标签:array cat last 输入 运算表达式 参数 字符串 四则运算 存在
??栈的英文为(stack),是一个先入后出(FILO-First In Last Out)的有序列表。其限制线性表中元素的插入和删除只能在线性表的同一端进行的一种特殊线性表。允许插入和删除的一端,为变化的一端,称为栈顶(Top),另一端为固定的一端,称为栈底(Bottom)。根据栈的定义可知,最先放入栈中元素在栈底,最后放入的元素在栈顶,而删除元素刚好相反,最后放入的元素最先删除,最先放入的元素最后删除。
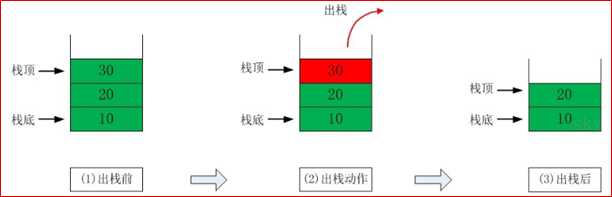
出栈(pop)
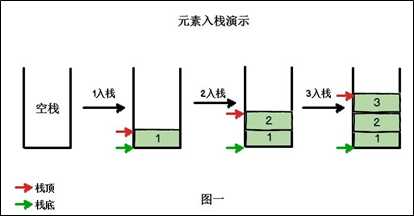
入栈(push)
应用场景
子程序的调用:在跳往子程序前,会先将下个指令的地址存到堆栈中,直到子程序执行完后再将地址取出,以回到原来的程序中。
处理递归调用:和子程序的调用类似,只是除了储存下一个指令的地址外,也将参数、区域变量等数据存入堆栈中。
表达式的转换[中缀表达式转后缀表达式]与求值(实际解决)。
二叉树的遍历。
图形的深度优先(depth一first)搜索法。
指定栈的最大容量(maxSize)。
top记录栈顶元素,初始化为-1。
存取时注意栈满栈空以及top指针的移动。
package com.atguigu.stack;import java.util.Scanner;
public class ArrayStackDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) { //测试 ArrayStack s = new ArrayStack(4); String key = ""; boolean loop = true; //控制是否退出 Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in); while(loop){ System.out.println("show: 表示显示栈"); System.out.println("exit: 退出程序"); System.out.println("push: 入栈"); System.out.println("pop: 出栈"); System.out.println("请输入选择:"); key = sc.next(); switch (key){ case "show": s.show(); break; case "exit": sc.close(); //关闭IO流! loop = false; break; case "push": System.out.println("请输入要入栈的数据:"); int t = sc.nextInt(); s.push(t); break; case "pop": //出栈时可能会有运行时异常 try{ int res = s.pop(); System.out.printf("出栈的数据是:%d\n",res); }catch(Exception e){ System.out.println(e.getMessage()); } break; default: break; } } System.out.println("程序退出了!"); }}
class ArrayStack{
private int maxSize; private int[] stack; private int top = -1; ArrayStack(int maxSize){ this.maxSize = maxSize; stack = new int[this.maxSize]; } public boolean isFull(){ return top == maxSize-1; } public boolean isEmpty(){ return top == -1; } //入栈 public void push(int v){ if(isFull()){ System.out.println("栈满,不能添加元素"); return; } top++; stack[top] = v; } //出栈 public int pop(){ if(isEmpty()){ //System.out.println("栈空,不能删除元素"); //return -1; 有返回值不能返回-1 throw new RuntimeException("栈空,不能删除元素"); } int res = stack[top]; top--; return res; } //遍历栈(从栈顶开始遍历,而不是从0开始) public void show(){ if(isEmpty()){ System.out.println("栈空"); return; } for(int j = top; j>=0; j--){ System.out.printf("stack[%d] = %d\n",j,stack[j]); } }}
暂无
?? 题目描述

对于上述问题,使用栈来实现综合计算器并自定义优先级[priority]。
?? 问题分析

?? 代码实现
使用数组栈实现,基于上述栈实现代码添加新的方法,如【返回运算符的优先级】【判断是不是一个运算符】【四则运算计算方法】。
字符串中的数字可能是多位数,因此读取数字时,要向下扫描直至遇到符号,将本次扫描的数字入栈。
package com.atguigu.stack;public class Calculator {
