标签:博客 += def 模板题 sub operation freopen 记录 cli
树链剖分是我开始有点手熟的数据结构,未免遗忘,总结。
其他数据结构会一一补上,而且会多次修订,欢迎指教。
完成博客编辑。
树链剖分干的事其实很简单:把树进行以某个依据进行的拆分,放到数组上,这样就可以进行区间操作降低复杂度了。可以将链上操作、子树操作降为\(\mathrm{O(log_2n)}\)级别。
树链剖分可分为轻重链剖分、长链剖分等,本文主要记录轻重链剖分相关内容。
对于一棵树 :
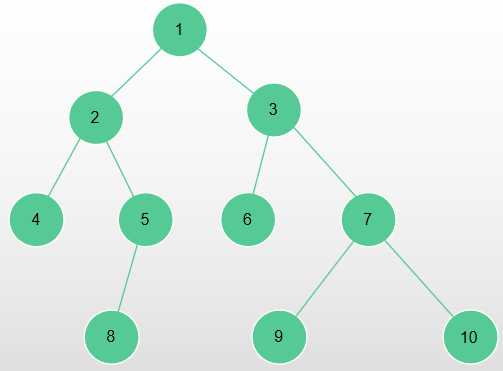
进行剖分之后长这样:
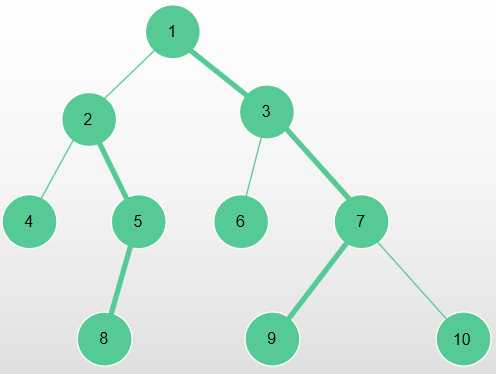
放在数组上形如:
| 1 3 7 9 | 10 | 6 | 2 5 8 | 4
当然还有其他更加广泛的用途。
本文记录基本操作。
我们需要预处理一些数组,具体如下:
int top[N]; \\ 每一个点对应的链的顶端
int f[N]; \\ 每个点的父节点
int si[N], d[N]; \\ 子树大小、节点深度
int hs[N]; \\ 每个点的最重儿子(子树最大)
int tr[N], pr[N]; \\ 树上点对应数组中点、 数组中点对应树上点
其实也不多,每个都有效果。
树链剖分的预处理需要两次DFS。
第一次处理子树深度、子树大小、父节点、重儿子, 这些都可以一次求出来。
第二次处理链的顶端、数组与树的映射。
具体操作如下:
void dfs(int u, int fa) {
si[u] = 1;
S_H(T, i, u) {
int v = T.to[i];
if (v == fa) continue;
f[v] = u, d[v] = d[u] + 1, dfs(v, u);
// 父节点、深度处理
si[u] += si[v];
// 子树大小累加
hs[u] = si[hs[u]] < si[v] ? v : hs[u];
// 重儿子为子树大小最大的儿子;
}
} // 第一次
void dfs_chain(int u, int k) {
top[pr[tr[u] = ++vs] = u] = k;
// 建立映射, 处理链的顶端
if (!hs[u]) return void();
dfs_chain(hs[u], k);
// 当前链会传递给重儿子
S_H(T, i, u) {
int v = T.to[i];
if (v == f[u] || v == hs[u]) continue;
dfs_chain(v, v);
// 轻儿子就要另起门户,自成链顶
}
} // 第二次
树剖求 LCA 其实到这步就好了,已经可以求 LCA 了。
原理是:每次深度大的点跳到上一条链,直到两点在同一条链上,深度小的点就是 LCA,可以发现复杂度为 \(\mathrm{O(log_2n)}\)。
\(\mathrm{Code:}\)
inline int Lca(int x, int y) {
while(top[x] ^ top[y])
(d[top[x]] < d[top[y]] ? swap(x, y) : 0), x = f[top[x]];
d[x] < d[y] ? swap(x, y) : 0;
return y;
}
我们现在成功把树放在一条链上,接下来就要用数据结构维护了,一般选用线段树。
线段树写在结构体 \(\texttt{Segmentree}\) 里,有一个变量 Se。
因为我们可以一次对一条重链上的所有点操作并做到 \(\mathrm{log_2n}\), 我们可以每次操作之后往上跳一条重链。
直到两点处于同一条重链,直接操作就好了。
比如对于这个例子:
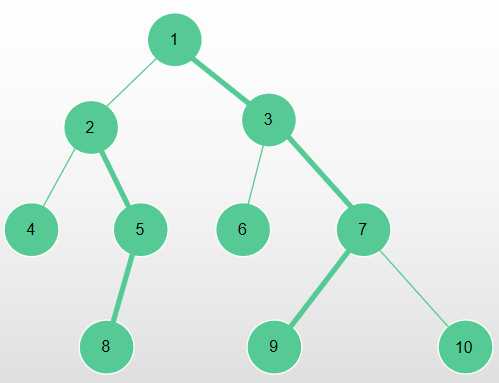
如果我们要对 4 到 10 路径上的所有点进行 +1 的操作,则跳的过程如下:
数组区间为:
| 1 3 7 9 | 10 | 6 | 2 5 8 | 4
1. x, y = 4, 10; 对[5, 5] + 1; 10向上跳到7;
2. x, y = 4, 7 ; 对[10, 10] + 1; 4向上跳到2;
3. x, y = 2, 7 ; 对[7, 7] + 1; 2向上跳到1;
4. x, y = 1, 7 ; 对[1, 3] + 1; 操作结束;
注意:if (d[top[x]] < d[top[y]]) swap(x, y);这句保证了操作顺序的正确性,使某个点不会被重复加两次。
\(\mathrm{Code:}\)
inline void Add_chain(int x, int y, int z) {
while (top[x] ^ top[y]) {
d[top[x]] < d[top[y]] ? swap(x, y) : 0;
Se.Change(1, tr[top[x]], tr[x], 1, n, z), x = f[top[x]];
}
(d[x] < d[y] ? swap(x, y) : 0), Se.Change(1, tr[y], tr[x], 1, n, z);
return void();
}
查询操作差不多,就是把线段树操作从修改变成了查询。
\(\mathrm{Code:}\)
inline ll Ask_chain(int x, int y) {
