标签:effect ide this rev off app -- values 协议

2.源码解析
1.相关命令如下:
{"hset",hsetCommand,4,"wmF",0,NULL,1,1,1,0,0},
{"hsetnx",hsetnxCommand,4,"wmF",0,NULL,1,1,1,0,0},
{"hget",hgetCommand,3,"rF",0,NULL,1,1,1,0,0},
{"hmset",hmsetCommand,-4,"wm",0,NULL,1,1,1,0,0},
{"hmget",hmgetCommand,-3,"r",0,NULL,1,1,1,0,0},
{"hincrby",hincrbyCommand,4,"wmF",0,NULL,1,1,1,0,0},
{"hincrbyfloat",hincrbyfloatCommand,4,"wmF",0,NULL,1,1,1,0,0},
{"hdel",hdelCommand,-3,"wF",0,NULL,1,1,1,0,0},
{"hlen",hlenCommand,2,"rF",0,NULL,1,1,1,0,0},
{"hstrlen",hstrlenCommand,3,"rF",0,NULL,1,1,1,0,0},
{"hkeys",hkeysCommand,2,"rS",0,NULL,1,1,1,0,0},
{"hvals",hvalsCommand,2,"rS",0,NULL,1,1,1,0,0},
{"hgetall",hgetallCommand,2,"r",0,NULL,1,1,1,0,0},
{"hexists",hexistsCommand,3,"rF",0,NULL,1,1,1,0,0},
{"hscan",hscanCommand,-3,"rR",0,NULL,1,1,1,0,0},
2.ziplist数据结构
/* We use this function to receive information about a ziplist entry. * Note that this is not how the data is actually encoded, is just what we * get filled by a function in order to operate more easily. */ typedef struct zlentry { unsigned int prevrawlensize; /* Bytes used to encode the previous entry len*/ unsigned int prevrawlen; /* Previous entry len. */ unsigned int lensize; /* Bytes used to encode this entry type/len. For example strings have a 1, 2 or 5 bytes header. Integers always use a single byte.*/ unsigned int len; /* Bytes used to represent the actual entry. For strings this is just the string length while for integers it is 1, 2, 3, 4, 8 or 0 (for 4 bit immediate) depending on the number range. */ unsigned int headersize; /* prevrawlensize + lensize. */ unsigned char encoding; /* Set to ZIP_STR_* or ZIP_INT_* depending on the entry encoding. However for 4 bits immediate integers this can assume a range of values and must be range-checked. */ unsigned char *p; /* Pointer to the very start of the entry, that is, this points to prev-entry-len field. */ } zlentry;
3.hashtable数据结构
typedef struct dictEntry { void *key; union { void *val; uint64_t u64; int64_t s64; double d; } v; struct dictEntry *next; } dictEntry; typedef struct dictType { uint64_t (*hashFunction)(const void *key); void *(*keyDup)(void *privdata, const void *key); void *(*valDup)(void *privdata, const void *obj); int (*keyCompare)(void *privdata, const void *key1, const void *key2); void (*keyDestructor)(void *privdata, void *key); void (*valDestructor)(void *privdata, void *obj); } dictType; /* This is our hash table structure. Every dictionary has two of this as we * implement incremental rehashing, for the old to the new table. */ typedef struct dictht { dictEntry **table; unsigned long size; unsigned long sizemask; unsigned long used; } dictht; typedef struct dict { dictType *type; void *privdata; dictht ht[2]; long rehashidx; /* rehashing not in progress if rehashidx == -1 */ unsigned long iterators; /* number of iterators currently running */ } dict;
hset