public static void main(String[] args) { //要计算的表达式 String expression = "70+200*6-5"; //创建两个栈:数栈与符号栈 ArrayStackForCalculator numStack = new ArrayStackForCalculator(10); ArrayStackForCalculator operStack = new ArrayStackForCalculator(10); //定义相关变量 int index = 0; //用于扫描表达式字符串 int num1 = 0, num2 = 0; //用于运算的两个数 int oper = 0; //用于运算的字符 int res = 0; char ch = ‘ ‘; //将每次扫描的得到的char保存到ch中 String keepNum = ""; //用于拼接多位数字 while (true){ //ch = expression.substring(index, index+1).charAt(0); ch = expression.charAt(index); if(operStack.isOper(ch)){ //是运算符 if(!operStack.isEmpty()){ if(operStack.priority(ch) <= operStack.priority(operStack.peek())){ num1 = numStack.pop(); num2 = numStack.pop(); oper = operStack.pop(); res = numStack.cal(num2, num1, oper); numStack.push(res); operStack.push(ch); //当前符号入栈! }else{ operStack.push(ch); } }else{ operStack.push(ch); } }else{ //是数字,考虑是否为多位数字 //numStack.push(ch - 48); //1 = ‘1‘ - ‘0‘ keepNum += ch; while(index < expression.length()){ if(index == expression.length()-1){ //最后一个字符不用考虑 break; } if(operStack.isOper(expression.charAt(index+1))){ break; }else{ keepNum += expression.charAt(index+1); index++; } } //System.out.printf("keepNum = %s", keepNum); numStack.push(Integer.parseInt(keepNum)); keepNum = ""; } index++; //扫描下一个字符 if(index >= expression.length() ){ break; } } //当表达式扫描完毕,就顺序的从[数栈和符号栈]中pop出相应的数和符号,并计算 while(true){ //如果符号栈为空,则计算结束。此时,数栈中只有一个数字 if(operStack.isEmpty()){ break; } num1 = numStack.pop(); num2 = numStack.pop(); oper = operStack.pop(); res = numStack.cal(num2, num1, oper); numStack.push(res); } System.out.printf("表达式 %s = %d ", expression, numStack.pop()); }}
class ArrayStackForCalculator{
private int maxSize; private int[] stack; private int top = -1; ArrayStackForCalculator(int maxSize){ this.maxSize = maxSize; stack = new int[this.maxSize]; } public boolean isFull(){ return top == maxSize-1; } public boolean isEmpty(){ return top == -1; } //显示栈顶元素,但并不拿出栈顶元素 public int peek(){ /*if(isEmpty()){ throw new RuntimeException("栈空,不能删除元素"); }*/ return stack[top]; } //入栈 public void push(int v){ if(isFull()){ System.out.println("栈满,不能添加元素"); return; } top++; stack[top] = v; } //出栈 public int pop(){ if(isEmpty()){ //System.out.println("栈空,不能删除元素"); //return -1; 有返回值不能返回-1 throw new RuntimeException("栈空,不能删除元素"); } int res = stack[top]; top--; return res; } //遍历栈(从栈顶开始遍历,而不是从0开始) public void show(){ if(isEmpty()){ System.out.println("栈空"); return; } for(int j = top; j>=0; j--){ System.out.printf("stack[%d] = %d\n",j,stack[j]); } } //返回运算符的优先级 //优先级用数字表示,数字越大,优先级越高 public int priority(int oper){ //char可以用int表示 if(oper == ‘*‘ || oper == ‘/‘){ return 1; }else if(oper == ‘+‘ || oper == ‘-‘){ return 0; }else{ return -1; } } //判断是不是一个运算符 public boolean isOper(char val){ return val == ‘+‘ || val == ‘-‘ || val == ‘*‘ || val == ‘/‘; } //计算方法 public int cal(int num1, int num2, int oper){ int res = 0; switch (oper){ case ‘+‘: res = num1 + num2; break; case ‘-‘: res = num1 - num2; break; case ‘*‘: res = num1 * num2; break; case ‘/‘: res = num1 / num2; break; default: break; } return res; }}
实际上,上述实现计算器的方式就是中缀表达式规则!
