标签:group nbsp tor ++ edr inpu @param 递归树 onclick
给定一个无重复元素的数组 candidates 和一个目标数 target ,找出 candidates 中所有可以使数字和为 target 的组合。
candidates 中的数字可以无限制重复被选取。
说明:
target)都是正整数。示例 1:
输入: candidates =[2,3,6,7],target =7, 所求解集为: [ [7], [2,2,3] ]
示例 2:
输入: candidates = [2,3,5], target = 8,
所求解集为:
[
[2,2,2,2],
[2,3,3],
[3,5]
]
思路:根据示例 1:输入: candidates = [2,3,6,7],target = 7。
2 ,如果找到了 7 - 2 = 5 的所有组合,再在之前加上 2 ,就是 7 的所有组合;3,如果找到了 7 - 3 = 4 的所有组合,再在之前加上 3 ,就是 7 的所有组合,依次这样找下去;其实这里思路已经介绍完了,大家可以自己尝试在纸上画一下这棵树。然后编码实现,如果遇到问题,再看下面的文字。
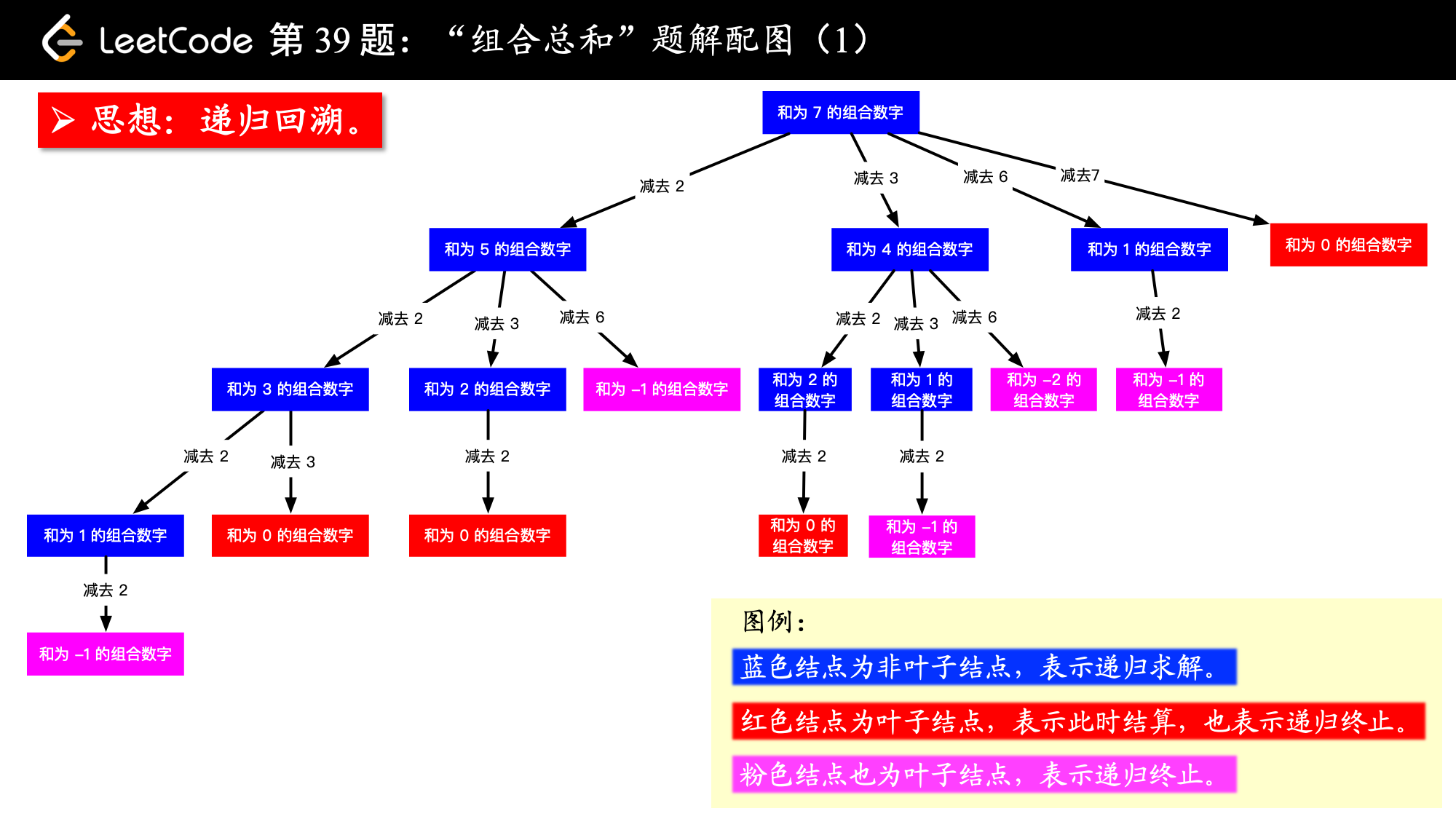
说明:
target = 7 为根结点,每一个分支做减法;0)的路径,就是题目要我们找的一个组合。把文字的部分去掉。
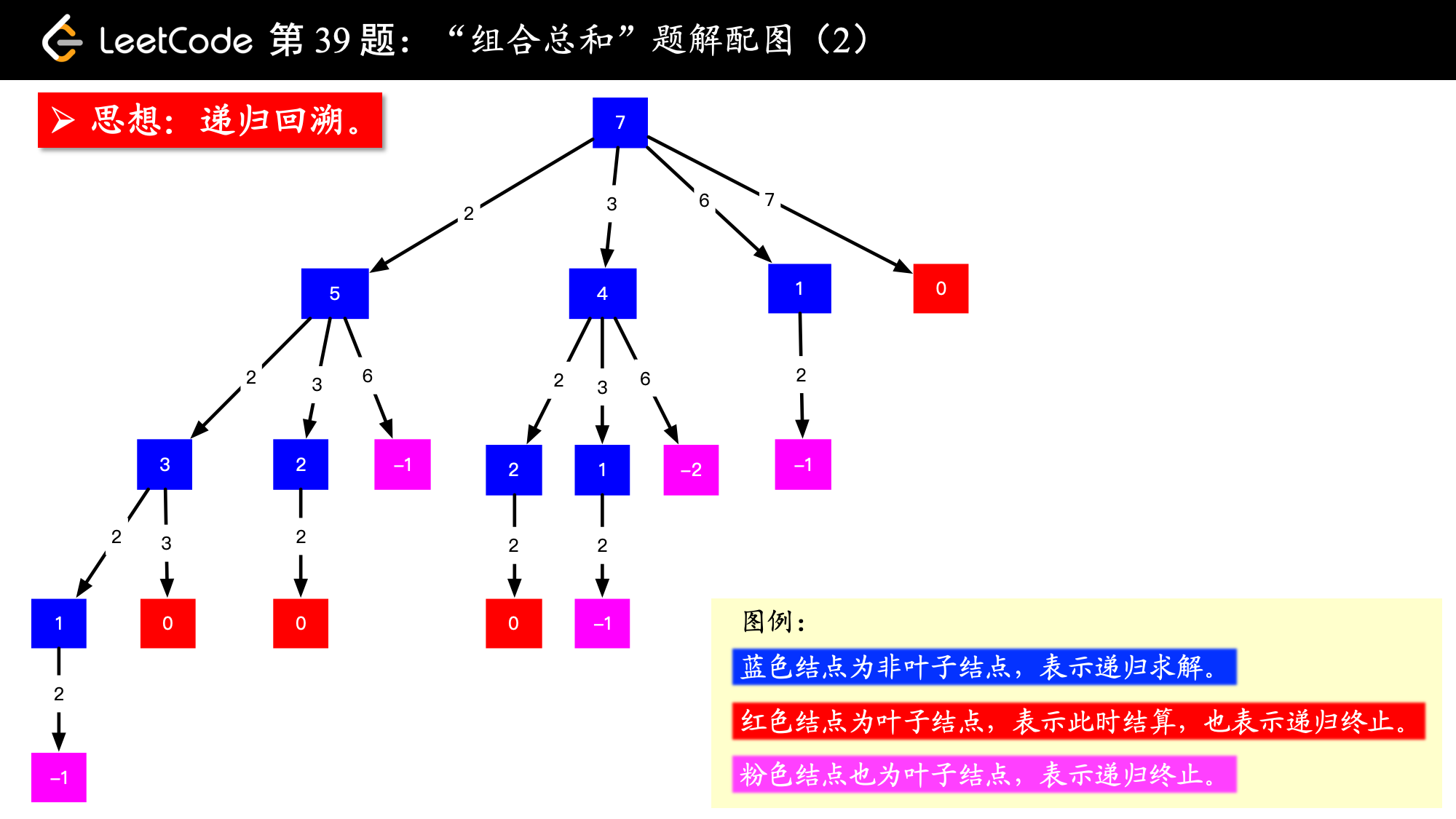
如果这样编码的话,会发现提交不能通过,这是因为递归树画的有问题,下面看一下是什么原因。
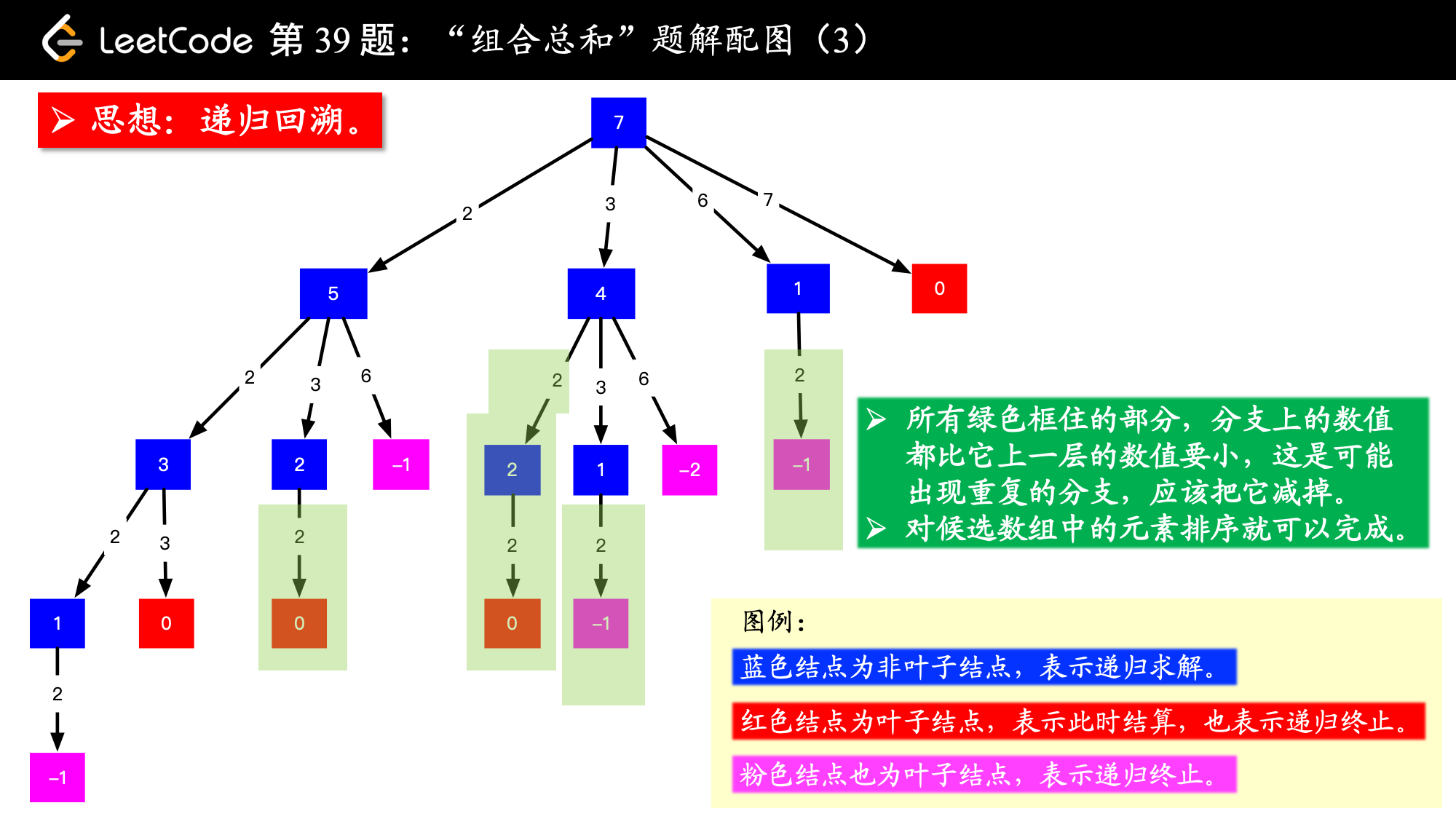
画出图以后,我看了一下,我这张图画出的结果有 个 ,对应的路径是 [[2, 2, 3], [2, 3, 2], [3, 2, 2], [7]],而示例中的解集只有 [[7], [2, 2, 3]],很显然,重复的原因是在较深层的结点值考虑了之前考虑过的元素,因此我们需要设置“下一轮搜索的起点”即可(这里可能没有说清楚,已经尽力了)。
begin ,由于一个数可以使用多次,下一层的结点从这个搜索起点开始搜索;begin 之前的数因为以前的分支搜索过了,所以一定会产生重复。如果一个数位搜索起点都不能搜索到结果,那么比它还大的数肯定搜索不到结果,基于这个想法,我们可以对输入数组进行排序,以减少搜索的分支;
排序是为了提高搜索速度,非必要;
搜索问题一般复杂度较高,能剪枝就尽量需要剪枝。把候选数组排个序,遇到一个较大的数,如果以这个数为起点都搜索不到结果,后面的数就更搜索不到结果了。
这里感谢 @rmokerone 提供的 C++ 代码实现。
import java.util.ArrayDeque;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Deque;
