标签:can str gre 核心 运行 state row 系统 nta
Flutter动画中有4个比较重要的角色:Animation、Controller、Curve、Tween,先来了解一下这四个角色
Animation是Flutter动画库中的核心类,用于插入指导动画的值
Animation对象知道动画当前的状态(比如开始还是停止),可以使用addListener和addStatusListener监听动画状态改变。
animation.addListener((){
//调用setState来刷新界面
setState(() {
});
});
animation.addStatusListener((status){
debugPrint(‘status $status‘);
switch (status){
//动画一开始就停止了
case AnimationStatus.dismissed:
break;
//动画从头到尾都在播放
case AnimationStatus.forward:
break;
//动画从结束到开始倒着播放
case AnimationStatus.reverse:
break;
//动画播放完停止
case AnimationStatus.completed:
break;
}
});
在Flutter中,Animation对象本身和UI渲染没有任何关系。Animation是一个抽象类,它拥有其当前值和状态(完成或停止)。其中一个比较常用的Animation类是 Animation<double> ,还可以生成除double之外的其他类型值,如: Animation<Color> 或 Animation<Size> 。
用来管理Animation,它继承自Animation, 是个特殊的Animation ,屏幕每刷新一帧,它都会生成一个新值,需要一个vsync参数, vsync的存在可以防止后台动画消耗不必要的资源 。
vsync的值怎么获得,可以让stateful对象扩展使用TickerProviderStateMixin比如:
class AnimationDemoHome extends StatefulWidget {
@override
_AnimationDemoHomeState createState() => _AnimationDemoHomeState();
}
class _AnimationDemoHomeState extends State<AnimationDemoHome> with TickerProviderStateMixin{...}
AnimationController在默认情况下,在给定的时间段内,AnimationController会生成0.0到1.0的数字。
它可以控制动画,比如使用 .forward() 方法可以启动一个动画, .stop() 可以结束一个动画, .reverse() 启动反向动画。
AnimationController({
double value,
this.duration,
this.reverseDuration,
this.debugLabel,
this.lowerBound = 0.0,
this.upperBound = 1.0,
this.animationBehavior = AnimationBehavior.normal,
@required TickerProvider vsync,
})
看一下AnimationController的构造方法,有一个必须的参数TickerProvider,就是前面给定的TickerProviderStateMixin
在StatefulWidget中创建一个AnimationController对象
animationController = AnimationController(
// lowerBound: 32.0,
// upperBound: 100.0,
duration: Duration(milliseconds: 2000),
vsync: this
);
定义动画曲线,运动过程,比如匀速,先加速在减速等等
CurvedAnimation({
@required this.parent,
@required this.curve,
this.reverseCurve,
})
它有两个必要的参数parent和curve。parent就是前面的AnimationController对象,curve就是动画运行的曲线,相当于Android属性动画中的插值器curve都有哪些取值呢
| curve曲线 | 动画过程 |
|---|
linear|匀速的
decelerate|匀减速
ease|先加速后减速
easeIn|开始慢后面快
easeout|开始快后面慢
easeInOut|先慢在快在慢
上面是常用的一些曲线,还有很多中曲线运动的方式可以去curve.dart源码中去看,源码注释中有mp4的链接,可以清楚的看到动画运动的视频。
abstract class Curve {
const Curve();
double transform(double t) {
assert(t >= 0.0 && t <= 1.0);
if (t == 0.0 || t == 1.0) {
return t;
}
return transformInternal(t);
}
@protected
double transformInternal(double t) {
throw UnimplementedError();
}
...
