标签:style blog http io color ar os sp for
概述:
协作性过滤,是一种目前广泛运用于电子商务、交友网站、在线广告等互联网领域的一项技术。其主要作用是为指定用户在广大的用户群中找到品味相同或者相似的人,从而帮助网站针对性的推荐产品给特定的用户,与此同时,用户本人也可以从一堆纷繁复杂的信息中,迅速找到自己喜欢的、感兴趣的那部分信息。
其主要有两种实现方法,一种是基于用户的(user-based),即通过分析用户间的相似性,生成最近的邻居,将邻居中“得分”最高的项目推荐给用户;另一种是基于物品的(item-based),即通过分析用户群体对物品的评价计算出每个物品的“得分”,然后根据用户对某件物品的评价,将与该物品相似度最高的物品推荐给用户,典型的例子是亚马逊的图书推荐。两者在不同的应用中,各有千秋。
一般实现需要三个步骤:
收集用户偏好:
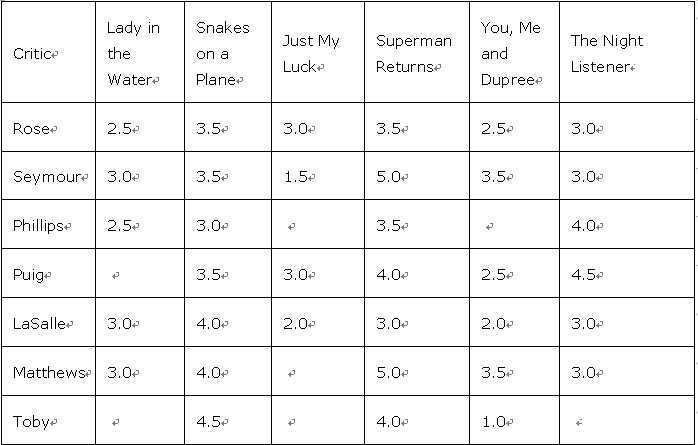
收集用户偏好是协作性过滤的基础,数据的来源也可以多种多样。集体智慧编程示例数据是一份电影评价。具体如下:
找到相似的用户或者物品:
相似度计算:计算用户间或者物品间相似度的方法很多,该书中主要介绍了两种方法。
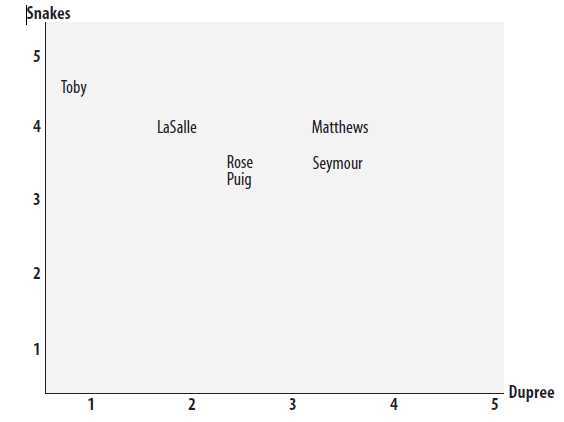
一是欧几里得距离,可以以电影为坐标轴,将评价者按评分在坐标系中一一标出,然后计算两者的距离,距离越近就越相似。
数学公式为:
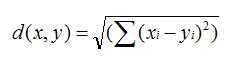
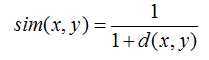
另一种称为皮尔逊相关系数,可以以评价者作为坐标轴将电影在坐标系内标出,计算最佳拟合线。该取值在 [-1,+1] 之间。

数学公式:
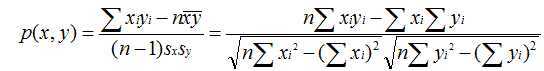
计算推荐:
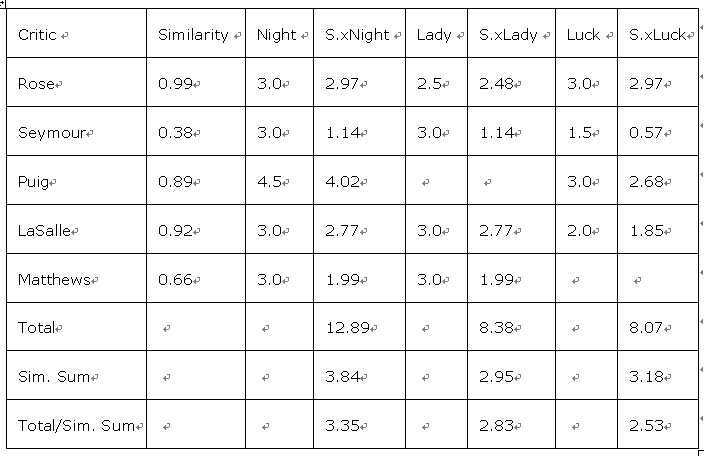
如上表格,是给其中一位名为Toby的评论者推荐他没有看过的电影的过程。首先运用欧几里得或者皮尔逊方法得到相似度值(Similarity 列)。然后用相似度值乘以每一位评论者的打分,从而得到一个新的“得分”。最后将得分总和除以相似度值的总和得到每部电影最终的“推荐值”。“推荐值”越高,越可能得到Toby的认可。
代码实现:

1 # -*- coding: utf-8 -*- 2 3 # A dictionary of movie critics and their ratings of a small 4 # set of movies 5 critics = {‘Lisa Rose‘: {‘Lady in the Water‘: 2.5, ‘Snakes on a Plane‘: 3.5, 6 ‘Just My Luck‘: 3.0, ‘Superman Returns‘: 3.5, ‘You, Me and Dupree‘: 2.5, 7 ‘The Night Listener‘: 3.0}, 8 ‘Gene Seymour‘: {‘Lady in the Water‘: 3.0, ‘Snakes on a Plane‘: 3.5, 9 ‘Just My Luck‘: 1.5, ‘Superman Returns‘: 5.0, ‘The Night Listener‘: 3.0, 10 ‘You, Me and Dupree‘: 3.5}, 11 ‘Michael Phillips‘: {‘Lady in the Water‘: 2.5, ‘Snakes on a Plane‘: 3.0, 12 ‘Superman Returns‘: 3.5, ‘The Night Listener‘: 4.0}, 13 ‘Claudia Puig‘: {‘Snakes on a Plane‘: 3.5, ‘Just My Luck‘: 3.0, 14 ‘The Night Listener‘: 4.5, ‘Superman Returns‘: 4.0, 15 ‘You, Me and Dupree‘: 2.5}, 16 ‘Mick LaSalle‘: {‘Lady in the Water‘: 3.0, ‘Snakes on a Plane‘: 4.0, 17 ‘Just My Luck‘: 2.0, ‘Superman Returns‘: 3.0, ‘The Night Listener‘: 3.0, 18 ‘You, Me and Dupree‘: 2.0}, 19 ‘Jack Matthews‘: {‘Lady in the Water‘: 3.0, ‘Snakes on a Plane‘: 4.0, 20 ‘The Night Listener‘: 3.0, ‘Superman Returns‘: 5.0, ‘You, Me and Dupree‘: 3.5}, 21 ‘Toby‘: {‘Snakes on a Plane‘: 4.5, ‘You, Me and Dupree‘: 1.0, ‘Superman Returns‘: 4.0}} 22 23 from math import sqrt 24 25 def sim_distance(prefs, person1, person2): 26 si = {} 27 for item in prefs[person1]: 28 if item in prefs[person2]: 29 si[item] = 1 