标签:index rap ann 语言 ack item bre inpu cas
题目集1-3-的总结
前言:
第一次题目的难度对我来说还是比较简单,其中的算法和代码结构与C语言较相似用最基本的操作就可以完成。在完成这次题目时主要用到的知识点有:if()选择结构、Java的输入对象的建立、for()循环的使用、Java的控制台输出。其中在使用PTA测试与提交源码时学到了一些新手入坑必备的使用技巧:1、提交Java源码时,Java的代码的public修饰的类名必须时以Main命名的,且不能带入Java代码文件储存报包的开头,不然将会被PTA报错。2、还有在题集1中的第8题的角的运算中由于都是float型的数据量数据的相乘要允许极小的误差检测,不然不能PTA的检测。
第二次的题目相对于第一次的题目难度来说是变得更难了,但难度还算是适中,中要多注意其中的检测点和编辑代码是自己的逻辑不要混乱,在网上学习合适的算法并加以运用就可完成此次的作业。在完成此次作业的过程中最主要学习到的新知识有:字符的分割与相关运算、数组对象的建立申请与相关使用、Boolean变量类型的使用、swich――case的使用、
第三次题目的难度不论较前两次来说,你还是对于我的个人来说都比较的难,在写此次作业的过成中主要用到的新知识有,Java类的编写机器对象的建立与使用、正则表达式的编写与使用、String类相关的使用,与其中相关方法的运用。
设计与分析:
题目集1部分题目的分析及其源代码(7-8):
先从键盘输入一个整数n,n代表需要排序的整数数量,然后再从键盘输入n个整数,对这些数从小到大排序并输出。
先从键盘输入一个整数n,之后回车 再从键盘输入n个整数,整数之间用一个或多个空格分隔
按如下示例输出排序后的数据:The sorted numbers are:排序后的n个数,每个输出的整数之后有一个空格作为分隔符
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
10
3 5 2 4 76 89 56 4 3 8在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
The sorted numbers are:2 3 3 4 4 5 8 56 76 89 1 public class Main { 2 3 public static void main(String[] args) { 4 java.util.Scanner in = new java.util.Scanner(System.in); 5 int n; 6 n=in.nextInt(); 7 int []a=new int[n]; 8 int i=0,j=0,b; 9 for(i=0;i<n;i++) 10 { 11 a[i]=in.nextInt(); 12 } 13 for(i=0;i<n;i++) 14 { 15 for(j=i;j<n;j++) 16 { 17 if(a[i]>a[j]) 18 { 19 b=a[i]; 20 a[i]=a[j]; 21 a[j]=b; 22 } 23 } 24 } 25 for(i=0;i<n;i++) 26 { 27 if(i==0) 28 {System.out.print("The sorted numbers are:" + a[i]+" ");} 29 else 30 { 31 System.out.print(a[i]+" "); 32 } 33 34 } 35 } 36 }
题目与代码分析如下:
该题主要功能是排序与相应的输入:
输入主要是用for循环进行输入,排序我的主要使用选择排序(如下)

心得:要注意排序过程中的算法与开始于最后的数的变换。
输入三角形三条边,判断该三角形为什么类型的三角形。
在一行中输入三角形的三条边的值(实型数),可以用一个或多个空格或回车分隔,其中三条边的取值范围均为[1,200]。
(1)如果输入数据非法,则输出“Wrong Format”; (2)如果输入数据合法,但三条边不能构成三角形,则输出“Not a triangle”; (3)如果输入数据合法且能够成等边三角形,则输出“Equilateral triangle”; (3)如果输入数据合法且能够成等腰直角三角形,则输出“Isosceles right-angled triangle”; (5)如果输入数据合法且能够成等腰三角形,则输出“Isosceles triangle”; (6)如果输入数据合法且能够成直角三角形,则输出“Right-angled triangle”; (7)如果输入数据合法且能够成一般三角形,则输出“General triangle”。
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
50 50 50.0在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
Equilateral triangle在这里给出一组输入。例如:
60.2 60.2 80.56在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
Isosceles triangle在这里给出一组输入。例如:
0.5 20.5 80在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
