标签:list except 否则 bre boolean catch queue ica cat
队列:是限只允许在一端进行插入操作,而在另一端进行删除操作的线性表。
先进先出原则,简称FIFO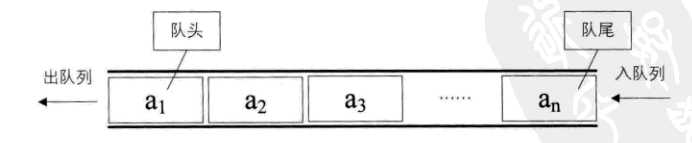
队列也有类似线性表的各种操作,不同的是

实际场景:银行叫号排队
package com.queue;
/**
* 普通队列只是一次性储存
* 不能复用前面的空间
* front指向第一个元素的【前面】!
* rear指向最后一个元素
* 判断空,两指针相等
* 判断满,尾指针指向最大下标
*/
public class ArrayQueue {
private int maxSize;
private int front;
private int rear;
private int[] arr;
// 创建队列的构造器
public ArrayQueue(int maxSize) {
this.maxSize = maxSize;
// 创建指定长度的数组模拟队列
arr = new int[maxSize];
// 指向队列头部,不包含那个数,比如指向0,实际:下标1才是队列头
this.front = -1;
// 指向队列尾部,包含!比如指向10,实际:下标10就是队尾
this.rear = -1;
}
/**
* 判断队列是否满
* 无参
* @return
*/
public boolean isFull() {
return rear == maxSize - 1;
}
/**
* 判断队列是否空
* 无参
* @return
*/
public boolean isEmpty() {
return rear == front;
}
/**
* 入队
*
* @param n 添加的数据
*/
public void addQueue(int n) {
// 首先判断是否满
if (isFull()) {
System.out.println("队列已满,无法加入");
return;
}
// 尾指针后移
rear++;
arr[rear] = n;
}
/**
* 出队
* @return
*/
public int getQueue() {
// 先判断是否为空
if (isEmpty()) {
throw new RuntimeException("队列为空,不能取数据");
}
// 头指针后移
front++;
return arr[front];
}
/**
* 打印队列中的有效数据
*
*/
public void show() {
// 遍历
if (isEmpty()) {
System.out.println("队列为空");
return;
}
for (int i = front + 1; i <= rear; i++) {
System.out.print(arr[i] + "\t");
}
}
/**
* 不是出队入队
* @return 返回队首元素
*/
public int headQueue() {
// 先判断是否为空
if (isEmpty()) {
throw new RuntimeException("队列为空,不能取数据");
}
return arr[front + 1];
}
/**
* 不是出队入队
* @return 返回队尾元素
*/
public int tailQueue() {
// 先判断是否为空
if (isEmpty()) {
throw new RuntimeException("队列为空,不能取数据");
}
return arr[rear];
}
}
package com.queue;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建一个队列,最大储存4个元素
ArrayQueue queue = new ArrayQueue(4);
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int op = -1;
do {
System.out.println("请选择测试功能");
System.out.println("1.显示队列");
System.out.println("2.入队操作");
System.out.println("3.出队操作");
System.out.println("4.查看头元素");
System.out.println("5.查看尾元素");
System.out.println("0.退出");
op = sc.nextInt();
switch (op) {
case 1:
System.out.print("队列中的数据:");
queue.show();
break;
case 2:
System.out.print("请输入入队元素:");
int n = sc.nextInt();
queue.addQueue(n);
System.out.print("队列中的数据:");
queue.show();
break;
case 3:
try {
queue.getQueue();
System.out.print("队列中的数据:");
queue.show();
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
}
break;
case 4:
try {
System.out.println("队头元素"+queue.headQueue());
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
}
break;
case 5:
try {
System.out.println("队尾元素"+queue.tailQueue());
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
}
break;
default:
break;
}
System.out.println();
System.out.println();
} while (op != 0);
System.out.println("测试结束");
}
}
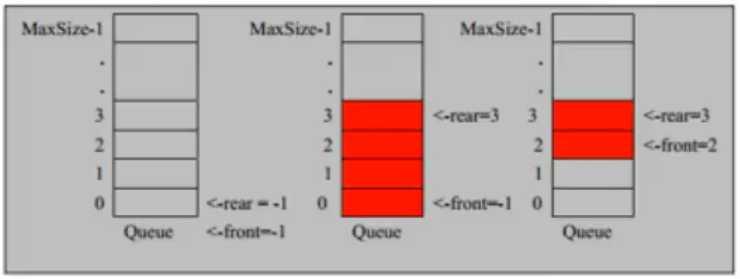
把队列头尾相接的顺序存储结构称为循环队列
对前面的队列存在“假溢出”的问题进行优化,充分利用数组
将数组看成一个环形的,通过取模的方式即可实现。


package com.queue;
/**
* 循环队列可以充分利用空间
* front 指向队列的【第一个】元素
* rear 指向最后一个元素的【后一个】
* 判断为【空】 rear == front
* 判断为【满】(rear + 1)% maxSize == front
*/
public class CircleArrayQueue {
private int maxSize;
private int front;
private int rear;
private int[] arr;
// 创建队列的构造器
public CircleArrayQueue(int maxSize) {
this.maxSize = maxSize;
// 创建指定长度的数组模拟队列
arr = new int[maxSize];
// 指向队列头部,包含那个数
this.front = 0;
// 指向队列尾部的后一个
this.rear = 0;
}
/**
* 判断队列是否满
* 无参
*
* @return
*/
public boolean isFull() {
return (rear + 1) % maxSize == front;
}
/**
* 判断队列是否空
* 无参
*
* @return
*/
public boolean isEmpty() {
return rear == front;
}
/**
* 入队
* @param n 添加的数据
*/
public void addQueue(int n) {
// 首先判断是否满
if (isFull()) {
System.out.println("队列已满,无法加入");
return;
}
// 先入队再后移
arr[rear] = n;
// rear++ 会出现下标溢出
