标签:rac HERE move 好的 次数 comm training assign 通过
authors: Mingbao Lin, Rongrong Ji, etc.
comments: IJCAL2020
cite: [2001.08565v3] Channel Pruning via Automatic Structure Search (arxiv.org)
code: https://github.com/lmbxmu/ABCPruner (official)
In this paper, we propose a new channel pruning method based on artificial bee colony algorithm (ABC), dubbed as ABCPruner, which aims to efficiently find optimal pruned structure, i.e., channel number in each layer, rather than selecting “important” channels as previous works did.
方法:ABCPruner [channel level], artificial bee colony algorithm
不同处:旨在找出最优剪枝结构而不是和以往研究一样挑选出最重要的channel。
..., we first propose to shrink the combinations where the preserved channels are limited to a specific space, ... . And then, we formulate the search of optimal pruned structure as an optimization problem
and integrate the ABC algorithm to solve it in an automatic manner to lessen human interference.
具体做法:将通道组合压缩到一个特定空间,然后将“(在这个特定空间)搜索最优剪枝结构”作为一个优化问题。
? 并且使用ABCPruner 来自动求解这个优化问题。
Channel pruning targets at removing the entire channel in each layer, which is straightforward but challenging because removing channels in one layer might drastically change the input of the next layer.
通道剪枝的弊端:删除某一个层中的一部分通道,极大可能会影响了下一层的输入。
(只是提了一下,并没有给出解决方法)
Most cutting-edge practice implements channel pruning by selecting channels (filters) based on rule-of-thumb designs.
The first is to identify the most important filter weights in a pre-trained model, ...
The second performs channel pruning based on handcrafted rules to regularize the retraining of a full model followed by pruning and fine-tuning...
现有大多数方法是根据经验规则实现通道剪枝:一类是根据预训练模型的每个filter的权重,来决定这些filter中哪些权重需要被舍弃;另一个是手工规则,即人工决定剪枝率等超参数进行剪枝。
The motivation of our ABCPruner is two-fold.
First, [Liu et al., 2019b] showed that the essence of channel pruning lies in finding optimal pruned structure, i.e., channel number in each layer, instead of selecting “important” channels.
- Second, [He et al., 2018b] proved the feasibility of applying automatic methods for controlling hyper-parameters to channel pruning, which requires less human interference.
作者根据上面总结的两个现象,以及他人论文,表明:首先通道剪枝的本质是寻找最优剪枝结构,而不是重要的通道;再者认为较少的人为干涉会好的,同时通过他人文章,将超参数自动控制方法应用到剪枝中可以达到这个目的。
(提出自己的方法)
Given a CNN with L layers, the combinations of pruned structure could be \(\prod _ { j = 1 } ^ { L } c _ { j }\), \(L\) is layers number, \(c_j\) is channel number in the \(j\)-th layer. The combination overhead is extremely intensive.
To solve this problem, we propose to shrink the combinations by limiting the number of preserved channels to \(\{ 0.1 c _{ j } , 0.2 c _{ j } , \ldots , \alpha c _{ j } \}\) where the value of α falls in {10%,20%, ...,100%}, which shows that there are 10α feasible solutions for each layer, ...
(作者开始介绍自己的方法,先提到方法中的一部分,即上面将通道组合压缩到一个特定空间)
给定卷积网络后,因为作者不会对每层裁剪多少个通道数量做限制,但是不做限制后经过组合后的方案太多,所以作者提出限制每层只能按照固定的百分比进行选择。这样方案就少了,也就是作者说的:将通道组合压缩到一个特定空间。
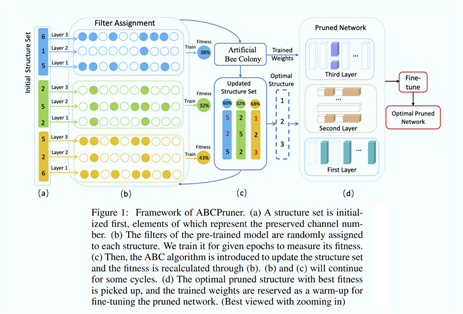
As shown in Fig.1, we first initialize a structure set, each element of which represents the preserved channel number in each layer.