练习:加入小括号。
前缀表达式又称波兰表达式,前缀表达式的运算符位于操作数之前。
举例说明: (3+4)×5-6 对应的前缀表达式就是 - × + 3 4 5 6

中缀表达式就是常见的运算表达式,如(3+4)×5-6。
中缀表达式的求值是人最熟悉的,但是对计算机来说却不好操作,因此,在计算结果时,往往会将中缀表达式转成其它表达式来操作(一般转成后缀表达式)。
后缀表达式又称逆波兰表达式,与前缀表达式相似,只是运算符位于操作数之后。
举例说明: (3+4)×5-6 对应的后缀表达式就是 3 4 + 5 × 6 –

其他例子:
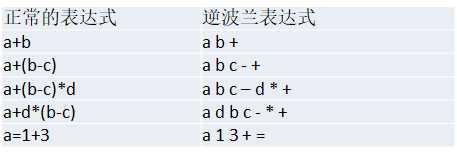

将中缀表达式 1+((2+3)×4)-5 转换为后缀表达式的过程如下:
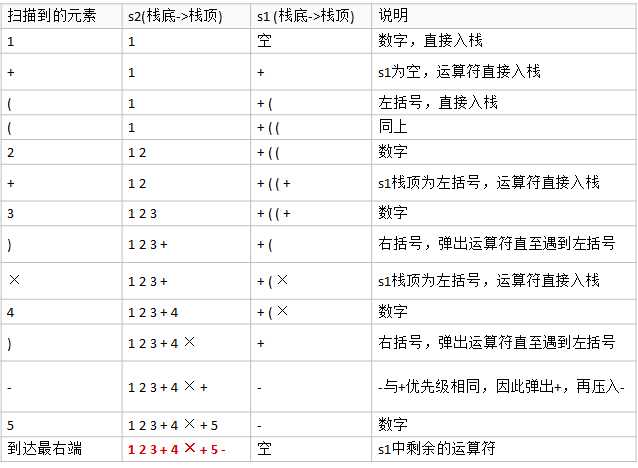
栈s2的输出是 - 5 + * 4 + 3 2 1,逆序结果 1 2 3 + 4 * + 5 - 为转换后的后缀表达式。
package com.atguigu.stack;import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Stack;public class Infix2Postfix {
public static void main(String[] args) { String expression = "1+((2+3)*4)-5"; System.out.println(expression); //将中缀表达式转成对应的List List<String> infixExpression = toInfixExpressionList(expression); System.out.println(infixExpression); //中缀转后缀(ArrayList类型) List<String> res = parseSuffixExpressionList(infixExpression); System.out.println("中缀转后缀:" + res); int r = PolandNotation.calculate(res); //int r = calculate(res); //需要引入包import static com.atguigu.stack.PolandNotation.calculate; System.out.println("最终的计算结果是: "+r); } //将中缀的List转为后缀的List public static List<String> parseSuffixExpressionList(List<String> ls){ //定义两个栈 Stack<String> s1 = new Stack<>(); //符号栈 //Stack<String> s2 = new Stack<>(); //中间结果栈 //由于s2栈没有出栈操作,且结果要逆序输出,此处采用ArrayList代替Stack结构 List<String> s2 = new ArrayList<>(); //中间结果 //遍历ls for(String item: ls){ if(item.matches("\\d+")){ //匹配多位数 s2.add(item); }else if(item.equals("(")){ s1.push(item); }else if(item.equals(")")){ while(!s1.peek().equals("(")){ s2.add(s1.pop()); } s1.pop(); //将左括号["("]弹出丢弃 }else{ // 运算符 //当item运算符的优先级小于s1栈顶,s1弹出压入s2,并将item与新的s1栈顶比较 while (s1.size()!=0 && Operation.getValue(s1.peek()) >= Operation.getValue(item)){ s2.add(s1.pop()); } s1.push(item); // s1为空、item优先级>=s1栈顶、s1栈顶为"("【满足优先级,左括号优先级默认返回0】 } } //遍历结束,将s1中剩余的元素压入s2 while(!s1.empty()){ s2.add(s1.pop()); } return s2; //由于使用的是ArrayList,因此不需要逆序输出。 } // 将中缀表达式转成对应的List public static List<String> toInfixExpressionList(String s){ List<String> ls = new ArrayList<>(); int index = 0; // 遍历字符串 String str; // 对多位数的拼接 char ch; // 存储当前遍历到的字符 // 非数字(运算符与括号)直接加入到ls,数字要考虑多位数字的情况(拼接) do{ ch = s.charAt(index); if(!Character.isDigit(ch)){ //[0-9]对应的ASCII是[48-57] ls.add(ch+""); index++; }else{ str = ""; while(index < s.length() && Character.isDigit(ch)){ str += ch; index++; if(index < s.length()){ //考虑字符串越界问题 ch = s.charAt(index); } } ls.add(str); } }while(index < s.length()); return ls; }}
// Operation 可以返回一个运算符的优先级
class Operation{private static int ADD = 1; private static int SUB = 1; private static int MUL = 2; private static int DIV = 2; //返回对应优先级数字 public static int getValue(String oper){ int res = 0; switch (oper){ case "+": res = ADD; break; case "-": res = SUB; break; case "*": res = MUL; break; case "/": res = DIV; break; default: System.out.println("不存在该运算符"); break; } return res; }}
输入一个逆波兰表达式(后缀表达式),使用栈(Stack),计算其结果。要求支持小括号和多位数整数。
package com.atguigu.stack;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Stack;