rear = (rear + 1) % maxSize;
}
/**
* 出队
* @return 返回队列第一个元素,同时指针后移
*/
public int getQueue() {
// 先判断是否为空
if (isEmpty()) {
throw new RuntimeException("队列为空,不能取数据");
}
// 头指针后移
int value = arr[front];
front = (front + 1) % maxSize;
return value;
}
/**
* 打印队列中的有效数据
*/
public void show() {
// 遍历
if (isEmpty()) {
System.out.println("队列为空");
return;
}
for (int i = front ; i < front + size(); i++) {
// i 可能会溢出,所以要取模循环
int idx = i % maxSize;
System.out.print(arr[idx] + "\t");
}
}
public int size() {
return (rear + maxSize -front)%maxSize;
}
/**
* 不是出队入队
*
* @return 返回队首元素
*/
public int headQueue() {
// 先判断是否为空
if (isEmpty()) {
throw new RuntimeException("队列为空,不能取数据");
}
return arr[front];
}
/**
* 不是出队入队
*
* @return 返回队尾元素
*/
public int tailQueue() {
// 先判断是否为空
if (isEmpty()) {
throw new RuntimeException("队列为空,不能取数据");
}
return arr[rear-1];
}
}
测试代码
package com.queue;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建一个队列,最大储存4个元素
// ArrayQueue queue = new ArrayQueue(4);
// 创建一个循环队列,需要留出一个空位判断是否满,所以最大储存4个元素
CircleArrayQueue queue = new CircleArrayQueue(5);
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int op = -1;
do {
System.out.println("请选择测试功能");
System.out.println("1.显示队列");
System.out.println("2.入队操作");
System.out.println("3.出队操作");
System.out.println("4.查看头元素");
System.out.println("5.查看尾元素");
System.out.println("0.退出");
op = sc.nextInt();
switch (op) {
case 1:
System.out.print("队列中的数据:");
queue.show();
break;
case 2:
System.out.print("请输入入队元素:");
int n = sc.nextInt();
queue.addQueue(n);
System.out.print("队列中的数据:");
queue.show();
break;
case 3:
try {
queue.getQueue();
System.out.print("队列中的数据:");
queue.show();
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
}
break;
case 4:
try {
System.out.println("队头元素"+queue.headQueue());
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
}
break;
case 5:
try {
System.out.println("队尾元素"+queue.tailQueue());
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
}
break;
default:
break;
}
System.out.println();
System.out.println();
} while (op != 0);
System.out.println("测试结束");
}
}
| 区别 | 普通队列 | 循环队列 |
|---|---|---|
| 指针 | 指针向前(front指向前一个) | 指针向后(rear指向后一个) |
| 初始值 | 两个都是-1 | 两个都是0 |
| 判断空 | rear == front | rear == front |
| 判断满 | rear == maxSize -1 | (rear + 1) % maxSize == front |
| 指针后移 | ++ | 加1取模 |
| 队列元素个数 | rear-front | rear -front 或 (rear - 0) + (maxSize - front) 合并公式 (rear + maxSize - front) % maxSize |
队列的链式存储结构,其实就是线性表的单链表,只不过它只能尾进头出而已,简称为链队列。
为了操作上的方便,我们将队头指针指向链队列的头结点,
package com.queue;
public class LinkQueue {
// 队头指针,队尾指针
private QNode front;
private QNode rear;
public LinkQueue() {
//初始化头结点
front = new QNode();
rear = front;
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
return front == rear;
}
public void addQueue(int num) {
QNode qNode = new QNode(num);
rear.next = qNode;
rear = qNode;
}
public int delQueue() {
if (isEmpty()) {
throw new RuntimeException("队空了");
}
// 第一个结点没有数据
int value = front.next.data;
// 头结点要一直保留,跳过第一个有数据的结点
front.next = front.next.next;
// 如果无数据结点,尾指针归位。
if (front.next == null) {
rear = front;
}
return value;
}
public void list() {
if (isEmpty()) {
System.out.println("队空了");
}
QNode temp = front.next;
while (temp != null) {
System.out.print(temp.data + "\t");
temp = temp.next;
}
}
}
class QNode{
public int data;
public QNode next;
public QNode() {}
public QNode(int data) {
this.data = data;
}
}
栈和队列都是特殊的线性表,只不过对插入和删除操作做了限制
栈:是限定仅在表尾进行插入和删除操作的线性表
队列:是只允许在一端进行插入操作,在另一端进行删除操作的线性表
他们均可用线性表的顺序存储结构实现,都存在则顺序存储的一些弊端。
也都可以通过链式存储结构实现,原则上与线性表基本相同。
标签:list except 否则 bre boolean catch queue ica cat
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/1101-/p/13252551.html