Wrong Format1 public class Main { 2 3 public static void main(String[] args) { 4 java.util.Scanner in = new java.util.Scanner(System.in); 5 double a,b,c,d; 6 a=in.nextDouble(); 7 b=in.nextDouble(); 8 c=in.nextDouble(); 9 10 if(a<1||a>200||b<1||b>200||c<1||c>200) 11 { 12 System.out.println("Wrong Format"); 13 } 14 else 15 { 16 if(b>a&&b>c) 17 { 18 d=b; 19 b=a; 20 a=d; 21 } 22 if(c>a&&c>b) 23 { 24 d=c; 25 c=a; 26 a=d; 27 } 28 if((b+c)<=a) 29 { 30 System.out.println("Not a triangle"); 31 } 32 if((b+c)>a&&(b*b+c*c)-a*a<=0.0000001) 33 { 34 if(b==c) 35 { 36 System.out.println("Isosceles right-angled triangle"); 37 } 38 else 39 { 40 System.out.println("Right-angled triangle"); 41 } 42 } 43 if((b+c)>a&&(b*b+c*c)-a*a>0.0000001) 44 { 45 if(a==b||a==c||b==c) 46 { 47 if(a==b&&a==c) 48 { 49 System.out.println("Equilateral triangle"); 50 } 51 else 52 {System.out.println("Isosceles triangle");} 53 } 54 else 55 { 56 System.out.println("General triangle"); 57 } 58 } 59 60 } 61 62 63 } 64 }
实现该题功能的主要算法是判断角的状态,前期可以比较两角的核查相比,后面要注重直角的判断要主要的是由于输入的数据为float型的,所以遇到直角的判段要允许要有极小的误差存在

不然会有测试点会过不了。
心得:本题主要要注意的是标准数据的输入于及判断;要用(float型的)
输入年月日的值(均为整型数),输出该日期的下一天。 其中:年份的合法取值范围为[1820,2020] ,月份合法取值范围为[1,12] ,日期合法取值范围为[1,31] 。 注意:不允许使用Java中和日期相关的类和方法。
要求:Main类中必须含有如下方法,签名如下:
public static void main(String[] args);//主方法
public static boolean isLeapYear(int year) ;//判断year是否为闰年,返回boolean类型
public static boolean checkInputValidity(int year,int month,int day);//判断输入日期是否合法,返回布尔值
public static void nextDate(int year,int month,int day) ; //求输入日期的下一天在一行内输入年月日的值,均为整型数,可以用一到多个空格或回车分隔。
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
2020 3 10在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
Next date is:2020-3-11在这里给出一组输入。例如:
2025 2 10在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
Wrong Format本题解题代码如下:
1 public class Main { 2 public static void main(String[] args) { 3 java.util.Scanner in = new java.util.Scanner(System.in); 4 int a,b,c; 5 a=in.nextInt();//年 6 b=in.nextInt();//月 7 c=in.nextInt();//日 8 if(Main.checkInputValidity(a,b,c)) 9 { 10 Main.nextDate(a,b,c); 11 } 12 else 13 { 14 System.out.println("Wrong Format"); 15 } 16 } 17 public static boolean isLeapYear(int year) 18 { 19 if((year%100!=0&&year%4==0)||(year%400==0)) 20 { 21 return true; 22 } 23 else 24 { 25 return false; 26 } 27 } 28 public static boolean checkInputValidity(int year,int month,int day) 29 { 30 if(isLeapYear(year)) 31 { 32 if(month==2&&(day<=0||day>29)) 33 { 34 return false; 35 } 36 } 37 if(!isLeapYear(year)) 38 { 39 if(month==2&&(day<=0||day>28)) 40 { 41 return false; 42 } 43 } 44 if(month==1||month==3||month==5||month==7||month==8||month==10||month==12) 45 { 46 if(day<=0||day>31) 47 { 48 return false; 49 } 50 } 51 if(month==4||month==6||month==9||month==11) 52 { 53 if(day<=0||day>30) 54 { 55 return false; 56 } 57 } 58 if(year<1820||year>2020||month<1||month>12||day<1||day>31) 59 { 60 return