuNode));
q->queue_front = q->queue_rear = NULL;
}
//销毁队列q
static void destroy_queue(LinkQuNode *&q)
{
DataNode *p = q->queue_front; //p指向队头数据结点
DataNode *r;
if(p != NULL)
{
r = p->next; //r指向队列中第一个数据结点
while(r != NULL)
{
free(p);
//p,r同步后移一个结点
p = r;
r = p->next;
}
}
free(p);
free(q);
}
//判断队列q是否空
static bool queue_empty(LinkQuNode *q)
{
return (q->queue_rear == NULL);
}
//入队
static void en_queue(LinkQuNode *&q, ElemType e)
{
DataNode *p; //创建新结点p
p = (DataNode *)malloc(sizeof(DataNode));
p->data = e;
p->next = NULL;
// 若链队为空,则新结点既是队首结点又是队尾结点
if(q->queue_rear == NULL)
q->queue_front = q->queue_rear = p;
else
{
//将新结点p链到队尾,并将queue_rear指向它
q->queue_rear->next = p;
q->queue_rear = p;
}
}
//出队
static bool de_queue(LinkQuNode *&q, ElemType &e)
{
DataNode *t;
if(q->queue_rear == NULL) //队列为空
return false;
t = q->queue_front; //t指向第一个数据结点
if(q->queue_front == q->queue_rear) //队列中只有一个结点时
{
q->queue_front = q->queue_rear = NULL;
}
else //队列中有多个结点时
{
q->queue_front = q->queue_front->next; //队首指针后移一个结点
}
e = t->data; //从t结点中提取数据元素
free(t);
return true;
}
int main()
{
ElemType e;
LinkQuNode *q;
printf("链队的基本运算如下:\n");
printf(" (1)初始化链队q\n");
init_queue(q);
printf(" (2)依次进链队元素a、b、c\n");
en_queue(q, ‘a‘);
en_queue(q, ‘b‘);
en_queue(q, ‘c‘);
printf(" (3)链队为%s\n", (queue_empty(q) ? "空" : "非空"));
if(!de_queue(q, e))
printf("\t提示:队空,不能出队\n");
else
printf(" (4)出队一个元素%c\n", e);
printf(" (5)依次进链队元素d、e、f\n");
en_queue(q, ‘d‘);
en_queue(q, ‘e‘);
en_queue(q, ‘f‘);
printf(" (6)出链队序列: ");
while(!queue_empty(q))
{
de_queue(q, e);
printf("%c ", e);
}
printf("\n");
printf(" (7)释放链队\n");
destroy_queue(q);
}



//本题书上代码有误,运行后为死循环输出不了所有路径
//本题代码学习于CSDN作者- 不想悲伤到天明
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstdlib>
using namespace std ;
const int MAX = 105 ;
int mg[MAX][MAX] ={
{1,1,1,1,1,1},
{1,0,0,0,1,1},
{1,0,1,0,0,1},
{1,0,0,0,1,1},
{1,1,0,0,0,1},
{1,1,1,1,1,1}
};//迷宫地图
struct Point{
int x ;// 路径横坐标
int y ;// 路径纵坐标 ;
int di ;// 方向
};
typedef struct{
int top ;
Point data[MAX] ;
}Stack;
class STACK{
public:
void InitStack(Stack *&s);
bool StackEmpty(Stack *&s);
bool Push(Stack *&s ,Point &e);
bool Pop(Stack *&s ,Point &e);
bool GetTop(Stack *&s ,Point &e);
};
void STACK::InitStack(Stack *&s)
{
s = (Stack *)malloc(sizeof(Stack)) ;
s->top = -1 ;
return ;
}
bool STACK::StackEmpty(Stack *&s)
{
return (s->top ==-1) ;
}
bool STACK::Push(Stack *&s ,Point &e)
{
if(s->top == MAX -1)
{
return false ;
}
s->top++ ;
s->data[s->top] = e ;
return true ;
}
bool STACK::Pop(Stack *&s ,Point &e)
{
if(s->top ==-1)
{
return false ;
}
e = s->data[s->top] ;
s->top-- ;
return true ;
}
bool STACK::GetTop(Stack *&s ,Point &e)
{