public class PolandNotation {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//逆波兰表达式
//(3+4)*5-6 => 3 4 + 5 * 6 - => 29
//String suffixExpression = "3 4 + 5 * 6 -";
// 4 * 5 - 8 + 60 + 8 /2 => 4 5 * 8 - 60 + 8 2 / + =>76
String suffixExpression = "4 5 * 8 - 60 + 8 2 / +";
List<String> rpnList = getListString(suffixExpression);
System.out.println("rpnList = "+rpnList);
System.out.println("计算的结果是: "+ calculate(rpnList));
}
//将逆波兰表达式中的数字与运算符存入ArrayList中
public static List<String> getListString(String suffixExpression){
String[] split = suffixExpression.split(" ");
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
for(String ele: split){
list.add(ele);
}
return list;
}
//完成对逆波兰表达式的运算
/*
*从左至右扫描表达式,遇到数字时,将数字压入堆栈,遇到运算符时,弹出栈顶的两个数,
*用运算符对它们做相应的计算(次顶元素 和 栈顶元素),并将结果入栈;
*重复上述过程直到表达式最右端,最后运算得出的值即为表达式的结果。
*/
public static int calculate(List<String> ls){
Stack<Integer> s = new Stack();
for(String item: ls){
if(item.matches("\\d+")){ //正则表达式,匹配多位数
s.push(Integer.parseInt(item));
}else{
int num2 = s.pop();
int num1 = s.pop();
int res = 0;
if(item.equals("+")){
res = num1 + num2;
}else if(item.equals("-")){ //注意顺序,后弹出的-先弹出的
res = num1 - num2;
}else if(item.equals("*")){
res = num1 * num2;
}else if(item.equals("/")){ //注意顺序,后弹出的/先弹出的
res = num1 / num2;
}else{
throw new RuntimeException("运算符有误!");
}
s.push(res);
}
}
return s.pop();
}
}
package com.atguigu.stack;
//完整计算器
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Stack;
import java.util.regex.Pattern;
public class ReversePolishMultiCalc {
/**
* 匹配 + - * / ( ) 运算符
*/
// 【或|】 【加号\+】【减号-】【乘号\*】【除号/】【左括号\\(】【右括号\\)】
static final String SYMBOL = "\\+|-|\\*|/|\\(|\\)";
static final String LEFT = "(";
static final String RIGHT = ")";
static final String ADD = "+";
static final String MINUS= "-";
static final String TIMES = "*";
static final String DIVISION = "/";
/**
* 加減 + -
*/
static final int LEVEL_01 = 1;
/**
* 乘除 * /
*/
static final int LEVEL_02 = 2;
/**
* 括号
*/
static final int LEVEL_HIGH = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
static Stack<String> stack = new Stack<>();
//ArrayList是非线程安全的,要实现List的线程安全,可以使用 Collections.synchronizedList。
static List<String> data = Collections.synchronizedList(new ArrayList<String>());
/**
* 去除所有空白符
* @param s
* @return
*/
public static String replaceAllBlank(String s ){
// \\s+ 匹配任何空白字符,包括空格、制表符、换页符等等, 等价于[ \f\n\r\t\v]
return s.replaceAll("\\s+","");
}
/**
* 判断是不是数字 int double long float
* @param s
* @return
*/
public static boolean isNumber(String s){
Pattern pattern = Pattern.compile("^[-\\+]?[.\\d]*$");
return pattern.matcher(s).matches();
}
/**
* 判断是不是运算符
* @param s
* @return
*/
public static boolean isSymbol(String s){
return s.matches(SYMBOL);
}
/**
* 匹配运算等级
* @param s
* @return
*/
public static int calcLevel(String s){
if("+".equals(s) || "-".equals(s)){
return LEVEL_01;
} else if("*".equals(s) || "/".equals(s)){
return LEVEL_02;
}
return LEVEL_HIGH;
}
/**
* 匹配
* @param s
* @throws Exception
*/