ll sum = 0;
while(top[x] ^ top[y]) {
if (d[top[x]] < d[top[y]]) swap(x, y);
Add(sum, Se.Ask(1, tr[top[x]], tr[x], 1, n)), x = f[top[x]];
}
if (d[x] < d[y]) swap(x, y);
return add(sum, Se.Ask(1, tr[y], tr[x], 1, n));
}
我们发现一个性质:子树上的点在数组上是一段连续的区间。
| 1 3 7 9 | 10 | 6 | 2 5 8 | 4
你看:3 的子树在 [2, 6],5 的子树在 [8, 9]。
如此,便可以直接操作了。操作基本类似于
inline int Ask(int x) { return Se.Ask(1, tr[x], tr[x] + si[x] - 1, 1, n); }
修改查询都类似。
但是我们有时候需要考虑换根, 但是我们也不可能真的去换根,因为再做一遍预处理的时间复杂度有点吃不消。
所以这时候需要用到小 Trick。
我们有三个固定点:查询点 x, 当前根 root, 原始根 1。
考虑几种情况:
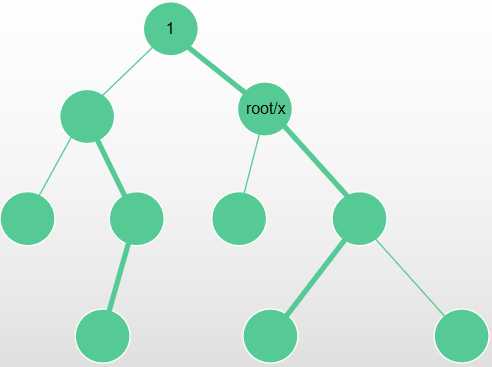
\(Lca(x, root) != x\), 此时 root ?不在 x 的以 1 为根的子树内,所以 x 的子树不变,按照上边的\(\mathrm{Common\ Operation}\)操作即可。
形如:
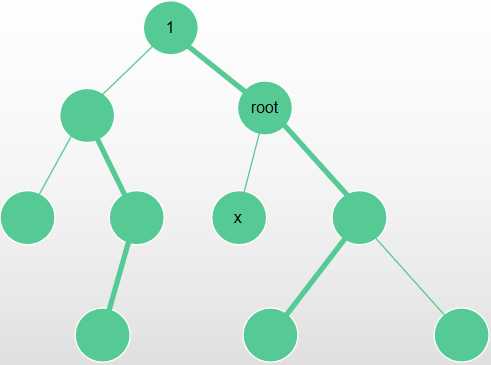
\(Lca(x, root) == x\),此时\(x\)的子树为原本不在他子树内的所有点。我们先总体修改一遍,再减去不包括它的重儿子所在的子树。
形如:
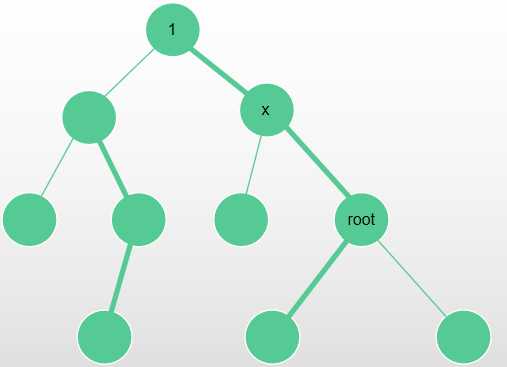
此时 x 的子树为 所有点 -x 到 root 路径上里 x 最近一点的子树大小。修改 & 查询时可以先对整棵树操作, 再在那个点(离 x 最近的点)的子树内逆向操作。
\(\mathrm{Code:}\)
inline int Getsub(int x, int y) {
while (top[x] ^ top[y]) {
d[top[x]] < d[top[y]] ? swap(x, y) : 0;
if (f[top[x]] == y) return top[x];
x = f[top[x]];
}
d[x] < d[y] ? swap(x, y) : 0;
return hs[y];
} // 寻找x到root路径上到x最近的点
inline void Add_subtree(int x, int v) {
if (x == root) return Se.Change(1, 1, n, 1, n, v);
int lca = Lca(x, root);
if (lca != x) return Se.Change(1, tr[x], tr[x] + si[x] - 1, 1, n, v);
int fs = Getsub(x, root);
Se.Change(1, 1, n, 1, n, v), Se.Change(1, tr[fs], tr[fs] + si[fs] - 1, 1, n, -v);
return void();
} // 分类讨论换根,下同
inline ll Ask_subtree(int x) {
if (x == root) return Se.Ask(1, 1, n, 1, n);
int lca = Lca(x, root);
if (lca != x) return Se.Ask(1, tr[x], tr[x] + si[x] - 1, 1, n);
int fs = Getsub(x, root);
return Se.Ask(1, 1, n, 1, n) - Se.Ask(1, tr[fs], tr[fs] + si[fs] - 1, 1, n);
}
树链剖分的部分操作(链上操作)可以被倍增代替,所以说实话如果只有链上操作,写树剖有点难调。
但是子树操作 + 链上操作是树剖比较有优势的。同时,树链剖分可以维护动态\(dp\)等算法,具体可见 UOJ、\(\mathrm{luogu}\)。
其实只要你肯写,很多树上操作题都可以用树剖实现。
模板题完整代码, \(\mathrm{Code:}\)
#include <climits>
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#define rint register int
typedef long long ll;
#define FOR(i, a, b) for (rint i = (a); i <= (b); ++i)
#define S_H(T, i, u) for (rint i = T.fl[u]; i; i = T.net[i])
#define swap(x, y) (x ^= y ^= x ^= y)
const int N = 1e5 + 10;
int n, m, root;
int a[N];
inline ll add(ll a, ll b) {return a + b;}