The filter weights of the full model are randomly selected and assigned to initialize each structure.
We train it for a given number of epochs to measure its fitness, a.k.a, accuracy performance in this paper.
Then, ABC is introduced to update the structure set.
Similarly, filter assignment, training and fitness calculation for the updated structures are conducted. We continue the search for some cycles.
Finally, the one with the best fitness is considered as the optimal pruned structure, and its trained weights are reserved as a warm-up for fine-tuning.
整个剪枝方案:
Network Pruning: weight pruning and channel pruning.
AutoML: automatic pruning
大概说了一下权重剪枝和通道剪枝的特性和情况,然后提到AutoML的好处,又因为[1810.05270] Rethinking the Value of Network Pruning (arxiv.org)这里面提到的“通道剪枝的关键在于剪枝结构而不是选择‘重要’通道”,启发了现在的方法。
Given a CNN model \(N\) that contains \(L\) convolutional layers and its filters set \(W\), we refer to \(C = (c_1, c_2, ..., c_L)\) as the network structure of \(N\), where \(c_j\) is the channel number of the \(j\)-th layer. Channel pruning aims to remove a portion of filters in \(W\) while keeping a comparable or even better accuracy.
For any pruned model N0, we denote its structure as \(C^ { \prime } = \left( c _ { 1 } ^ { \prime } , c _ { 2 } ^ { \prime } , \ldots , c _ { L } ^ { \prime } \right)\), where \(c _ { j } ^ { \prime } \leq c _ { j }\) is the channel number of the pruned model in the \(j\)-th layer.
定义一下参数:模型 \(N\)、卷积层数 \(L\)、过滤器集合 \(W\)、结构集合 \(C = (c_1, c_2, ..., c_L)\) , \(c_j\) 是每层中的通道数。而剪枝中网络使用的机构集合定义为 \(C^ { \prime } = \left( c _ { 1 } ^ { \prime } , c _ { 2 } ^ { \prime } , \ldots , c _ { L } ^ { \prime } \right)\), \(c _ { j } ^ { \prime } \leq c _ { j }\)。
目标:移除过滤器集合 \(W\) 中一部分过滤器,精度基本不变
在前面提到,每层的 $c _ { j } ^ { \prime } \(的大小由\)c_j$ 即 filter 数量决定上限,如果不做处理,整个模型所有层一组合,情况太多。所以作者这边做了限制,每层的$c _ { j } ^ { \prime } \(只能取值为设定的\)c_j\(的梯度百分比,具体形式为:\)c _{ i } ^ { \prime } \in \left{ 0.1 c _{ i } , 0.2 c _{ i } , \ldots , \alpha c _{ i } \right} ^ { L }$
Given the training set \(\mathcal { T } _ { \text {train} }\) and test set , \(\mathcal { T } _ { \text {test} }\) we aim to find the optimal combination of \(C ^ { \prime }\), such that the pruned model \(\mathcal { N } ^ { \prime }\) trained/fine-tuned on\(\mathcal { T } _ { \text {train} }\) obtains the best accuracy. To that effect, we formulate our channel pruning problem as:
\[\left( C ^ { \prime } \right) ^ { * } = \underset { C ^ { \prime } } { \arg \max } \operatorname { acc } \left( \mathcal { N } ^ { \prime } \left( C ^ { \prime } , \mathbf { W } ^ { \prime } ; \mathcal { T } _ { \text {train} } \right) ; \mathcal { T } _ { \text {test} } \right) \]\(c _{ i } ^ { \prime } \in \left\{ 0.1 c _{ i } , 0.2 c _{ i } , \ldots , \alpha c _{ i } \right\} ^ { L }\)
where \(\mathbf { W } ^ { \prime }\) is the weights of pruned model trained/fine-tuned on \(\mathcal { T } _ { \text {train} }\), and \(acc(·)\) denotes the accuracy on \(\mathcal { T } _ { \text {test} }\) for \(\mathcal { N } ^ { \prime }\) with structure \(\mathcal { C } ^ { \prime }\).