if(s->top ==-1)
{
return false ;
}
e = s->data[s->top ] ;
return true ;
}
int count = 1 ; // 记录路径数目
int minlen = 0x3f3f; //最短路径长度,先设为最大
Point path[MAX] ;
void dfs(Point start ,Point end)
{
bool find ;
Point head ;
STACK a ;
Stack *s ;
a.InitStack(s);
start.di = -1 ;// 开始点,且还没有尝试 ;
a.Push(s,start);
mg[start.x][start.y] = -1 ;
while(!a.StackEmpty(s))
{
head;// 栈顶元素
a.GetTop(s,head) ;
if(head.x == end.x && head.y == end.y)
{
count++ ;
printf("Map %d :\n",count-1);
for(int k = 0 ;k<=s->top ;k++)
{
printf("(%d ,%d) ",s->data[k].x,s->data[k].y);
if((k+1)%5==0) //输出上更好直观判断最短路径
cout<<endl;
}
printf("\n\n");
if(s->top+1 <minlen)
{
for(int k = 0 ;k<=s->top ;k++)
{
path[k] = s->data[k] ;
}
// 更新最短路径
minlen = s->top+1 ;
}
// 退栈,重新走
mg[s->data[s->top].x][s->data[s->top].y] = 0 ;
s->top--;
head.x = s->data[s->top].x ;
head.y = s->data[s->top].y ;
head.di = s->data[s->top].di ;
}
find = false ;
while(head.di<4 && !find)
{
head.di++ ;
switch(head.di){
case 0:head.x=s->data[s->top].x -1 ;head.y =s->data[s->top].y;break;//上面
case 1:head.x=s->data[s->top].x ;head.y =s->data[s->top].y+1;break;//右边
case 2:head.x=s->data[s->top].x +1 ;head.y =s->data[s->top].y;break;//下面
case 3:head.x=s->data[s->top].x ;head.y =s->data[s->top].y-1;break;//左边
}
if(mg[head.x][head.y]==0)
{
find = true ;
}
}
if(find)
{
//如果有路
s->data[s->top].di = head.di ; // 修改原来栈顶的方向值
s->top++;
s->data[s->top].x = head.x ;// 入栈
s->data[s->top].y = head.y ;
s->data[s->top].di = -1 ;// 此点还没有进行过尝试
mg[head.x][head.y] = -1 ;//访问过了
}
else
{
//回溯
mg[s->data[s->top].x][s->data[s->top].y] = 0 ;
s->top --;
}
}
printf("最短路径长度为 :%d\n",minlen);
printf("最短路径 :");
for(int k = 0 ;k <minlen ;k++)
{
printf("(%d,%d)",path[k].x,path[k].y) ;
}
cout<<endl;
}
int main()
{
Point start ,end ;
start.x = 1 ;
start.y = 1 ;
end.x = 4 ;
end.y = 4 ;
dfs(start,end);
}


#include <stdio.h>
#include <malloc.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
#define MAX_SIZE 100
typedef char ElemType;
typedef struct
{
ElemType data[MAX_SIZE];
int top; //栈顶指针
}SeqStack;
//初始化顺序栈
static void init_stack(SeqStack *&s)
{
s = (SeqStack *)malloc(sizeof(SeqStack));
s->top = -1;
}
//销毁顺序栈
static void destroy_stack(SeqStack *&s)
{
free(s);
}
//判断栈空否
static bool stack_empty(SeqStack *s)
{
return (s->top == -1);
}
//进栈
static bool push(SeqStack *&s, ElemType e)
{
if(s->top == (MAX_SIZE - 1)) //栈满的情况,栈上溢出
return false;
s->top++;
s->data[s->top] = e;
return true;
}
//出栈
static bool pop(SeqStack *&s, ElemType &e)
{
if(s->top == -1) //栈为空的情况,即栈下溢出
return false;
e = s->data[s->top];
s->top--;
return true;
}
//取栈顶元素
static bool get_top(SeqStack *s, ElemType &e)
{
if(s->top == -1) //栈为空的情况,即栈下溢出