import java.util.List;
public class Solution {
<span class="hljs-keyword">public</span> List<List<Integer>> combinationSum(<span class="hljs-keyword">int</span>[] candidates, <span class="hljs-keyword">int</span> target) {
List<List<Integer>> res = <span class="hljs-keyword">new</span> ArrayList<>();
<span class="hljs-keyword">int</span> len = candidates.length;
<span class="hljs-comment">// 排序是为了提前终止搜索</span>
Arrays.sort(candidates);
dfs(candidates, len, target, <span class="hljs-number">0</span>, <span class="hljs-keyword">new</span> ArrayDeque<>(), res);
<span class="hljs-keyword">return</span> res;
}
<span class="hljs-comment">/**
* <span class="hljs-doctag">@param</span> candidates 数组输入
* <span class="hljs-doctag">@param</span> len 输入数组的长度,冗余变量
* <span class="hljs-doctag">@param</span> residue 剩余数值
* <span class="hljs-doctag">@param</span> begin 本轮搜索的起点下标
* <span class="hljs-doctag">@param</span> path 从根结点到任意结点的路径
* <span class="hljs-doctag">@param</span> res 结果集变量
*/</span>
<span class="hljs-function"><span class="hljs-keyword">private</span> <span class="hljs-keyword">void</span> <span class="hljs-title">dfs</span><span class="hljs-params">(<span class="hljs-keyword">int</span>[] candidates,
<span class="hljs-keyword">int</span> len,