}
如果系统提供的运动曲线仍然无法满足我们的需求,那就可以继承Curve来自己实现一个。上面的代码可以看到Curve是一个抽象类,继承它并重写transform方法即可。比如我们可以自己在里面实现一个sin或者cos函数的曲线。例如
class ShakeCurve extends Curve {
@override
double transform(double t) {
return math.sin(t * math.PI * 2);
}
}
创建一个CurvedAnimation对象
CurvedAnimation curvedAnimation =
CurvedAnimation(parent: animationController,curve: Curves.bounceOut);
给动画对象插入一个范围值
默认情况下,AnimationController对象的范围从0.0到1.0,如果我们想要更大的范围,就需要使用到Tween了。比如
Tween tween = Tween(begin: 32.0,end: 100.0);
class Tween<T extends dynamic> extends Animatable<T> Tween继承自Animatable,接收一个begin和一个end值,Tween的职责就是定义从输入范围到输出范围的映射。所以这两个值必须能进行加减乘的运算。
要使用Tween对象,调用其animate()方法,传入一个控制器对象,返回一个Animation对象。例如,
Animation animation = Tween(begin: 32.0,end: 100.0).animate(curvedAnimation);
Animation animationColor = ColorTween(begin: Colors.red,end: Colors.green).animate(curvedAnimation);
动画的四个角色都了解了,下面开始使用这些角色来构建一个动画,动画效果如下图
有一个心形的button,点击的时候放大并且颜色渐变,在点击的时候原路返回
class AnimateDemo1 extends StatefulWidget {
@override
_AnimateDemo1State createState() => _AnimateDemo1State();
}
class _AnimateDemo1State extends State<AnimateDemo1> with SingleTickerProviderStateMixin{
AnimationController animationController;
Animation animationSize;
Animation animationColor;
CurvedAnimation curvedAnimation;
//Tween sizeTween;
//Tween colorTween;
@override
void initState() {
super.initState();
animationController = AnimationController(
duration: Duration(milliseconds: 1000),
vsync: this
);
//设置插值器 这里使用一个默认的插值器bounceInOut
curvedAnimation = CurvedAnimation(parent: animationController,curve: Curves.bounceOut);
animationSize = Tween(begin: 32.0,end: 100.0).animate(curvedAnimation);
animationColor = ColorTween(begin: Colors.red,end: Colors.green).animate(curvedAnimation);
animationController.addListener((){
//刷新界面
setState(() {});
});
}
@override
void dispose() {
super.dispose();
animationController.dispose();
}
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Center(
child: IconButton(
icon: Icon(Icons.favorite),
iconSize: animationSize.value,
color: animationColor.value,
//iconSize: sizeTween.evaluate(curvedAnimation),
//color: colorTween.evaluate(curvedAnimation),
onPressed: (){
switch(animationController.status){
case AnimationStatus.completed:
animationController.reverse();
break;
default:
animationController.forward();
}
},
),
);
}
}
sizeTween.evaluate(curvedAnimation)
2.1中每次写动画都需要在addListener中设置setState来更新UI,有点麻烦,系统给提供了一个AnimatedWidget,它内部封装了addListener和setState的逻辑,我们只需要传给它AnimationController和Animation就行了。
而且我们可以自定义一个Widget继承它,让动画跟原来的视图代码分离
class AnimationDemo2 extends StatefulWidget {
@override
_AnimationDemo2State createState() => _AnimationDemo2State();
}
class _AnimationDemo2State extends State<AnimationDemo2> with SingleTickerProviderStateMixin{
AnimationController animationController;
Animation animationSize;
Animation animationColor;
CurvedAnimation curvedAnimation;
@override
void initState() {
super.initState();
animationController = AnimationController(
duration: Duration(milliseconds: 1000),
vsync: this
);
//设置插值器 这里使用一个默认的插值器bounceInOut
curvedAnimation = CurvedAnimation(parent: animationController,curve: Curves.bounceOut);
animationSize = Tween(begin: 32.0,end: 100.0).animate(curvedAnimation);
animationColor = ColorTween(begin: Colors.red,end: Colors.green).animate(curvedAnimation);