inline void Add(ll &a, ll b) {return a = add(a, b), void();}
inline ll del(ll a, ll b) {return a - b;}
inline void Del(ll &a, ll b) {return a = del(a, b), void();}
struct Tree {
int net[N << 1], to[N << 1];
int fl[N], len;
inline void inc(int x, int y) {
to[++len] = y;
net[len] = fl[x];
fl[x] = len;
}
} T;
int si[N], hs[N], f[N], d[N];
int top[N], tr[N], vs = 0, pr[N];
struct Segmentree {
class Point {public: ll sum, la;} t[N << 2];
inline void Push(int p) {
return t[p].sum = add(t[p << 1].sum, t[p << 1 | 1].sum), void();
}
void Build(int p, int l, int r) {
t[p].sum = t[p].la = 0;
if (l == r) {
t[p].sum = 1LL * pr[l];
return void();
}
int mid = (l + r) >> 1;
Build(p << 1, l, mid), Build(p << 1 | 1, mid + 1, r), Push(p);
}
inline void Update(int p, int ls, int rs) {
if (!t[p].la) return void();
Add(t[p << 1].la, t[p].la), Add(t[p << 1 | 1].la, t[p].la);
Add(t[p << 1].sum, t[p].la * ls), Add(t[p << 1 | 1].sum, t[p].la * rs);
t[p].la = 0;
return void();
}
inline void Change(int p, int l, int r, int x, int y, int v) {
if (l <= x && y <= r) {
Add(t[p].sum, 1LL * (y - x + 1) * v), Add(t[p].la, 1LL * v);
return void();
}
if (r < x || l > y) return void();
int mid = (x + y) >> 1;
Update(p, mid - x + 1, y - mid);
Change(p << 1, l, r, x, mid, v), Change(p << 1 | 1, l, r, mid + 1, y, v), Push(p);
}
inline ll Ask(int p, int l, int r, int x, int y) {
if (l <= x && y <= r) return t[p].sum;
if (r < x || l > y) return 0;
int mid = (x + y) >> 1;
Update(p, mid - x + 1, y - mid);
return add(Ask(p << 1, l, r, x, mid), Ask(p << 1 | 1, l, r, mid + 1, y));
}
} Se; //以上结构体线段树
inline int read() {
int s = 0, w = 1;
char c = getchar();
while ((c < ‘0‘ || c > ‘9‘) && c != ‘-‘) c = getchar();
if (c == ‘-‘) w = -1, c = getchar();
while(c <= ‘9‘ && c >= ‘0‘) s = (s << 1) + (s << 3) + c - ‘0‘, c = getchar();
return s * w;
}
template <class T>
inline void write(T x) {
if (x < 0) x = ~x + 1, putchar(‘-‘);
if (x > 9) write(x / 10);
putchar(x % 10 + 48);
return void();
}
// Definition
void dfs(int u, int fa) {
si[u] = 1;
S_H(T, i, u) {
int v = T.to[i];
if (v == fa) continue;
f[v] = u, d[v] = d[u] + 1;
dfs(v, u);
si[u] += si[v];
hs[u] = si[hs[u]] < si[v] ? v : hs[u];
}
}
void dfs_chain(int u, int k) {
top[pr[tr[u] = ++vs] = u] = k, pr[vs] = a[u];
if (!hs[u]) return void();
dfs_chain(hs[u], k);
S_H(T, i, u) {