<span class="hljs-keyword">int</span> residue,
<span class="hljs-keyword">int</span> begin,
Deque<Integer> path,
List<List<Integer>> res)</span> </span>{
<span class="hljs-keyword">if</span> (residue == <span class="hljs-number">0</span>) {
<span class="hljs-comment">// 由于 path 全局只使用一份,到叶子结点的时候需要做一个拷贝</span>
res.add(<span class="hljs-keyword">new</span> ArrayList<>(path));
<span class="hljs-keyword">return</span>;
}
<span class="hljs-keyword">for</span> (<span class="hljs-keyword">int</span> i = begin; i < len; i++) {
<span class="hljs-comment">// 在数组有序的前提下,剪枝</span>
<span class="hljs-keyword">if</span> (residue - candidates[i] < <span class="hljs-number">0</span>) {
<span class="hljs-keyword">break</span>;
}
path.addLast(candidates[i]);
dfs(candidates, len, residue - candidates[i], i, path, res);
path.removeLast();
}
}
}
from typing import List
class Solution:
def combinationSum(self, candidates: List[int], target: int) -> List[List[int]]:
size = len(candidates)
if size == 0:
return []
<span class="hljs-comment"># 剪枝是为了提速,在本题非必需</span>
candidates.sort()
<span class="hljs-comment"># 在遍历的过程中记录路径,它是一个栈</span>
path = []
res = []
<span class="hljs-comment"># 注意要传入 size ,在 range 中, size 取不到</span>
self.__dfs(candidates, <span class="hljs-number">0</span>, size, path, res, target)