return false;
e = s->data[s->top];
return true;
}
//对栈中元素排序
/**
* 功能:对栈st中元素排序
* @param st:要排序的栈
* 思路:
* 采用一个额外的栈tmpst存放临时数据。
* 处理st栈的某个栈顶元素e,出栈元素e,将其存放在tmpst中。若临时栈tmpst为空,直接
* 将e进入tmpst中;若tmpst栈不空,将它的元素退栈(放入st栈中)直到tmpst栈顶元素小于e,再
* 将tmp进入到tmpst中,进行这样的过程直到st为空,而tmpst中元素从栈底到栈顶是递增的。再
* 将tmpst中所有元素退栈并进栈到st中。
*/
static void sort(SeqStack *&st)
{
SeqStack *tmpst; //临时栈
ElemType e, e1;
init_stack(tmpst); //初始化临时栈
while(!stack_empty(st)) //st栈不空循环
{
pop(st, e); //出栈元素e
printf(" st:出栈%c=> ", e);
while(!stack_empty(tmpst)) //tmpst栈不空循环
{
get_top(tmpst, e1); //取栈顶元素e1
printf("tmpst:取栈顶元素%c", e1);
if(e1 > e)
{
printf("因%c>%c ", e1, e);
printf("tmpst:退栈%c ", e1);
pop(tmpst, e1);
printf("s:进栈%c ", e1);
push(st, e1);
}
else
{
printf("因%c<%c,退出循环", e1, e);
break;
}
}
push(tmpst, e);
printf("tmpst:进栈%c\n", e);
}
while(!stack_empty(tmpst))
{
pop(tmpst, e);
push(st, e);
}
destroy_stack(tmpst);
}
int main()
{
ElemType e;
SeqStack *s;
init_stack(s);
printf("(1)依次进栈元素1,3,4,2\n");
push(s, ‘1‘);
push(s, ‘3‘);
push(s, ‘4‘);
push(s, ‘2‘);
printf("(2)栈s排序过程:\n");
sort(s);
printf("(3)栈s排序完毕\n");
printf("(4)s的出栈序列:");
while(!stack_empty(s))
{
pop(s, e);
printf("%c ", e);
}
printf("\n");
destroy_stack(s);
}

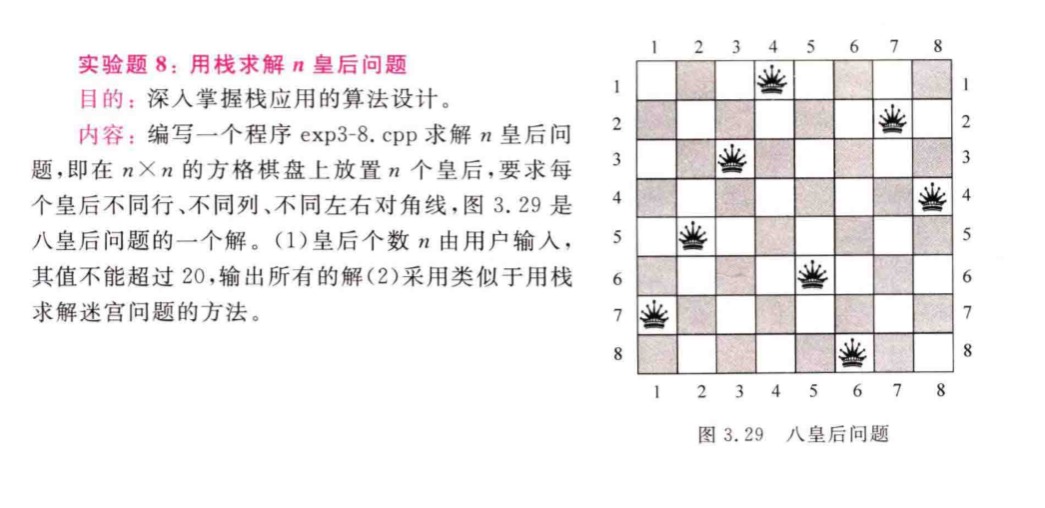
//学习于CSDN作者- _奶酪
#include <iostream>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <cmath>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
#define maxn 100
int n,num=1;//num定义为全局变量
typedef struct node {
int col[maxn];//col[i]表示第i个n皇后的列数,(i,col[i])即为坐标
int top;
}stacktype;
void display(stacktype st)
{
printf(" 第%d个解为:",num++);
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
printf("(%d,%d) ",i,st.col[i]);
printf("\n");
}
bool place(stacktype st,int k,int j)
{
int i=1;
if(k==1) return true; //第一个皇后直接放入,没有任何冲突
while(i<=k-1) //遍历前k-1个皇后,判断第k个皇后是否可以放在(k,j)处
{
if((st.col[i]==j)||(abs(st.col[i]-j)==abs(i-k)))
return false;
i++;
}
return true;
}
void queen(int n)
{
int k;
bool find;
stacktype st;
st.top=1;
st.col[st.top]=0;
while(st.top!=0)
{
k=st.top; //记录栈顶皇后的个数
find=false;
for(int j=st.col[k]+1;j<=n;j++) //回溯时要遍历当前列后面的列数,且下一个皇后的初始化列数为0
if(place(st,k,j))
{
st.col[k]=j;
find=true;
break; //找到第一个可以放入的位置
}
if(find)
{
if(k==n)
{
display(st); //每次能放完n个皇后都要输出
}
else
{
st.top++;
st.col[st.top]=0;
}
}
else st.top--; //回溯,最后while结束时是当第一个皇后放在(1,n)位置时无法将n个皇后都放下,st.top=0
}
if(num==1)
printf(" 此%d皇后问题无解!\n",n);
}
int main()
{
printf("n皇后问题求解:n=");
scanf("%d",&n);
if(n>20) printf("n必须小于20\n");
else
{
printf(" %d皇后问题的求解情况如下:\n",n);
queen(n);
}
}

标签:tar end 必须 class 回溯 开始 n皇后问题 lazy 坐标
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/wangzheming35/p/13170869.html