int v = T.to[i];
if (v == f[u] || v == hs[u]) continue;
dfs_chain(v, v);
}
}
// Preparation
inline int Lca(int x, int y) {
while(top[x] ^ top[y])
(d[top[x]] < d[top[y]] ? swap(x, y) : 0), x = f[top[x]];
d[x] < d[y] ? swap(x, y) : 0;
return y;
}
inline int Getsub(int x, int y) {
while (top[x] ^ top[y]) {
d[top[x]] < d[top[y]] ? swap(x, y) : 0;
if (f[top[x]] == y) return top[x];
x = f[top[x]];
}
d[x] < d[y] ? swap(x, y) : 0;
return hs[y];
}
inline void Add_chain(int x, int y, int z) {
while (top[x] ^ top[y]) {
d[top[x]] < d[top[y]] ? swap(x, y) : 0;
Se.Change(1, tr[top[x]], tr[x], 1, n, z), x = f[top[x]];
}
(d[x] < d[y] ? swap(x, y) : 0), Se.Change(1, tr[y], tr[x], 1, n, z);
return void();
}
inline void Add_subtree(int x, int v) {
if (x == root) return Se.Change(1, 1, n, 1, n, v);
int lca = Lca(x, root);
if (lca != x) return Se.Change(1, tr[x], tr[x] + si[x] - 1, 1, n, v);
int fs = Getsub(x, root);
Se.Change(1, 1, n, 1, n, v), Se.Change(1, tr[fs], tr[fs] + si[fs] - 1, 1, n, -v);
return void();
}
inline ll Ask_chain(int x, int y) {
ll sum = 0;
while(top[x] ^ top[y]) {
if (d[top[x]] < d[top[y]]) swap(x, y);
Add(sum, Se.Ask(1, tr[top[x]], tr[x], 1, n)), x = f[top[x]];
}
if (d[x] < d[y]) swap(x, y);
return add(sum, Se.Ask(1, tr[y], tr[x], 1, n));
}
inline ll Ask_subtree(int x) {
if (x == root) return Se.Ask(1, 1, n, 1, n);
int lca = Lca(x, root);
if (lca != x) return Se.Ask(1, tr[x], tr[x] + si[x] - 1, 1, n);
int fs = Getsub(x, root);
return Se.Ask(1, 1, n, 1, n) - Se.Ask(1, tr[fs], tr[fs] + si[fs] - 1, 1, n);
}
// Operation
signed main(void) {
freopen("tree.in", "r", stdin);
freopen("tree.out", "w", stdout);
n = read(), root = 1;
FOR(i, 1, n) a[i] = read();
FOR(i, 1, n - 1) {
int x = read();
T.inc(i + 1, x), T.inc(x, i + 1);
}
dfs(root, 0), dfs_chain(root, root), Se.Build(1, 1, n);
m = read();
FOR(i, 1, m) {
int opt = read(), x = read();
if (opt == 1) root = x;
if (opt == 2) {
int y = read(), z = read();
Add_chain(x, y, z);
}
if (opt == 3) {
int z = read();
Add_subtree(x, z);
}
if (opt == 4) {
int y = read();
write(Ask_chain(x, y)), putchar(10);
}
if (opt == 5) write(Ask_subtree(x)), putchar(10);
// Working
}
return 0;
}
未完待续,还有一些内容需要补充。
标签:博客 += def 模板题 sub operation freopen 记录 cli
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/zqytcl/p/13204760.html