<span class="hljs-keyword">return</span> res
<span class="hljs-function"><span class="hljs-keyword">def</span> <span class="hljs-title">__dfs</span><span class="hljs-params">(self, candidates, begin, size, path, res, target)</span>:</span>
<span class="hljs-comment"># 先写递归终止的情况</span>
<span class="hljs-keyword">if</span> target == <span class="hljs-number">0</span>:
<span class="hljs-comment"># Python 中可变对象是引用传递,因此需要将当前 path 里的值拷贝出来</span>
<span class="hljs-comment"># 或者使用 path.copy()</span>
res.append(path[:])
<span class="hljs-keyword">return</span>
<span class="hljs-keyword">for</span> index <span class="hljs-keyword">in</span> range(begin, size):
residue = target - candidates[index]
<span class="hljs-comment"># “剪枝”操作,不必递归到下一层,并且后面的分支也不必执行</span>
<span class="hljs-keyword">if</span> residue < <span class="hljs-number">0</span>:
<span class="hljs-keyword">break</span>
path.append(candidates[index])
<span class="hljs-comment"># 因为下一层不能比上一层还小,起始索引还从 index 开始</span>
self.__dfs(candidates, index, size, path, res, residue)
path.pop()
if name == ‘main‘:
candidates = [2, 3, 6, 7]
target = 7
solution = Solution()
result = solution.combinationSum(candidates, target)
print(result)
// author:rmokerone
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
