标签:ram inpu lazy src ase finally using source ext
In this example, the primary and secondary synchronization signals are created and mapped to a resource grid.
Set up the cell-wide settings. Create a structure and specify the cell-wide settings as its fields.
enb.NDLRB = 9; enb.CyclicPrefix = ‘Normal‘; enb.CellRefP = 1; enb.NCellID = 1; enb.NSubframe = 0; enb.DuplexMode = ‘FDD‘;
Generate the PSS symbols n with the cell-wide settings specified.
pss = ltePSS(enb);
Next, generate the PSS indices. These indices map the PSS complex symbols to the subframe resource grid. Using the specified cell-wide settings and antenna number. In this case, since only one antenna port is used, specify antenna as 0.
antenna = 0; pssIndices = ltePSSIndices(enb, antenna);
Generate the SSS symbols with the cell-wide settings specified.
sss = lteSSS(enb);
Next, generate the SSS indices. These indices map the SSS complex symbols to the subframe resource grid. Providing the cell-wide settings enb and the antenna port number antenna.
antenna = 0; sssIndices = lteSSSIndices(enb, antenna);
Generate the subframe resource grid . An empty resource grid for one subframe is created.
subframe = lteDLResourceGrid(enb);
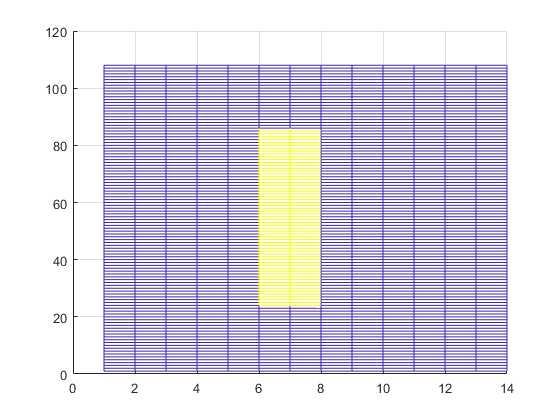
Finally, map the PSS and SSS symbols directly to the resource grid using the generated indices. Show the synchronization symbols mapped in RE grid.
subframe(pssIndices) = pss; subframe(sssIndices) = sss;
Reference,
1. TS 36.211
2. MathWorks
LTE - Create Synchronization Signals
标签:ram inpu lazy src ase finally using source ext
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/zzyzz/p/13246595.html