标签:集合 二叉搜索树 ++ col add init 排序 整数 efi
给你 root1 和 root2 这两棵二叉搜索树。
请你返回一个列表,其中包含 两棵树 中的所有整数并按 升序 排序。
示例 1:
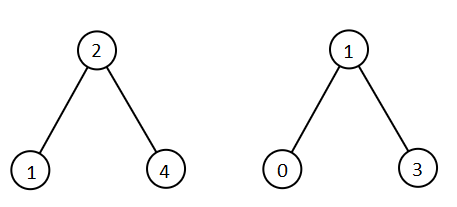
输入:root1 = [2,1,4], root2 = [1,0,3]
输出:[0,1,1,2,3,4]
示例 2:
输入:root1 = [0,-10,10], root2 = [5,1,7,0,2]
输出:[-10,0,0,1,2,5,7,10]
示例 3:
输入:root1 = [], root2 = [5,1,7,0,2]
输出:[0,1,2,5,7]
示例 4:
输入:root1 = [0,-10,10], root2 = []
输出:[-10,0,10]
示例 5:
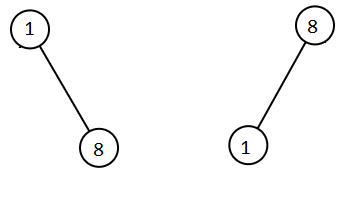
输入:root1 = [1,null,8], root2 = [8,1]
输出:[1,1,8,8]
这是一开始的想法。
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public List<Integer> getAllElements(TreeNode root1, TreeNode root2) {
List<Integer> list1 =new ArrayList<Integer>();
List<Integer> list2 =new ArrayList<Integer>();
List<Integer> list =new ArrayList<Integer>();
list1=minsearch(root1, list1);
list2=minsearch(root2, list2);
int i=0,j=0;
for(;i<list1.size()&&j<list2.size();) {
if(list1.get(i)<list2.get(j)) {
list.add(list1.get(i));
i++;
}else {
list.add(list2.get(j));
j++;
}
}
if(i>=list1.size()) {
for(;j<list2.size();j++) {
list.add(list2.get(j));
}
}
if(j>=list2.size()) {
for(;i<list1.size();i++) {
list.add(list1.get(i));
}
}
return list;
}
public List<Integer> minsearch(TreeNode q,List<Integer> listp) {
if(q==null)
return listp;
minsearch(q.left,listp);
listp.add(q.val);
minsearch(q.right,listp);
return listp;
}
}
**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public List<Integer> getAllElements(TreeNode root1, TreeNode root2) {
List<Integer> list1 =new ArrayList<Integer>();
list1=minsearch(root1, list1);
list1=minsearch(root2, list1);
Collections.sort(list1);
return list1;
}
public List<Integer> minsearch(TreeNode q,List<Integer> listp) {
if(q==null)
return listp;
minsearch(q.left,listp);
listp.add(q.val);
minsearch(q.right,listp);
return listp;
}
}
运行时间比上面合并排序要快
标签:集合 二叉搜索树 ++ col add init 排序 整数 efi
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/code-fun/p/13768482.html