// t_hash.c, set key field value void hsetCommand(client *c) { int update; robj *o; // 1. 查找hash的key是否存在,不存在则新建一个,然后在其上进行数据操作 if ((o = hashTypeLookupWriteOrCreate(c,c->argv[1])) == NULL) return; // 2. 检查2-3个参数是否需要将简单版(ziplist)hash表转换为复杂的hash表,转换后的表通过 o->ptr 体现 hashTypeTryConversion(o,c->argv,2,3); // 3. 添加kv到 o 的hash表中 update = hashTypeSet(o,c->argv[2]->ptr,c->argv[3]->ptr,HASH_SET_COPY); addReply(c, update ? shared.czero : shared.cone); // 变更命令传播 signalModifiedKey(c->db,c->argv[1]); notifyKeyspaceEvent(NOTIFY_HASH,"hset",c->argv[1],c->db->id); server.dirty++; } // 1. 获取db外部的key, 即整体hash数据实例 // t_hash.c robj *hashTypeLookupWriteOrCreate(client *c, robj *key) { robj *o = lookupKeyWrite(c->db,key); if (o == NULL) { // 此处创建的hashObject是以 ziplist 形式的 o = createHashObject(); dbAdd(c->db,key,o); } else { // 不是hash类型的键已存在,不可覆盖,返回错误 if (o->type != OBJ_HASH) { addReply(c,shared.wrongtypeerr); return NULL; } } return o; } // object.c, 创建hashObject, 以 ziplist 形式创建 robj *createHashObject(void) { unsigned char *zl = ziplistNew(); robj *o = createObject(OBJ_HASH, zl); o->encoding = OBJ_ENCODING_ZIPLIST; return o; } // ziplist.c static unsigned char *createList() { unsigned char *zl = ziplistNew(); zl = ziplistPush(zl, (unsigned char*)"foo", 3, ZIPLIST_TAIL); zl = ziplistPush(zl, (unsigned char*)"quux", 4, ZIPLIST_TAIL); zl = ziplistPush(zl, (unsigned char*)"hello", 5, ZIPLIST_HEAD); zl = ziplistPush(zl, (unsigned char*)"1024", 4, ZIPLIST_TAIL); return zl; } // 2. 检查参数,是否需要将 ziplist 形式的hash表转换为真正的hash表 /* Check the length of a number of objects to see if we need to convert a * ziplist to a real hash. Note that we only check string encoded objects * as their string length can be queried in constant time. */ void hashTypeTryConversion(robj *o, robj **argv, int start, int end) { int i; if (o->encoding != OBJ_ENCODING_ZIPLIST) return; for (i = start; i <= end; i++) { // 参数大于设置的 hash_max_ziplist_value (默认: 64)时,会直接将 ziplist 转换为 ht // OBJ_ENCODING_RAW, OBJ_ENCODING_EMBSTR // 循环检查参数,只要发生了一次转换就结束检查(没必要继续了) if (sdsEncodedObject(argv[i]) && sdslen(argv[i]->ptr) > server.hash_max_ziplist_value) { // 这个转换过程很有意思,我们深入看看 hashTypeConvert(o, OBJ_ENCODING_HT); break; } } } // t_hash.c, 转换编码方式 (如上, ziplist -> ht) void hashTypeConvert(robj *o, int enc) { if (o->encoding == OBJ_ENCODING_ZIPLIST) { // 此处我们只处理这种情况 hashTypeConvertZiplist(o, enc); } else if (o->encoding == OBJ_ENCODING_HT) { serverPanic("Not implemented"); } else { serverPanic("Unknown hash encoding"); } } // t_hash.c, 转换编码 ziplist 为目标 enc (实际只能是 OBJ_ENCODING_HT) void hashTypeConvertZiplist(robj *o, int enc) { serverAssert(o->encoding == OBJ_ENCODING_ZIPLIST); if (enc == OBJ_ENCODING_ZIPLIST) { /* Nothing to do... */ } else if (enc == OBJ_ENCODING_HT) { hashTypeIterator *hi; dict *dict; int ret; // 迭代器创建 hi = hashTypeInitIterator(o); // 一个hash的数据结构就是一个 dict, 从这个级别来说, hash 与 db 是一个级别的 dict = dictCreate(&hashDictType, NULL); // 依次迭代 o, 赋值到 hi->fptr, hi->vptr // 依次添加到 dict 中 while (hashTypeNext(hi) != C_ERR) { sds key, value; // 从 hi->fptr 中获取key // 从 hi->vptr 中获取value key = hashTypeCurrentObjectNewSds(hi,OBJ_HASH_KEY); value = hashTypeCurrentObjectNewSds(hi,OBJ_HASH_VALUE); // 添加到 dict 中 ret = dictAdd(dict, key, value); if (ret != DICT_OK) { serverLogHexDump(LL_WARNING,"ziplist with dup elements dump", o->ptr,ziplistBlobLen(o->ptr)); serverPanic("Ziplist corruption detected"); } } // 释放迭代器 hashTypeReleaseIterator(hi); zfree(o->ptr); // 将变更反映到o对象上返回 o->encoding = OBJ_ENCODING_HT; o->ptr = dict; } else { serverPanic("Unknown hash encoding"); } } // 2.1. 迭代ziplist元素 // t_hash.c, 迭代器 /* Move to the next entry in the hash. Return C_OK when the next entry * could be found and C_ERR when the iterator reaches the end. */ int hashTypeNext(hashTypeIterator *hi) { if (hi->encoding == OBJ_ENCODING_ZIPLIST) { unsigned char *zl; unsigned char *fptr, *vptr; // 每次都是基于原始字符器进行计算偏移 // 迭代的是 fptr,vptr zl = hi->subject->ptr; fptr = hi->fptr; vptr = hi->vptr; // 第一次查找时使用index查找,后续则使用 fptr,vptr 进行迭代 if (fptr == NULL) { /* Initialize cursor */ serverAssert(vptr == NULL); fptr = ziplistIndex(zl, 0); } else { /* Advance cursor */ serverAssert(vptr != NULL); fptr = ziplistNext(zl, vptr); } if (fptr == NULL) return C_ERR; /* Grab pointer to the value (fptr points to the field) */ vptr = ziplistNext(zl, fptr); serverAssert(vptr != NULL); /* fptr, vptr now point to the first or next pair */ hi->fptr = fptr; hi->vptr = vptr; } else if (hi->encoding == OBJ_ENCODING_HT) { if ((hi->de = dictNext(hi->di)) == NULL) return C_ERR; } else { serverPanic("Unknown hash encoding"); } return C_OK; } // ziplist.c, 查找 index 的元素 /* Returns an offset to use for iterating with ziplistNext. When the given * index is negative, the list is traversed back to front. When the list * doesn‘t contain an element at the provided index, NULL is returned. */ unsigned char *ziplistIndex(unsigned char *zl, int index) { unsigned char *p; unsigned int prevlensize, prevlen = 0; if (index < 0) { // 小于0时,反向查找 index = (-index)-1; p = ZIPLIST_ENTRY_TAIL(zl); if (p[0] != ZIP_END) { ZIP_DECODE_PREVLEN(p, prevlensize, prevlen); while (prevlen > 0 && index--) { p -= prevlen; ZIP_DECODE_PREVLEN(p, prevlensize, prevlen); } } } else { p = ZIPLIST_ENTRY_HEAD(zl); while (p[0] != ZIP_END && index--) { p += zipRawEntryLength(p); } } // 迭代完成还没找到元素 p[0]=ZIP_END // index 超出整体ziplist大小则遍历完成后 index>0 return (p[0] == ZIP_END || index > 0) ? NULL : p; } // ziplist.c, 由 fptr,vptr 进行迭代元素 /* Return pointer to next entry in ziplist. * * zl is the pointer to the ziplist * p is the pointer to the current element * * The element after ‘p‘ is returned, otherwise NULL if we are at the end. */ unsigned char *ziplistNext(unsigned char *zl, unsigned char *p) { ((void) zl); /* "p" could be equal to ZIP_END, caused by ziplistDelete, * and we should return NULL. Otherwise, we should return NULL * when the *next* element is ZIP_END (there is no next entry). */ if (p[0] == ZIP_END) { return NULL; } // 当前指针偏移当前元素长度(根据ziplist协议),即到下一元素指针位置 p += zipRawEntryLength(p); if (p[0] == ZIP_END) { return NULL; } return p; } /* Return the total number of bytes used by the entry pointed to by ‘p‘. */ static unsigned int zipRawEntryLength(unsigned char *p) { unsigned int prevlensize, encoding, lensize, len; ZIP_DECODE_PREVLENSIZE(p, prevlensize); ZIP_DECODE_LENGTH(p + prevlensize, encoding, lensize, len); return prevlensize + lensize + len; } // 2.2. t_hash.c, 获取 hashTypeIterator 的具体值,写入 vstr, vlen 中 /* Return the key or value at the current iterator position as a new * SDS string. */ sds hashTypeCurrentObjectNewSds(hashTypeIterator *hi, int what) { unsigned char *vstr; unsigned int vlen; long long vll; hashTypeCurrentObject(hi,what,&vstr,&vlen,&vll); if (vstr) return sdsnewlen(vstr,vlen); return sdsfromlonglong(vll); } /* Higher level function of hashTypeCurrent*() that returns the hash value * at current iterator position. * * The returned element is returned by reference in either *vstr and *vlen if * it‘s returned in string form, or stored in *vll if it‘s returned as * a number. * * If *vll is populated *vstr is set to NULL, so the caller * can always check the function return by checking the return value * type checking if vstr == NULL. */ void hashTypeCurrentObject(hashTypeIterator *hi, int what, unsigned char **vstr, unsigned int *vlen, long long *vll) { if (hi->encoding == OBJ_ENCODING_ZIPLIST) { *vstr = NULL; hashTypeCurrentFromZiplist(hi, what, vstr, vlen, vll); } else if (hi->encoding == OBJ_ENCODING_HT) { sds ele = hashTypeCurrentFromHashTable(hi, what); *vstr = (unsigned char*) ele; *vlen = sdslen(ele); } else { serverPanic("Unknown hash encoding"); } } // t_hash.c, 从ziplist中获取某个 hashTypeIterator 的具体值,结果定稿 vstr, vlen /* Get the field or value at iterator cursor, for an iterator on a hash value * encoded as a ziplist. Prototype is similar to `hashTypeGetFromZiplist`. */ void hashTypeCurrentFromZiplist(hashTypeIterator *hi, int what, unsigned char **vstr, unsigned int *vlen, long long *vll) { int ret; serverAssert(hi->encoding == OBJ_ENCODING_ZIPLIST); // OBJ_HASH_KEY 从 fptr 中获取, 否则从 vptr 中获取 if (what & OBJ_HASH_KEY) { ret = ziplistGet(hi->fptr, vstr, vlen, vll); serverAssert(ret); } else { ret = ziplistGet(hi->vptr, vstr, vlen, vll); serverAssert(ret); } } // ziplist.c, /* Get entry pointed to by ‘p‘ and store in either ‘*sstr‘ or ‘sval‘ depending * on the encoding of the entry. ‘*sstr‘ is always set to NULL to be able * to find out whether the string pointer or the integer value was set. * Return 0 if ‘p‘ points to the end of the ziplist, 1 otherwise. */ unsigned int ziplistGet(unsigned char *p, unsigned char **sstr, unsigned int *slen, long long *sval) { zlentry entry; if (p == NULL || p[0] == ZIP_END) return 0; if (sstr) *sstr = NULL; // 按照ziplist的编码协议, 获取头部信息 zipEntry(p, &entry); if (ZIP_IS_STR(entry.encoding)) { if (sstr) { *slen = entry.len; *sstr = p+entry.headersize; } } else { if (sval) { *sval = zipLoadInteger(p+entry.headersize,entry.encoding); } } return 1; } // ziplist.c, 解析原始字符串为 zlentry /* Return a struct with all information about an entry. */ static void zipEntry(unsigned char *p, zlentry *e) { // 按照ziplist的编码协议,依次读取 prevrawlensize, prevrawlen ZIP_DECODE_PREVLEN(p, e->prevrawlensize, e->prevrawlen); // 指向下一位置偏移,按照ziplist的编码协议,依次读取 encoding, lensize, len ZIP_DECODE_LENGTH(p + e->prevrawlensize, e->encoding, e->lensize, e->len); // 除去header得到 body偏移 e->headersize = e->prevrawlensize + e->lensize; e->p = p; }
header
// ziplist.c /* Decode the length of the previous element, from the perspective of the entry * pointed to by ‘ptr‘. */ #define ZIP_DECODE_PREVLEN(ptr, prevlensize, prevlen) do { // 解析第1个字符为 prevlensize ZIP_DECODE_PREVLENSIZE(ptr, prevlensize); if ((prevlensize) == 1) { (prevlen) = (ptr)[0]; } else if ((prevlensize) == 5) { assert(sizeof((prevlensize)) == 4); // 当ptr[0]>254时,代表内容有点大,需要使用 5个字符保存上一字符长度 memcpy(&(prevlen), ((char*)(ptr)) + 1, 4); memrev32ifbe(&prevlen); } } while(0); /* Decode the number of bytes required to store the length of the previous * element, from the perspective of the entry pointed to by ‘ptr‘. */ #define ZIP_DECODE_PREVLENSIZE(ptr, prevlensize) do { if ((ptr)[0] < ZIP_BIGLEN) { (prevlensize) = 1; } else { (prevlensize) = 5; } } while(0); /* Decode the length encoded in ‘ptr‘. The ‘encoding‘ variable will hold the * entries encoding, the ‘lensize‘ variable will hold the number of bytes * required to encode the entries length, and the ‘len‘ variable will hold the * entries length. */ #define ZIP_DECODE_LENGTH(ptr, encoding, lensize, len) do { // 解析第1个字符为 编码格式 &ZIP_STR_MASK=0xc0 ZIP_ENTRY_ENCODING((ptr), (encoding)); if ((encoding) < ZIP_STR_MASK) { // 0 << 6 =0 // 具体解析如下代码, if ((encoding) == ZIP_STR_06B) { (lensize) = 1; (len) = (ptr)[0] & 0x3f; } // 1 << 6 =64 else if ((encoding) == ZIP_STR_14B) { (lensize) = 2; (len) = (((ptr)[0] & 0x3f) << 8) | (ptr)[1]; } // 2 << 6 =128 else if (encoding == ZIP_STR_32B) { (lensize) = 5; (len) = ((ptr)[1] << 24) | ((ptr)[2] << 16) | ((ptr)[3] << 8) | ((ptr)[4]); } else { assert(NULL); } } else { // 超过 0xc0 的长度了,直接使用 1,2,3,4 表示len (lensize) = 1; (len) = zipIntSize(encoding); } } while(0); /* Extract the encoding from the byte pointed by ‘ptr‘ and set it into * ‘encoding‘. */ #define ZIP_ENTRY_ENCODING(ptr, encoding) do { \ (encoding) = (ptr[0]); if ((encoding) < ZIP_STR_MASK) (encoding) &= ZIP_STR_MASK; } while(0) /* Different encoding/length possibilities */ #define ZIP_STR_MASK 0xc0 #define ZIP_INT_MASK 0x30 #define ZIP_STR_06B (0 << 6) // 0x00 #define ZIP_STR_14B (1 << 6) // 0x40 #define ZIP_STR_32B (2 << 6) // 0x80 #define ZIP_INT_16B (0xc0 | 0<<4) // 0xc0 #define ZIP_INT_32B (0xc0 | 1<<4) // 0xd0 #define ZIP_INT_64B (0xc0 | 2<<4) // 0xe0 #define ZIP_INT_24B (0xc0 | 3<<4) // 0xf0 #define ZIP_INT_8B 0xfe // 0xfe
添加kv到对应的key实例中:
