标签:str 工程 move 集合 Stub put except 客户 计算机科学
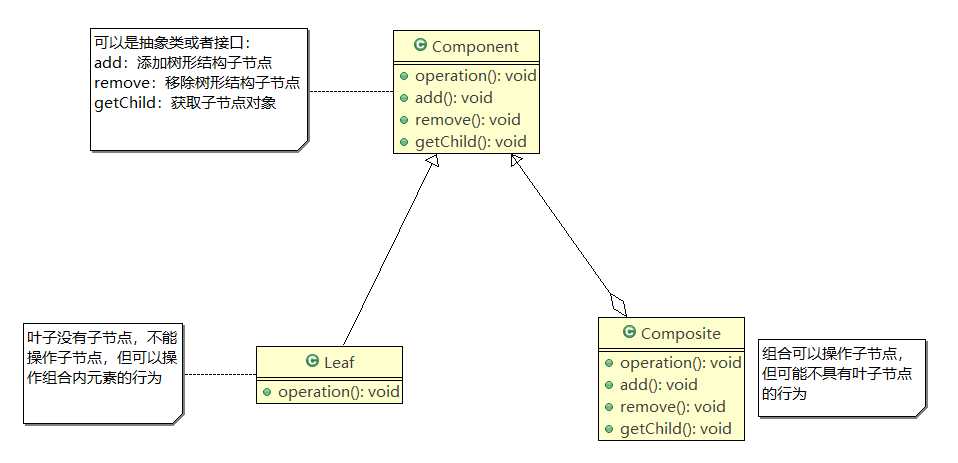
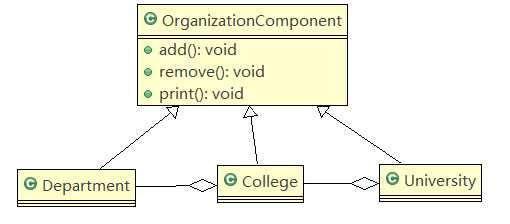
抽象类的设计
public abstract class OrganizationComponent {
private String name;
private String des;
//默认实现,因为叶子节点不需要实现
protected void add(OrganizationComponent organizationComponent) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
protected void remove(OrganizationComponent organizationComponent) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getDes() {
return des;
}
public void setDes(String des) {
this.des = des;
}
public OrganizationComponent(String name, String des) {
super();
this.name = name;
this.des = des;
}
//子类实现
public abstract void print()
}
Univresity类
public class University extends OrganizationComponent{
//管理子节点
List<OrganizationComponent> organizations = new ArrayList<>();
public University(String name, String des) {
super(name, des);
}
@Override
public void print() {
System.out.println("============"+getName()+"==============");
for(OrganizationComponent organizationComponent : organizations) {
organizationComponent.print();
}
}
@Override
protected void add(OrganizationComponent organizationComponent) {
organizations.add(organizationComponent);
}
@Override
protected void remove(OrganizationComponent organizationComponent) {
organizations.remove(organizationComponent);
}
}
其余非叶子节点
public class College extends OrganizationComponent{
List<OrganizationComponent> organizations = new ArrayList<>();
public College(String name, String des) {
super(name, des);
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
}
@Override
public void print() {
System.out.println("============"+getName()+"==============");
for(OrganizationComponent organizationComponent : organizations) {
organizationComponent.print();
}
}
@Override
protected void add(OrganizationComponent organizationComponent) {
//按需求扩展
organizations.add(organizationComponent);
}
@Override
protected void remove(OrganizationComponent organizationComponent) {
organizations.remove(organizationComponent);
}
}
叶子节点
public class Department extends OrganizationComponent{
public Department(String name, String des) {
super(name, des);
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
}
@Override
public void print() {
System.out.println(getName());
}
}
构建树型结构以及调用
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) {
University university = new University("清华大学","国内最好的大学之一");
College college1 = new College("计算机学院", "计算机学院");
College college2 = new College("信息工程学院", "信息工程学院");
college1.add(new Department("软件工程", "软件工程"));
college1.add(new Department("网络工程", "网络工程"));
college1.add(new Department("计算机科学与技术", "计算机科学与技术"));
college2.add(new Department("通信工程", "通信工程"));
university.add(college1);
university.add(college2);
university.print();
}
}
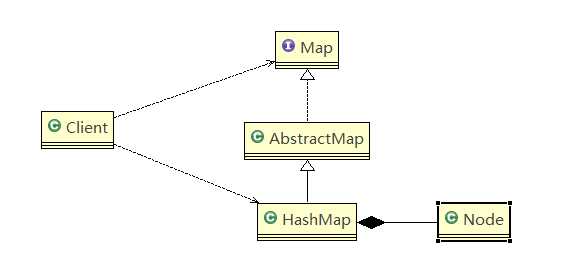
先看到Map接口,可以看到定义的众多方法中有两个我们常用的方法,put(),putAll(),他将被实现
public interface Map<K,V> {
………………
V put(K key, V value);
void putAll(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> m);
………………
}
接着来到AbstractMap,它实现了Map接口,由于Map的实现类会有很多,所以jdk中使用这个抽象类来作为缓冲类,将一些方法默认实现,使得该接口更具有扩展性,如下它默认实现了put()和putAll()
public abstract class AbstractMap<K,V> implements Map<K,V> {
……………………
//默认实现
public V put(K key, V value) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
public void putAll(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> m) {
for (Map.Entry<? extends K, ? extends V> e : m.entrySet())
put(e.getKey(), e.getValue());
}
……………………
}
然后我们来到最常用HashMap类中,可以看到它对接口和抽象类都进行了实现,发现了还有一个Node对象
public class HashMap<K,V> extends AbstractMap<K,V>
implements Map<K,V>, Cloneable, Serializable {
……………………
//来到put方法,看到这里进行了具体的实现
public V put(K key, V value) {
return putVal(hash(key), key, value, false, true);
}
//这里省略具体的操作,我们只关心设计模式,putAll也与put方法类似,就不讲述了,之后会再写一些关于java集合类的具体实现
final V putVal(int hash, K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent,
boolean evict) {
//这里用到了一个Node对象,我们进入到Node对象中观察
Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> p; int n, i;
………………………………
}
}
来到HashMap的内部类Node对象中,我们发现,他其实就是我们组合模式中所讲述的Leaf对象,它没有再组合任何的子节点,提供的也只有get方法和set方法
static class Node<K,V> implements Map.Entry<K,V> {
final int hash;
final K key;
V value;
Node<K,V> next;
Node(int hash, K key, V value, Node<K,V> next) {
this.hash = hash;
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
this.next = next;
}
public final K getKey() { return key; }
public final V getValue() { return value; }
public final String toString() { return key + "=" + value; }
public final int hashCode() {
return Objects.hashCode(key) ^ Objects.hashCode(value);
}
public final V setValue(V newValue) {
V oldValue = value;
value = newValue;
return oldValue;
}
public final boolean equals(Object o) {
if (o == this)
return true;
if (o instanceof Map.Entry) {
Map.Entry<?,?> e = (Map.Entry<?,?>)o;
if (Objects.equals(key, e.getKey()) &&
Objects.equals(value, e.getValue()))
return true;
}
return false;
}
}
如上,我们可以清晰地看出来,Map中的HashMap是应用了组合模式来实现的
标签:str 工程 move 集合 Stub put except 客户 计算机科学
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/JIATCODE/p/13202681.html