}
@override
void dispose() {
super.dispose();
animationController.dispose();
}
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Center(
child: AnimationHeart(
animations: [
animationSize,animationColor
],
controller: animationController,
),
);
}
}
//动画代码抽离
class AnimationHeart extends AnimatedWidget{
AnimationController controller;
List animations;
AnimationHeart({ this.animations,
this.controller,}):super(listenable:controller);
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return IconButton(
icon: Icon(Icons.favorite),
iconSize: animations[0].value,
color: animations[1].value,
onPressed: (){
switch(controller.status){
case AnimationStatus.completed:
controller.reverse();
break;
default:
controller.forward();
}
},
);
}
}
自定义一个AnimationHeart继承自AnimatedWidget,在构造方法中将AnimationController和Animation传过来。其余的跟2.1中一样,最终效果也一样。
Flutter中还可以使用AnimatedBuilder来构建一个动画
class AnimateDemo3 extends StatefulWidget {
@override
_AnimateDemo3State createState() => _AnimateDemo3State();
}
class _AnimateDemo3State extends State<AnimateDemo3> with SingleTickerProviderStateMixin{
AnimationController animationController;
Animation animationSize;
Animation animationColor;
CurvedAnimation curvedAnimation;
@override
void initState() {
super.initState();
animationController = AnimationController(
duration: Duration(milliseconds: 1000),
vsync: this
);
//设置插值器 这里使用一个默认的插值器bounceInOut
curvedAnimation = CurvedAnimation(parent: animationController,curve: Curves.bounceOut);
animationSize = Tween(begin: 32.0,end: 100.0).animate(curvedAnimation);
animationColor = ColorTween(begin: Colors.red,end: Colors.green).animate(curvedAnimation);
}
@override
void dispose() {
super.dispose();
animationController.dispose();
}
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return AnimatedBuilder(
animation: animationController,
builder: (context,child){
return Center(
child: IconButton(
icon: Icon(Icons.favorite),
iconSize: animationSize.value,
color: animationColor.value,
onPressed: (){
switch(animationController.status){
case AnimationStatus.completed:
animationController.reverse();
break;
default:
animationController.forward();
}
},
),
);
},
);
}
}
实例化四个动画元素的代码跟前面还是一样,主要是在build代码块中使用AnimatedBuilder构建,传入animation对象。看起来比2.2中的方式也没有简单多少,不过看一下它的构造方法,系统还给提供了一个可选的参数child,让它天然就支持封装。
const AnimatedBuilder({
Key key,
@required Listenable animation,
@required this.builder,
this.child,
})
上面的例子中我们是直接在builder中创建了一个控件,既然child可以传进来,那么我们可以把一个类型的动画封装一下比如缩放动画,渐变动画等,以后只要把需要此动画的小部件传进来,这个小部件就有这个动画了。
比如下面定义一个可以缩放的小部件。
class ScaleAnimate extends StatelessWidget {
final Animation animation;
final Widget child;
ScaleAnimate({@required this.animation,@required this.child});
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return AnimatedBuilder(
animation: animation,
builder: (context,child){
return SizedBox(
width: animation.value,
height: animation.value,
child: child,
);
},
child: child,
);
}
}
Hero动画很简单不过在平时的项目中也经常用到,主要用在路由页面之间切换。比如一个头像点击看大图,或者新闻列表页面,点击看详情,这种共享式的无缝切换。
动画效果如下图
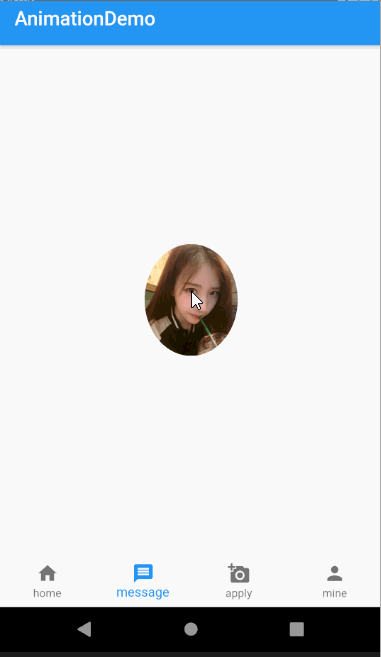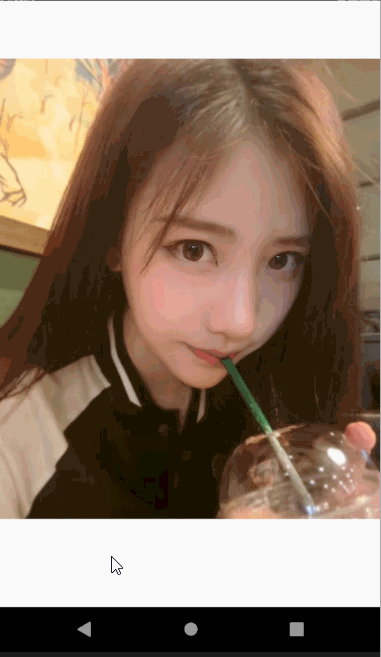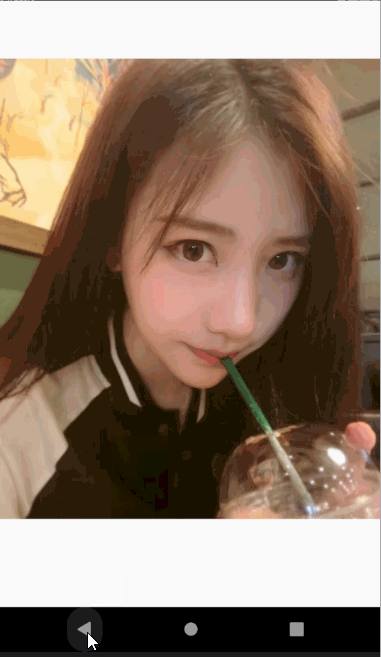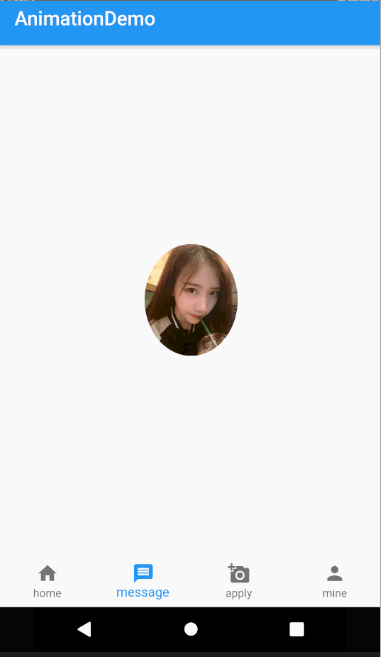
class AnimateDemo4 extends StatefulWidget {
@override
_AnimateDemo4State createState() => _AnimateDemo4State();