// 3. 添加kv到 hash表中, 稍微复杂 // t_hash.c, 做变更到hash表中 int hashTypeSet(robj *o, sds field, sds value, int flags) { int update = 0; // 针对ziplist 的添加, 与 ht 编码的添加, 自然是分别处理 if (o->encoding == OBJ_ENCODING_ZIPLIST) { unsigned char *zl, *fptr, *vptr; zl = o->ptr; // 找到ziplist 的头节点指针 fptr = ziplistIndex(zl, ZIPLIST_HEAD); if (fptr != NULL) { // 尝试查找该 field 对应的元素(从1开始),如果找到则先删除原值,然后统一添加 fptr = ziplistFind(fptr, (unsigned char*)field, sdslen(field), 1); if (fptr != NULL) { /* Grab pointer to the value (fptr points to the field) */ // value 不可以为null, 否则 ziplist 将无法工作 vptr = ziplistNext(zl, fptr); serverAssert(vptr != NULL); update = 1; /* Delete value */ // 先删除旧的 value, 再以插入的形式更新, 后续讲删除时再详解 zl = ziplistDelete(zl, &vptr); /* Insert new value */ // 重点,将value添加到 ziplist 中 zl = ziplistInsert(zl, vptr, (unsigned char*)value, sdslen(value)); } } // 没有找到对应元素,则直接将元素添加到尾部即可 if (!update) { /* Push new field/value pair onto the tail of the ziplist */ zl = ziplistPush(zl, (unsigned char*)field, sdslen(field), ZIPLIST_TAIL); zl = ziplistPush(zl, (unsigned char*)value, sdslen(value), ZIPLIST_TAIL); } o->ptr = zl; /* Check if the ziplist needs to be converted to a hash table */ // 大于设置的阀值后,转换ziplist为ht(默认: 512) if (hashTypeLength(o) > server.hash_max_ziplist_entries) hashTypeConvert(o, OBJ_ENCODING_HT); } else if (o->encoding == OBJ_ENCODING_HT) { dictEntry *de = dictFind(o->ptr,field); if (de) { sdsfree(dictGetVal(de)); if (flags & HASH_SET_TAKE_VALUE) { dictGetVal(de) = value; value = NULL; } else { dictGetVal(de) = sdsdup(value); } update = 1; } else { sds f,v; if (flags & HASH_SET_TAKE_FIELD) { f = field; field = NULL; } else { f = sdsdup(field); } if (flags & HASH_SET_TAKE_VALUE) { v = value; value = NULL; } else { v = sdsdup(value); } dictAdd(o->ptr,f,v); } } else { serverPanic("Unknown hash encoding"); } /* Free SDS strings we did not referenced elsewhere if the flags * want this function to be responsible. */ if (flags & HASH_SET_TAKE_FIELD && field) sdsfree(field); if (flags & HASH_SET_TAKE_VALUE && value) sdsfree(value); return update; } // 3.1. 使用ziplist进行保存 field -> value // ziplist.c, 查找某个 field 是否存在于ziplist中 /* Find pointer to the entry equal to the specified entry. Skip ‘skip‘ entries * between every comparison. Returns NULL when the field could not be found. */ unsigned char *ziplistFind(unsigned char *p, unsigned char *vstr, unsigned int vlen, unsigned int skip) { int skipcnt = 0; unsigned char vencoding = 0; long long vll = 0; while (p[0] != ZIP_END) { unsigned int prevlensize, encoding, lensize, len; unsigned char *q; // 解析整个字符串p的 prevlensize,encoding,lensize,len ZIP_DECODE_PREVLENSIZE(p, prevlensize); ZIP_DECODE_LENGTH(p + prevlensize, encoding, lensize, len); q = p + prevlensize + lensize; // 传入1, 代表要跳过一个元素, 比如: 查找key时,跳过1个v,然后继续迭代 // 跳过了n个元素后,再从此开始key的比对过程 if (skipcnt == 0) { /* Compare current entry with specified entry */ // 针对不同的编码使用不同的比较方式 if (ZIP_IS_STR(encoding)) { // 找到相应的元素,直接返回 p 指针 if (len == vlen && memcmp(q, vstr, vlen) == 0) { return p; } } else { /* Find out if the searched field can be encoded. Note that * we do it only the first time, once done vencoding is set * to non-zero and vll is set to the integer value. */ if (vencoding == 0) { if (!zipTryEncoding(vstr, vlen, &vll, &vencoding)) { /* If the entry can‘t be encoded we set it to * UCHAR_MAX so that we don‘t retry again the next * time. */ vencoding = UCHAR_MAX; } /* Must be non-zero by now */ assert(vencoding); } /* Compare current entry with specified entry, do it only * if vencoding != UCHAR_MAX because if there is no encoding * possible for the field it can‘t be a valid integer. */ if (vencoding != UCHAR_MAX) { long long ll = zipLoadInteger(q, encoding); if (ll == vll) { return p; } } } /* Reset skip count */ // 查找一次,跳过skip次 skipcnt = skip; } else { /* Skip entry */ skipcnt--; } /* Move to next entry */ p = q + len; } return NULL; } // ziplist.c, 添加value到ziplist中 // zl:ziplist实例, p:要插入的key字串, s:要插入的value字串, len:要插入的value的长度 /* Insert an entry at "p". */ unsigned char *ziplistInsert(unsigned char *zl, unsigned char *p, unsigned char *s, unsigned int slen) { return __ziplistInsert(zl,p,s,slen); } /* Insert item at "p". */ static unsigned char *__ziplistInsert(unsigned char *zl, unsigned char *p, unsigned char *s, unsigned int slen) { size_t curlen = intrev32ifbe(ZIPLIST_BYTES(zl)), reqlen; unsigned int prevlensize, prevlen = 0; size_t offset; int nextdiff = 0; unsigned char encoding = 0; long long value = 123456789; /* initialized to avoid warning. Using a value that is easy to see if for some reason we use it uninitialized. */ zlentry tail; /* Find out prevlen for the entry that is inserted. */ if (p[0] != ZIP_END) { ZIP_DECODE_PREVLEN(p, prevlensize, prevlen); } else { unsigned char *ptail = ZIPLIST_ENTRY_TAIL(zl); if (ptail[0] != ZIP_END) { prevlen = zipRawEntryLength(ptail); } } /* See if the entry can be encoded */ if (zipTryEncoding(s,slen,&value,&encoding)) { /* ‘encoding‘ is set to the appropriate integer encoding */ reqlen = zipIntSize(encoding); } else { /* ‘encoding‘ is untouched, however zipEncodeLength will use the * string length to figure out how to encode it. */ reqlen = slen; } /* We need space for both the length of the previous entry and * the length of the payload. */ // 加上prevlen,encoding,slen 的长度,以计算value的存放位置 reqlen += zipPrevEncodeLength(NULL,prevlen); reqlen += zipEncodeLength(NULL,encoding,slen); /* When the insert position is not equal to the tail, we need to * make sure that the next entry can hold this entry‘s length in * its prevlen field. */ nextdiff = (p[0] != ZIP_END) ? zipPrevLenByteDiff(p,reqlen) : 0; /* Store offset because a realloc may change the address of zl. */ // 存储当前偏移位置,以便在扩容之后,还能找到相应位置 // p = p -zl + zl offset = p-zl; zl = ziplistResize(zl,curlen+reqlen+nextdiff); p = zl+offset; /* Apply memory move when necessary and update tail offset. */ if (p[0] != ZIP_END) { /* Subtract one