在一次策略中(即一次自定义的结构集合中),根据\(C = (c_1, c_2, ..., c_L)\) 初始化不同的\(C^ { \prime } = \left( c _ { 1 } ^ { \prime } , c _ { 2 } ^ { \prime } , \ldots , c _ { L } ^ { \prime } \right)\),然后训练、微调并比较,获取精度最高时对应的参数
In particular, we initialize a set of \(n\) pruned structures \(\left\{ C _ { j } ^ { \prime } \right\} _ { j = 1 } ^ { n }\) with the \(i\)-th element \(c^{\prime}_{ji}\) of \(C^{\prime}_j\) randomly sampled from $ \left{ 0.1 c _{ i } , 0.2 c _{ i } , \ldots , \alpha c _{ i } \right}$. Accordingly, we obtain a set of pruned model \(\left\{ \mathcal { N } _ { j } ^ { \prime } \right\} _ { j = 1 } ^ { n }\) and a set of pruned weights \(\left\{ \mathbf { W } _ { j } ^ { \prime } \right\} _ { j = 1 } ^ { n }\).
Each pruned structure \(C^{\prime}_j\) represents a potential solution to the optimization problem.
自动结构搜索的具体做法是,随机初始化多组structures set。
然后作者得到多组 structures set 后,使用了ABC算法来更新这多组structures set。
这里插入ABC算法的相关介绍
ABC算法|[Artificial bee colony algorithm](Artificial bee colony algorithm - Wikipedia)
1、原理
标准的ABC算法将人工蜂群分为三类:被雇佣蜂,观察蜂以及侦察蜂。
- 被雇佣蜂负责采蜜,根据记忆中的食物位置,负责搜索食物邻域内的其他食物;
- 被雇佣蜂将找到的食物位置信息分享给观察蜂,观察蜂选择哪一个是更好的食物来源(当然,去了蜜源之后,也会在其领域周围随机搜索新蜜源);
- 当在限定的次数内都没有搜索到一个高于阈值的理想食物来源,需要抛弃食物来源,被雇佣蜂成为侦察蜂,随机搜索新的食物来源。
2、实现
2.1 刚开始,对整个蜂群进行初始化。蜂群的规模为2SN,被雇佣蜂和观察蜂的数量相等,均为SN。蜜源的数量与采蜜蜂相等,也为SN。使用 \({\displaystyle X_{i}=\{x_{i,1},x_{i,2},\ldots ,x_{i,n}\}}\) 表示第 \(i\) 次的搜索结构,\(n\) 表示维度。
2.2 现在受雇佣蜂根据记忆位置 \(X_{i}\) 生成新的位置 \(V_i\),生成公式为:
\[{\displaystyle v_{i,k}=x_{i,k}+\Phi _{i,k}\times (x_{i,k}-x_{j,k})} \]\(\Phi _{i,k}\) 是 [-1, 1] 中的随机数,\(x_{i,n}\) 是随机第 \(j\) 次方案的随机第 \(k\) 维度数据。
2.3 观察蜂观察这两个位置的食物:根据 \(X_i\) 和 \(V_i\) 的适应值(遗传算法中的一个说法)比较优劣,选择更优的那个。
2.4 在一定次数以后(称为 limit),对比这些蜜源位置的适应值,记录全局最优的蜜源。公式如下:$${\displaystyle P_{i}={\frac {\mathrm {fit} _{i}}{\sum _{j}{\mathrm {fit} _{j}}}}}$$
2.5 如果在一定次数内位置没有变化,那么就放弃这个食物来源,重现初始化一个食物来源
算法流程

[论文分享]Channel Pruning via Automatic Structure Search
标签:rac HERE move 好的 次数 comm training assign 通过
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/xiazheng/p/14118977.html