标签:imp hdpi draw close The 模块 创建 属性 widgets
一、Qt Widgets、QML、Qt Quick 的区别
参考:
1. Qt Widgets、QML、Qt Quick 的区别
2. Qt Widgets 和 Qt Quick / QML
二、基础教程
参考:
1. 使用QML进行界面开发
2. QML 三言两语
三、HelloWorld
使用Qt Creator直接新建工程,有如下选项(我的没有Canvas 3D,应该时没有安装)
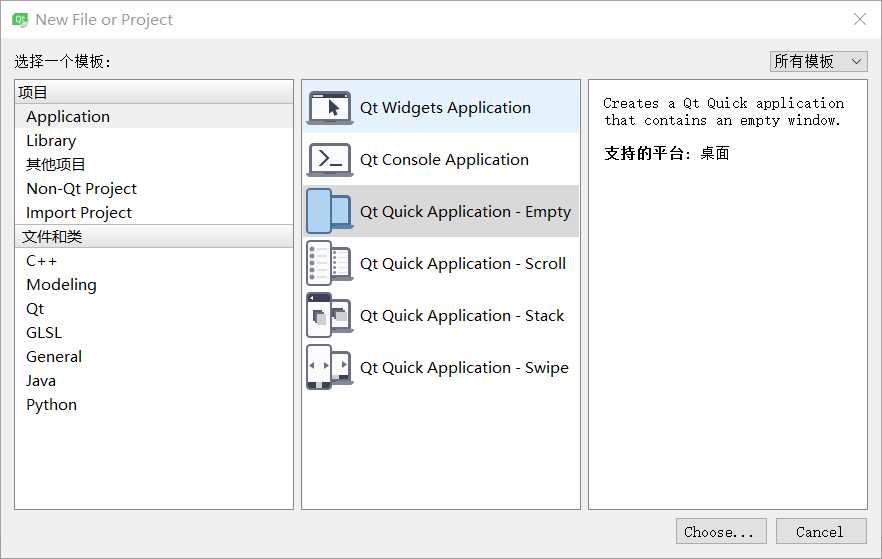
按照这里介绍,第一个Qt Quick Application - Empty 为空白窗体模板工程,Scroll 为带滚动条的窗体模板工程,Stack 为带分页的窗体模板工程, Swipe 为滑动窗体模板工程,(Canvas 3D 为3D动态模板工程)
一路默认创建完成只有运行分别长这样
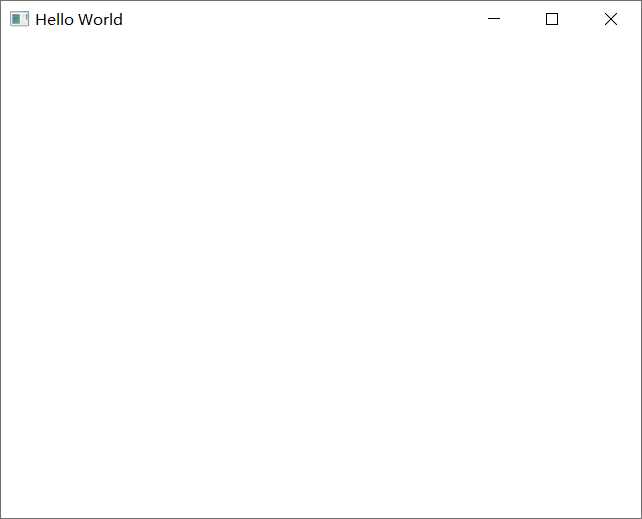
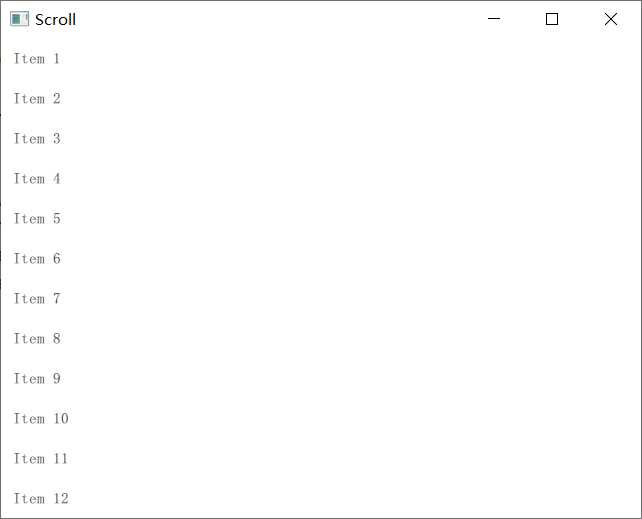
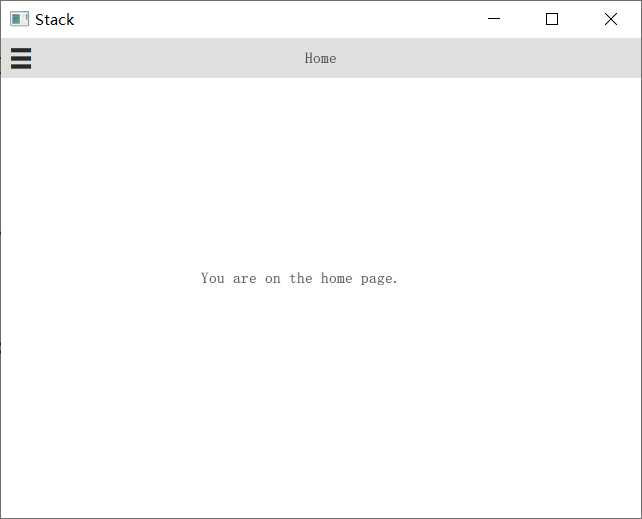
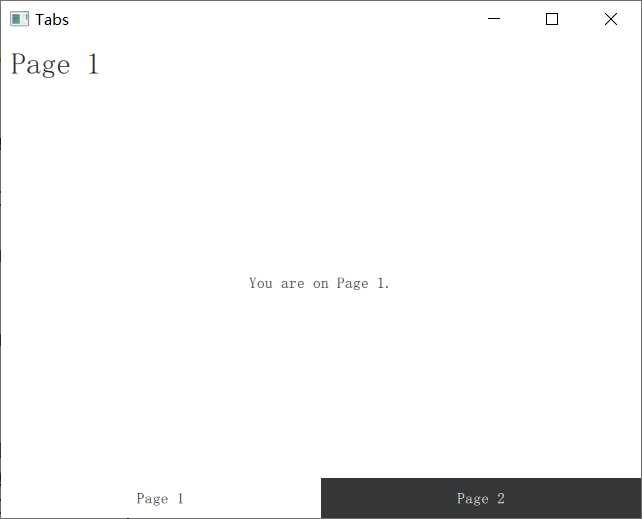
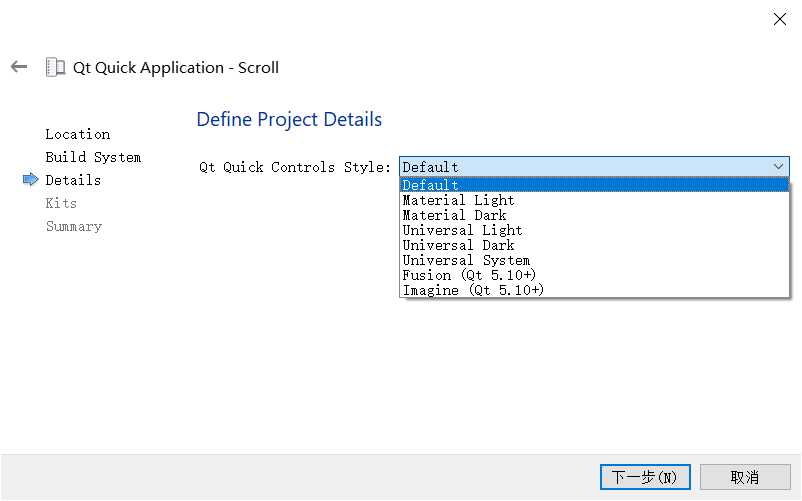
注意:从Scroll工程开始有一步选择Qt Quick Controls Styls的步骤,有如下几种样式:
第一个空项目只有main.cpp与main.qml两个文件
main.cpp
#include <QGuiApplication> #include <QQmlApplicationEngine> int main(int argc, char *argv[]) { QCoreApplication::setAttribute(Qt::AA_EnableHighDpiScaling); //使能高分屏(High-DPI),Qt从5.6.0开始支持 QGuiApplication app(argc, argv); QQmlApplicationEngine engine; //实现C++与QML混合编程 engine.load(QUrl(QStringLiteral("qrc:/main.qml"))); if (engine.rootObjects().isEmpty()) return -1; return app.exec(); }
main.qml
import QtQuick 2.9 import QtQuick.Window 2.2 Window { visible: true // 是否显示 width: 640 // 宽 height: 480 // 高 title: qsTr("Hello World") // 窗口标题 }
