标签:class queue 计算 push vector div col 技术 联系
给你一个 m x n 的矩阵,其中的值均为非负整数,代表二维高度图每个单元的高度,请计算图中形状最多能接多少体积的雨水。
示例:
给出如下 3x6 的高度图:
[
[1,4,3,1,3,2],
[3,2,1,3,2,4],
[2,3,3,2,3,1]
]
返回 4 。

如上图所示,这是下雨前的高度图[[1,4,3,1,3,2],[3,2,1,3,2,4],[2,3,3,2,3,1]] 的状态。
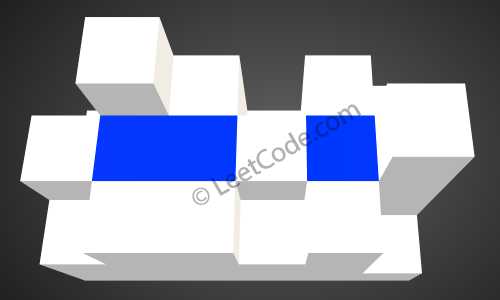
下雨后,雨水将会被存储在这些方块中。总的接雨水量是4。
提示:
1 <= m, n <= 110
0 <= heightMap[i][j] <= 20000
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/trapping-rain-water-ii
著作权归领扣网络所有。商业转载请联系官方授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
class Solution { public: //先确定木桶的外围,找到外围的最短板子后对其周围能填水的地方填水,然后更新木桶外围 struct Cell { int x, y, h; Cell(int x, int y, int h) :x(x), y(y), h(h) {}; bool operator < (const Cell& c) const { return h > c.h; } }; int trapRainWater(vector<vector<int> >& heightMap) { if (!heightMap.size() || !heightMap[0].size())return 0; int n = heightMap.size(), m = heightMap[0].size(); vector<vector<bool>> vis(n, vector<bool>(m)); priority_queue<Cell> pq; for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) if (i == 0 || j == 0 || i == n - 1 || j == m - 1) { pq.push({ i,j,heightMap[i][j] }); vis[i][j] = 1; } int dirs[] = { -1,0,1,0,-1 }; int res = 0; while (!pq.empty()) { Cell c = pq.top(); pq.pop(); for (int k = 0; k < 4; k++) { int xx = c.x + dirs[k]; int yy = c.y + dirs[k + 1]; if (xx >= 0 && yy >= 0 && xx < n && yy < m && !vis[xx][yy]) { if (heightMap[xx][yy] < c.h) res += c.h - heightMap[xx][yy]; pq.push({ xx,yy,max(heightMap[xx][yy],c.h) }); vis[xx][yy] = 1; } } } return res; } };
标签:class queue 计算 push vector div col 技术 联系
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/lancelee98/p/13261918.html