30 31 if len(si) == 0: return 0 32 sum_of_squares = sum( 33 [pow(prefs[person1][item] - prefs[person2][item], 2) for item in prefs[person1] if item in prefs[person2]]) 34 return 1 / (1 + sqrt(sum_of_squares)) 35 36 37 def sim_pearson(prefs, person1, person2): 38 si = {} 39 for item in prefs[person1]: 40 if item in prefs[person2]: 41 si[item] = 1 42 43 n = len(si) 44 if n == 0: return 1 45 46 sum1 = sum([prefs[person1][it] for it in si]) 47 sum2 = sum([prefs[person2][it] for it in si]) 48 49 sum1Sq = sum([pow(prefs[person1][it], 2) for it in si]) 50 sum2Sq = sum([pow(prefs[person2][it], 2) for it in si]) 51 52 pSum = sum([prefs[person1][it] * prefs[person2][it] for it in si]) 53 54 num = pSum - (sum1 * sum2 / n) 55 den = sqrt((sum1Sq - pow(sum1, 2) / n) * (sum2Sq - pow(sum2, 2) / n)) 56 if den == 0: return 0 57 58 r = num / den 59 return r 60 61 62 # Returns the best matches for person from the prefs dictionary. 63 # Number of results and similarity function are optional params. 64 def topMatches(prefs, person, n=5, similarity=sim_pearson): 65 scores = [(similarity(prefs, person, other), other) for other in prefs if other != person] 66 # Sort the list so the highest scores appear at the top 67 scores.sort() 68 scores.reverse() 69 return scores[0:n] 70 71 72 # Gets recommendations for a person by using a weighted average 73 # of every other user‘s rankings 74 def getRecommendations(prefs, person, similarity=sim_pearson): 75 totals = {} 76 simSums = {} 77 for other in prefs: 78 # don‘t compare me to myself 79 if other == person: continue 80 sim = similarity(prefs, person, other) 81 # ignore scores of zero or lower 82 if sim <= 0: continue 83 for item in prefs[other]: 84 # only score movies I haven‘t seen yet 85 if item not in prefs[person] or prefs[person][item] == 0: 86 # Similarity * Score 87 totals.setdefault(item, 0) 88 totals[item] += prefs[other][item] * sim 89 # Sum of similarities 90 simSums.setdefault(item, 0) 91 simSums[item] += sim 92 # Create the normalized list 93 rankings = [(total / simSums[item], item) for item, total in totals.items()] 94 # Return the sorted list 95 rankings.sort() 96 rankings.reverse() 97 return rankings 98 99 if __name__ == ‘__main__‘: 100 print getRecommendations(critics,‘Toby‘,similarity=sim_pearson)
标签:style blog http io color ar os sp for
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/cxy486/p/4090077.html