标签:col mina pos imp string ext images ecif ima
An inorder binary tree traversal can be implemented in a non-recursive way with a stack. For example, suppose that when a 6-node binary tree (with the keys numbered from 1 to 6) is traversed, the stack operations are: push(1); push(2); push(3); pop(); pop(); push(4); pop(); pop(); push(5); push(6); pop(); pop(). Then a unique binary tree (shown in Figure 1) can be generated from this sequence of operations. Your task is to give the postorder traversal sequence of this tree.
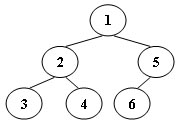
Each input file contains one test case.For each case, the first line contains a positive integer N (≤) which is the total number of nodes in a tree (and hence the nodes are numbered from 1 to N). Then 2 lines follow, each describes a stack operation in the format: "Push X" where X is the index of the node being pushed onto the stack; or "Pop" meaning to pop one node from the stack.
For each test case, print the postorder traversal sequence of the corresponding tree in one line. A solution is guaranteed to exist. All the numbers must be separated by exactly one space, and there must be no extra space at the end of the line.
6 Push 1 Push 2 Push 3 Pop Pop Push 4 Pop Pop Push 5 Push 6 Pop Pop
3 4 2 6 5 1
提测代码:
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <string.h> #define ERROR -1 #define Null -1; typedef int ElemType; typedef int Position; typedef struct SNode* Stack; struct SNode { ElemType* pData; Position top; Position maxSize; }; Stack CreateStack(int maxSize) { Stack S = (Stack)malloc(sizeof(int)); S->pData = (ElemType*)malloc(sizeof(int)*maxSize); S->top = -1; S->maxSize = maxSize; return S; } int IsFull(Stack S) { return (S->top == S->maxSize); } int Push(Stack S, ElemType data) { if (IsFull(S)) { return 0; } S->pData[++(S->top)] = data; return 1; } int IsEmpty(Stack S) { return (S->top == -1); } ElemType Pop(Stack S) { if (IsEmpty(S)) { return ERROR; } return S->pData[(S->top)--]; } void PostFromInAndPre(int pre[], int in[], int post[],int root, int left, int right) { static int counter = 0; if (left > right) { return; } ElemType data = pre[root]; int i = left; while (i < right && in[i] != data) ++i; PostFromInAndPre(pre, in, post, root + 1, left, i - 1); PostFromInAndPre(pre, in, post, root + 1 + i - left, i + 1, right); post[counter++] = data; } void PrintfTraversal(int tree[], int N) { if (N == 0) { return; } printf("%d", tree[0]); for (int i = 1; i < N; ++i) { printf(" %d", tree[i]); } } int main() { int N; scanf("%d", &N); Stack origin = CreateStack(N); int *pre = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int)*N); int *in = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int)*N); int *post = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int)*N); char strOperation[5]; int data; int preCounter = 0; int inCounter = 0; for(int i = 0; i < N*2; ++i) { scanf("%s", strOperation); if (strcmp(("Push"), strOperation) == 0) { scanf("%d", &data); Push(origin, data); pre[preCounter++] = data; } else { ElemType data = Pop(origin); in[inCounter++] = data; } } PostFromInAndPre(pre, in, post,0, 0, N - 1); PrintfTraversal(post, N); return 0; }
提测结果:
03-树3 Tree Traversals Again (25分)
标签:col mina pos imp string ext images ecif ima
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/2018shawn/p/13341055.html