public static List<String> doMatch (String s) throws Exception{
//s.trim() 去掉两端的空格
if(s == null || "".equals(s.trim())) throw new RuntimeException("data is empty");
if(!isNumber(s.charAt(0)+"")) throw new RuntimeException("data illeagle,start not with a number");
s = replaceAllBlank(s);
String each;
int start = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++) {
if(isSymbol(s.charAt(i)+"")){
each = s.charAt(i)+"";
//栈为空,(操作符,或者 操作符优先级大于栈顶优先级 && 操作符优先级不是( )的优先级 及是 ) 不能直接入栈
if(stack.isEmpty() || LEFT.equals(each)
|| ((calcLevel(each) > calcLevel(stack.peek())) && calcLevel(each) < LEVEL_HIGH)){
stack.push(each);
}else if( !stack.isEmpty() && calcLevel(each) <= calcLevel(stack.peek())){
//栈非空,操作符优先级小于等于栈顶优先级时出栈入列,直到栈为空,或者遇到了(,最后操作符入栈
while (!stack.isEmpty() && calcLevel(each) <= calcLevel(stack.peek()) ){
if(calcLevel(stack.peek()) == LEVEL_HIGH){
break;
}
data.add(stack.pop());
}
stack.push(each);
}else if(RIGHT.equals(each)){
// ) 操作符,依次出栈入列直到空栈或者遇到了第一个)操作符,此时)出栈
while (!stack.isEmpty() && LEVEL_HIGH >= calcLevel(stack.peek())){
if(LEVEL_HIGH == calcLevel(stack.peek())){
stack.pop();
break;
}
data.add(stack.pop());
}
}
start = i ; //前一个运算符的位置
}else if( i == s.length()-1 || isSymbol(s.charAt(i+1)+"") ){
each = start == 0 ? s.substring(start,i+1) : s.substring(start+1,i+1);
if(isNumber(each)) {
data.add(each);
continue;
}
throw new RuntimeException("data not match number");
}
}
//如果栈里还有元素,此时元素需要依次出栈入列,可以想象栈里剩下栈顶为/,栈底为+,应该依次出栈入列,可以直接翻转整个stack 添加到队列
Collections.reverse(stack);
data.addAll(new ArrayList<>(stack));
System.out.println(data);
return data;
}
/**
* 算出结果
* @param list
* @return
*/
public static Double doCalc(List<String> list){
Double d = 0d;
if(list == null || list.isEmpty()){
return null;
}
if (list.size() == 1){
System.out.println(list);
d = Double.valueOf(list.get(0));
return d;
}
ArrayList<String> list1 = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) {
list1.add(list.get(i));
if(isSymbol(list.get(i))){
Double d1 = doTheMath(list.get(i - 2), list.get(i - 1), list.get(i));
list1.remove(i);
list1.remove(i-1);
list1.set(i-2,d1+"");
list1.addAll(list.subList(i+1,list.size()));
break;
}
}
doCalc(list1);
return d;
}
/**
* 运算
* @param s1
* @param s2
* @param symbol
* @return
*/
public static Double doTheMath(String s1,String s2,String symbol){
Double result ;
switch (symbol){
case ADD : result = Double.valueOf(s1) + Double.valueOf(s2); break;
case MINUS : result = Double.valueOf(s1) - Double.valueOf(s2); break;
case TIMES : result = Double.valueOf(s1) * Double.valueOf(s2); break;
case DIVISION : result = Double.valueOf(s1) / Double.valueOf(s2); break;
default : result = null;
}
return result;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
//String math = "9+(3-1)*3+10/2";
String math = "12.8 + (2 - 3.55)*4+10/5.0";
try {
doCalc(doMatch(math));
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
标签:array cat last 输入 运算表达式 参数 字符串 四则运算 存在
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/miaomiaowu/p/13188290.html