false; 61 } 62 return true; 63 } 64 public static void nextDate(int year,int month,int day) 65 { 66 int i=0; 67 if(month==1||month==3||month==5||month==7||month==8||month==10) 68 { 69 i=1; 70 } 71 else if(month==12) 72 { 73 i=12; 74 } 75 else if(month==2) 76 { 77 i=2; 78 } 79 else 80 { 81 i=3; 82 } 83 switch(i) 84 { 85 case 1:if(day==31) { 86 System.out.println("Next date is:"+year+"-"+(month+1)+"-1"); 87 } 88 else { 89 System.out.println("Next date is:"+year+"-"+month+"-"+(day+1)); 90 } 91 break; 92 93 case 2: 94 if(Main.isLeapYear(year)) 95 { 96 if(day==29) { 97 System.out.println("Next date is:"+year+"-"+(month+1)+"-1"); 98 } 99 else { 100 System.out.println("Next date is:"+year+"-"+month+"-"+(day+1)); 101 } 102 } 103 else { 104 if(day==28) { 105 System.out.println("Next date is:"+year+"-"+(month+1)+"-1"); 106 } 107 else { 108 System.out.println("Next date is:"+year+"-"+month+"-"+(day+1)); 109 } 110 } 111 break; 112 113 114 case 3:if(day==30) { 115 System.out.println("Next date is:"+year+"-"+(month+1)+"-1"); 116 } 117 else { 118 System.out.println("Next date is:"+year+"-"+month+"-"+(day+1)); 119 } 120 break; 121 case 12:if(day==31) { 122 System.out.println("Next date is:"+(year+1)+"-"+"1"+"-"+"1"); 123 } 124 else { 125 System.out.println("Next date is:"+year+"-"+month+"-"+(day+1)); 126 } 127 break; 128 } 129 } 130 }
此题的分析如下:
这道题接触到的新知识由JAVA静态方法的构建与引用
实现这题功能的主要思想为对于输入年份和特殊日期的判断,要是特殊日期的话要进行相应的计算。
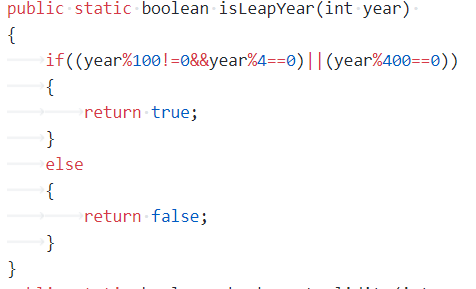
我的主要算法是用if else的选择嵌套和switch()case结构来判断并运算。
心得:要注意闰年二月底的日期,于每月的最后一天的判断。
输入年月日的值(均为整型数),同时输入一个取值范围在[-10,10] 之间的整型数n,输出该日期的前n天(当n > 0时)、该日期的后n天(当n<0时)。
其中年份取值范围为 [1820,2020] ,月份取值范围为[1,12] ,日期取值范围为[1,31] 。
注意:不允许使用Java中任何与日期有关的类或方法。
在一行中输入年月日的值以及n的值,可以用一个或多个空格或回车分隔。
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
2018 6 19 8 在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
8 days ago is:2018-6-11在这里给出一组输入。例如:
2018 6 19 -8 在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
-8 days ago is:2018-6-27
此题的代码如下:
1 public class Main { 2 public static void main(String[] args) { 3 java.util.Scanner in = new java.util.Scanner(System.in); 4 int a,b,c,d; 5 a=in.nextInt();//年 6 b=in.nextInt();//月 7 c=in.nextInt();//日Math.abs(); 8 d=in.nextInt(); 9 if(Main.checkInputValidity(a,b,c)) 10 { 11 Main.nextDate(a,b,c,d); 12 } 13 else 14 { 15 System.out.println("Wrong Format"); 16 } 17 } 18 public static boolean isLeapYear(int year) 19 { 20 if((year%100!