标签:刷题记录 for 技术 can integer 代码 pre image 题记

解题思路:一开始不知道怎么下手,暴力遍历也没有合适的方法。参考了题解,了解到回溯算法,结合他人的代码,写了出来
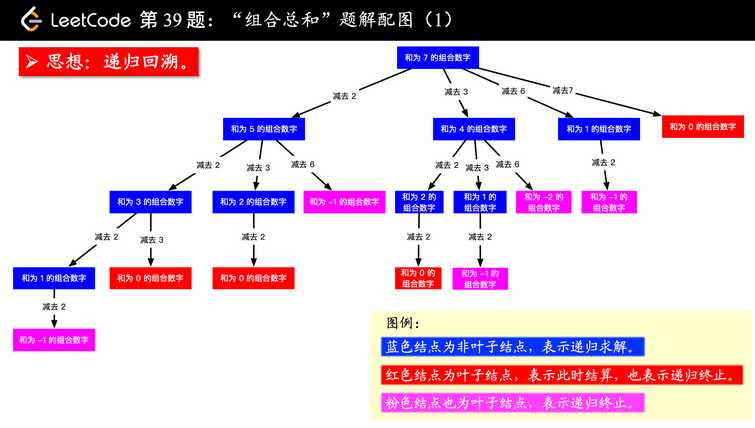
借用题解的决策树图:
1 //参考了题解的回溯算法 2 public static List<List<Integer>> combinationSum(int[] candidates, int target) { 3 //最终结果res 4 List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>(); 5 //类似二叉树遍历的指针,不过它保存了“当前路径” 6 ArrayList<Integer> track = new ArrayList<>(); 7 //遍历所谓的“决策树” 8 calc(0, candidates, track, res, target); 9 return res; 10 11 } 12 13 /** 14 * 15 * @param start 为了防止每次递归都从candidates[0]开始查找 16 * @param candidates 候选数组 17 * @param track 遍历的轨迹,可以看成一种“带有遍历轨迹的,遍历二叉树的指针” 18 * @param res 最终提交结果 19 * @param target 目标之和 20 */ 21 private static void calc(int start, int[] candidates, ArrayList<Integer> track, List<List<Integer>> res, int target) { 22 //计算“当前路径”的和 23 int sum = 0; 24 for (int i = 0; i < track.size(); i++) { 25 sum += track.get(i); 26 } 27 //递归的退出条件 28 if (sum == target) { 29 res.add(new ArrayList<>(track)); 30 return; 31 } 32 //选择树,i = start 防止每次递归都从candidates[0]开始查找,这样也能考虑自身的重复 33 for (int i = start; i < candidates.length; i++) { 34 //所谓的“剪枝”,减少递归次数,只有candidates[i] + sum <= target才有可能存在答案 35 if (candidates[i] + sum <= target) { 36 //尝试性加入一个候选元素 37 track.add(candidates[i]); 38 //递归调用,要么成功找到满足题目要求的路径,要么失败,什么也不做;不管成功失败,接下来都要:撤销最新的(尝试性加入一个候选元素的)选择 39 calc(i, candidates, track, res, target); 40 //撤销最新的(尝试性加入一个候选元素的)选择,进入下一次for循环,寻找新的路径 41 track.remove(track.size() - 1); 42 } 43 } 44 }
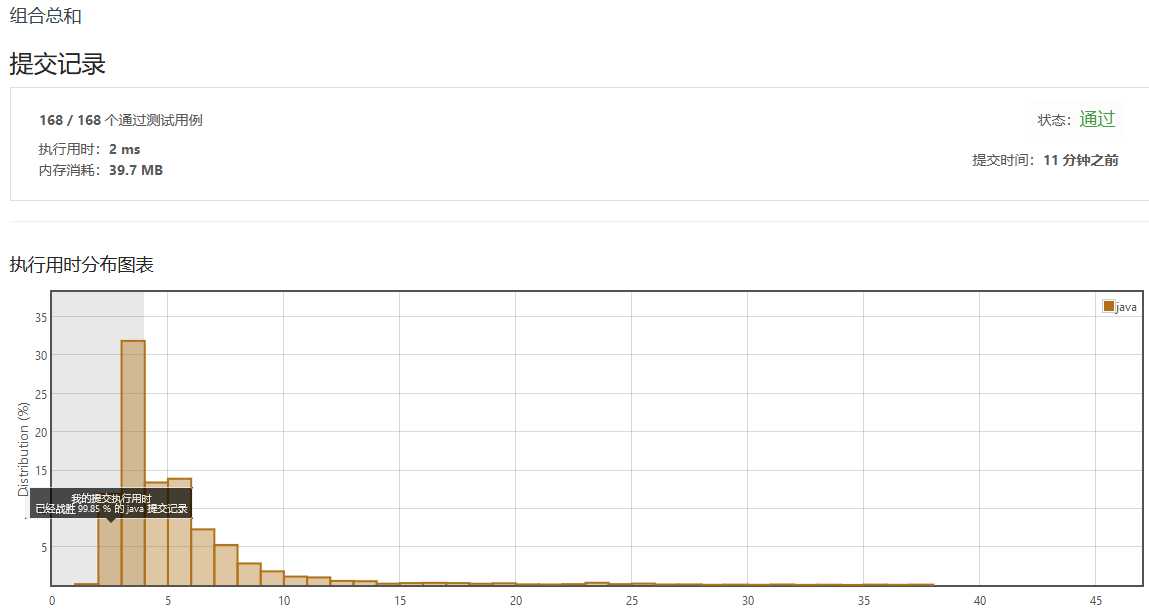
运行结果:
标签:刷题记录 for 技术 can integer 代码 pre image 题记
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/gilgamesh-hjb/p/13347913.html