class Solution {
private:
vector<int> candidates;
vector<vector<int>> res;
vector<int> path;
public:
void DFS(int start, int target) {
if (target == 0) {
res.push_back(path);
return;
}
for (int i = start;
i < candidates.size() && target - candidates[i] >= 0; i++) {
path.push_back(candidates[i]);
DFS(i, target - candidates[i]);
path.pop_back();
}
}
<span class="hljs-function"><span class="hljs-built_in">vector</span><<span class="hljs-built_in">vector</span><<span class="hljs-keyword">int</span>>> <span class="hljs-title">combinationSum</span><span class="hljs-params">(<span class="hljs-built_in">vector</span><<span class="hljs-keyword">int</span>> &candidates, <span class="hljs-keyword">int</span> target)</span> </span>{
<span class="hljs-built_in">std</span>::sort(candidates.begin(), candidates.end());
<span class="hljs-keyword">this</span>->candidates = candidates;
DFS(<span class="hljs-number">0</span>, target);
<span class="hljs-keyword">return</span> res;
}
};
附注:这道题我用的是减法,有兴趣的朋友还可以使用加法,加到 target 的时候结算,超过 target 的时候剪枝。
做完这题的朋友,不妨做一下 LeetCode 第 40 题:组合问题 II。
https://www.jianshu.com/p/e721418f89ee
标签:group nbsp tor ++ edr inpu @param 递归树 onclick
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/leetcodetijie/p/13200394.html