}
class _AnimateDemo4State extends State<AnimateDemo4> {
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Center(
child: InkWell(
child: Hero(
tag: "avator",
child: ClipOval(
child: Image.network(‘http://ww1.sinaimg.cn/large/0065oQSqly1fsfq1k9cb5j30sg0y7q61.jpg‘,width: 100,),
),
),
onTap: (){
Navigator.of(context).push(MaterialPageRoute(builder: (context){
return Scaffold(
body: Center(
child: Hero(
tag: "avator",
child: Image.network(‘http://ww1.sinaimg.cn/large/0065oQSqly1fsfq1k9cb5j30sg0y7q61.jpg‘),
),
),
);
}));
},
),
);
}
}
广州设计公司https://www.houdianzi.com 我的007办公资源网站https://www.wode007.com
有时候我们需要实现一组复杂的动画,比如在0.1-0.2秒缩放,从0.2-0.4秒颜色渐变,从0.4-0.8秒左右移动,这时候使用交织动画可以方便的完成,使用交织动画需要注意下面几点

class AnimateDemo5 extends StatefulWidget {
@override
_AnimateDemo5State createState() => _AnimateDemo5State();
}
class _AnimateDemo5State extends State<AnimateDemo5> with TickerProviderStateMixin{
AnimationController _controller;
@override
void initState() {
super.initState();
_controller = AnimationController(
duration: const Duration(milliseconds: 2000),
vsync: this
);
}
@override
void dispose() {
super.dispose();
_controller.dispose();
}
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Center(
child: Column(
children: <Widget>[
SizedBox(height: 30,),
Center(
child: StaggerAnimation(controller: _controller,),
),
SizedBox(height: 30,),
RaisedButton(
child: Text("点击开始"),
onPressed: () {
_play();
},
textColor: Theme.of(context).primaryColor,
splashColor: Colors.grey[400],
)
],
),
);
}
void _play() async{
//先正向执行动画
await _controller.forward().orCancel;
//再反向执行动画
await _controller.reverse().orCancel;
}
}
class StaggerAnimation extends StatelessWidget {
final AnimationController controller;
Animation<double> width,height;
Animation<EdgeInsets> padding;
Animation<Color> color;
Animation<BorderRadius> borderRadius;
StaggerAnimation({Key key,this.controller}): super(key:key){
height = Tween<double>(
begin: 0,
end: 200)
.animate(CurvedAnimation(parent: controller, curve: Interval(0.0,0.4,curve: Curves.ease)));
width = Tween<double>(
begin: 50,
end: 200)
.animate(CurvedAnimation(parent: controller, curve: Interval(0.0,0.4,curve: Curves.ease)));
padding = Tween<EdgeInsets>(
begin:EdgeInsets.only(left: .0),
end:EdgeInsets.only(left: 100.0),
).animate(CurvedAnimation(parent: controller, curve: Interval(0.6, 1.0, curve: Curves.ease)),);
color = ColorTween(
begin:Colors.green ,
end:Colors.red,
).animate(CurvedAnimation(parent: controller, curve: Interval(0.0, 0.4, curve: Curves.ease,)));
borderRadius = BorderRadiusTween(
begin: BorderRadius.circular(3),
end: BorderRadius.circular(35),
).animate(CurvedAnimation(parent: controller, curve: Interval(0.4, 0.6,curve: Curves.ease,),));
}
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return AnimatedBuilder(
animation: controller,
builder: (context,child){
return Container(
alignment: Alignment.bottomCenter,
padding:padding.value ,
child: Container(
width: width.value,
height: height.value,
decoration: BoxDecoration(
color: color.value,
border: Border.all(color: Colors.blue,width: 3),
borderRadius:borderRadius.value
),
),
);
},
);
}
}
标签:can str gre 核心 运行 state row 系统 nta
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/Qooo/p/13830875.html