because of the ZIP_END bytes */ // 字符拷贝 memmove(p+reqlen,p-nextdiff,curlen-offset-1+nextdiff); /* Encode this entry‘s raw length in the next entry. */ zipPrevEncodeLength(p+reqlen,reqlen); /* Update offset for tail */ ZIPLIST_TAIL_OFFSET(zl) = intrev32ifbe(intrev32ifbe(ZIPLIST_TAIL_OFFSET(zl))+reqlen); /* When the tail contains more than one entry, we need to take * "nextdiff" in account as well. Otherwise, a change in the * size of prevlen doesn‘t have an effect on the *tail* offset. */ zipEntry(p+reqlen, &tail); if (p[reqlen+tail.headersize+tail.len] != ZIP_END) { ZIPLIST_TAIL_OFFSET(zl) = intrev32ifbe(intrev32ifbe(ZIPLIST_TAIL_OFFSET(zl))+nextdiff); } } else { /* This element will be the new tail. */ ZIPLIST_TAIL_OFFSET(zl) = intrev32ifbe(p-zl); } /* When nextdiff != 0, the raw length of the next entry has changed, so * we need to cascade the update throughout the ziplist */ if (nextdiff != 0) { // 如果本次更新后数据位置变化,则需要更新后续的元素位置 offset = p-zl; zl = __ziplistCascadeUpdate(zl,p+reqlen); p = zl+offset; } /* Write the entry */ // 将 value 写入 p 中, 即写入了 ziplist 中 p += zipPrevEncodeLength(p,prevlen); p += zipEncodeLength(p,encoding,slen); if (ZIP_IS_STR(encoding)) { memcpy(p,s,slen); } else { zipSaveInteger(p,value,encoding); } ZIPLIST_INCR_LENGTH(zl,1); return zl; } // 另外,如果没有旧的元素值时,直接在hash表的末尾添加对应的field->value 即可 // ziplist.c, 在尾部进行添加元素,没有许多的情况要考虑,但是代码完全复用 __ziplistInsert() unsigned char *ziplistPush(unsigned char *zl, unsigned char *s, unsigned int slen, int where) { unsigned char *p; p = (where == ZIPLIST_HEAD) ? ZIPLIST_ENTRY_HEAD(zl) : ZIPLIST_ENTRY_END(zl); return __ziplistInsert(zl,p,s,slen); }
深入理解ziplist
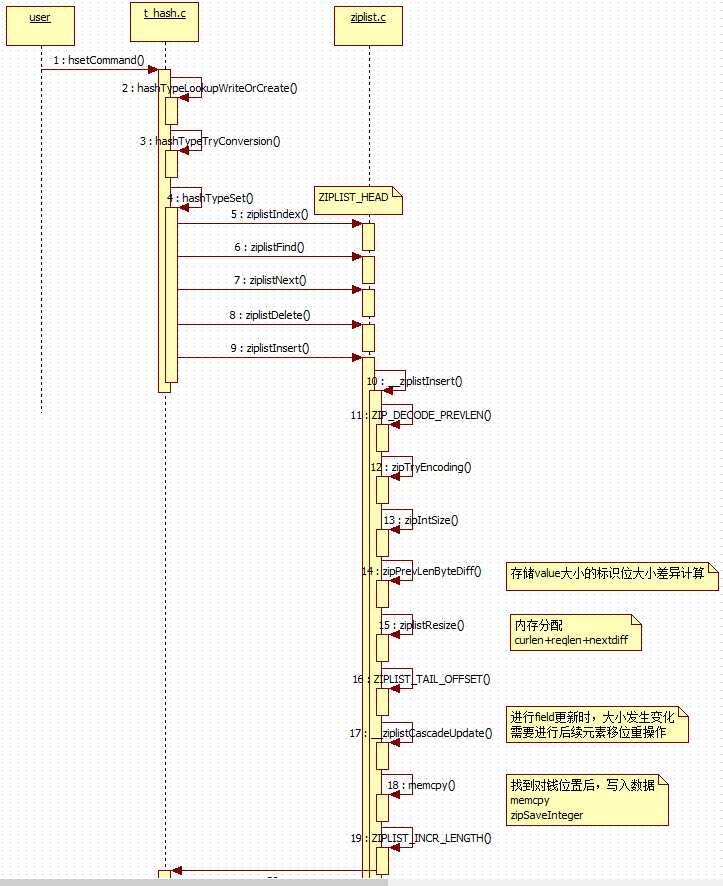
看起来没ziplist好像没那么简单呢,为啥还要搞这么复杂呢?其实以上代码,仅是在人看来复杂,对机器来说就是更多的移位计算操作,多消耗点cpu就换来了空间上的节省,是可以的。软件本身的复杂性带来了效益,是软件的价值体现,所以,并非所有的东西都是简单即美。
接下来,我们来看一下使用 HT 的编码又如何存储field->value呢?
// 3.2. OBJ_ENCODING_HT 的 field -> value 的添加 if (o->encoding == OBJ_ENCODING_HT) { // hash 表中查找对应的 field dictEntry *de = dictFind(o->ptr,field); if (de) { sdsfree(dictGetVal(de)); // hset 时使用 HASH_SET_COPY, 所以直接使用 sdsdup() 即可 if (flags & HASH_SET_TAKE_VALUE) { dictGetVal(de) = value; value = NULL; } else { dictGetVal(de) = sdsdup(value); } update = 1; } else { // 新增 field -> value sds f,v; if (flags & HASH_SET_TAKE_FIELD) { f = field; field = NULL; } else { f = sdsdup(field); } if (flags & HASH_SET_TAKE_VALUE) { v = value; value = NULL; } else { v = sdsdup(value); } // 添加到 hash 表中,前些篇章讲解过,大概就是计算hash,放入v的过程 dictAdd(o->ptr,f,v); } }
如此看来,OBJ_ENCODING_HT 的实现反而简单了哦。
总结下 hash的插入过程,hash 初始创建时都是使用ziplist 进行容纳元素的,在特定情况下会触发 ziplist 为 ht 的编码方式, 比如:
1. hset时自身的参数大于设置值(默认: 64)时直接转换 ziplist -> ht;
2. hash表的元素数量大于设置值(默认: 512)时转换 ziplist -> ht;
这么设计的原因是,元素较少且占用空间较小时,使用ziplist会节省空间,且时间消耗与hash表相关并不大,所以 ziplist 是优先的选择了。但是大量数据还是必须要使用hash表存储的。
Redis系列(九):数据结构Hash源码解析和HSET、HGET命令
标签:effect ide this rev off app -- values 协议
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/vic-tory/p/13216325.html