main.qml就像js一样,首先import核心的Qt Quick,然后要使用Window对象,再import Qt Quick.Window模块,下面定义了一个Window窗口对象
然后第二个Scroll项目,main.cpp是一样的,都是加载main.qml文件,其main.qml文件如下:
import QtQuick 2.9 import QtQuick.Controls 2.2 ApplicationWindow { visible: true width: 640 height: 480 title: qsTr("Scroll") // 滚动条对象 ScrollView { anchors.fill: parent ListView { width: parent.width // 宽度等于父对象,也就是Window的宽度 model: 20 // 元素数量 delegate: ItemDelegate { // 每一个元素对象 text: "Item " + (index + 1) width: parent.width } } } }
为了使用 ScrollView 类,import了 QtQuick.Controls 模块,窗口对象由 ApplicationWindow 类定义,除了窗口属性之外多了一个 ScrollView对象,该对象定义了一个滚动条视图,当item数量超出屏幕显示范围时会出现滚动条,但是这里的宽度好像并没有什么用。
此外还有个qtquickcontrols2.conf配置文件,其中定义了上面建项目时选的Qt Quick Controls Styls样式。
第三个Stack分屏项目,每个弹出页面分别定义了一个ui文件,然后在qml文件点击事件中加载
import QtQuick 2.9 import QtQuick.Controls 2.2 ApplicationWindow { id: window visible: true width: 640 height: 480 title: qsTr("Stack") // 头部工具栏 header: ToolBar { contentHeight: toolButton.implicitHeight // 页面切换按钮 ToolButton { id: toolButton // 按钮id text: stackView.depth > 1 ? "\u25C0" : "\u2630" // 按钮样式,三个横杠还是小三角形 font.pixelSize: Qt.application.font.pixelSize * 1.6 // 字体大小 onClicked: { // 点击事件 if (stackView.depth > 1) { stackView.pop() // 页面深度大于1则返回主页 } else { drawer.open() // 否则打开新特面 } } } // 工具栏标签 Label { text: stackView.currentItem.title // 工具栏标题为当前页面标题 anchors.centerIn: parent // 固定于父对象 } } // 弹出式页面选项遮罩层 Drawer { id: drawer width: window.width * 0.66 // 选项卡宽度 height: window.height // 高度 // 子页面选项元素定义 Column { anchors.fill: parent ItemDelegate { text: qsTr("Page 1") width: parent.width onClicked: { stackView.push("Page1Form.ui.qml") // 点击的时候加载新的ui文件 drawer.close() // 然后关闭选项卡 } } ItemDelegate { text: qsTr("Page 2") width: parent.width onClicked: { stackView.push("Page2Form.ui.qml") drawer.close() } } } } // 当前弹出页面对象 StackView { id: stackView initialItem: "HomeForm.ui.qml" anchors.fill: parent } }
第四个Swipe项目,和Stack页面一样,不过由弹出式的StackView对象变成了滑动式的SwipeView对象
import QtQuick 2.9 import QtQuick.Controls 2.2 ApplicationWindow { visible: true width: 640 height: 480 title: qsTr("Tabs") // 滑动页面对象 SwipeView { id: swipeView anchors.fill: parent currentIndex: tabBar.currentIndex // 两个可滑动页面元素,对象名就是对应的ui文件名 Page1Form { } Page2Form { } } // 没有头部工具栏,而是页脚,定义了两个按钮,没有页脚也可以滑动页面 footer: TabBar { id: tabBar currentIndex: swipeView.currentIndex TabButton { text: qsTr("Page 1") } TabButton { text: qsTr("Page 2") } } }
标签:imp hdpi draw close The 模块 创建 属性 widgets
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/jixiaohua/p/13363887.html