=0&&year%4==0)||(year%400==0)) 21 { 22 return true; 23 } 24 else 25 { 26 return false; 27 } 28 } 29 public static boolean checkInputValidity(int year,int month,int day) 30 { 31 32 if(isLeapYear(year)) 33 { 34 if(month==2&&(day<=0||day>29)) 35 { 36 return false; 37 } 38 } 39 if(!isLeapYear(year)) 40 { 41 if(month==2&&(day<=0||day>28)) 42 { 43 return false; 44 } 45 } 46 if(month==1||month==3||month==5||month==7||month==8||month==10||month==12) 47 { 48 if(day<=0||day>31) 49 { 50 return false; 51 } 52 } 53 if(month==4||month==6||month==9||month==11) 54 { 55 if(day<=0||day>30) 56 { 57 return false; 58 } 59 } 60 if(year<1820||year>2020||month<1||month>12||day<1||day>31) 61 { 62 return false; 63 } 64 return true; 65 } 66 public static void nextDate(int year,int month,int day,int d) 67 { int i=0; 68 d=-d; 69 if(month==1||month==3||month==5||month==7||month==8||month==10||month==12) 70 { 71 if(day+d>31) 72 { 73 if(month==12) 74 { 75 System.out.println((-d)+" days ago is:"+(year+1)+"-1"+"-"+(day+d-31)); 76 } 77 else 78 { 79 System.out.println((-d)+" days ago is:"+year+"-"+(month+1)+"-"+(day+d-31));} 80 } 81 else if(day+d>=1&&day+d<=31) 82 { 83 System.out.println((-d)+" days ago is:"+year+"-"+(month)+"-"+(day+d)); 84 } 85 else 86 { 87 if(month==1) 88 { 89 System.out.println((-d)+" days ago is:"+(year-1)+"-"+"12"+"-"+(day+d+31)); 90 } 91 else if(month==5||month==7||month==10||month==12) 92 { 93 System.out.println((-d)+" days ago is:"+year+"-"+(month-1)+"-"+(day+d+30)); 94 } 95 else if(month==3&&Main.isLeapYear(year)) 96 { 97 System.out.println((-d)+" days ago is:"+year+"-"+(month-1)+"-"+(day+d+29)); 98 } 99 else if(month==3&&!Main.isLeapYear(year)) 100 { 101 System.out.println((-d)+" days ago is:"+year+"-"+(month-1)+"-"+(day+d+28)); 102 } 103 else 104 { 105 System.out.println((-d)+" days ago is:"+year+"-"+(month-1)+"-"+(day+d+31)); 106 } 107 } 108 109 } 110 111 else if(month==2) 112 { 113 if(day+d>29&&Main.isLeapYear(year)) 114 { 115 System.out.println((-d)+" days ago is:"+year+"-"+(month+1)+"-"+(day+d-29)); 116 } 117 else if(day+d>28&&!Main.isLeapYear(year)) 118 { 119 System.out.println((-d)+" days ago is:"+year+"-"+(month+1)+"-"+(day+d-28)); 120 } 121 else if(day+d>=1&&day+d<=29) 122 { 123 System.out.println((-d)+" days ago is:"+year+"-"+month+"-"+(day+d)); 124 } 125 else 126 { 127 System.out.println((-d)+" days ago is:"+year+"-"+(month-1)+"-"+(day+d+31)); 128 } 129 } 130 else 131 { 132 if(day+d>30) 133 { 134 System.out.println((-d)+" days ago is:"+year+"-"+(month+1)+"-"+(day+d-30)); 135 } 136 else if(day+d>=1&&day+d<=30) 137 { 138 System.out.println((-d)+" days ago is:"+year+"-"+month+"-"+(day+d)); 139 } 140 else 141 { 142 System.out.println((-d)+" days ago is:"+year+"-"+(month-1)+"-"+(day+d+31)); 143 } 144 } 145 } 146 }
该题的分析于其思路如下
此题的分析下来与前一题的结构差不多,但要值得注意的是用户的输入的是前几天的天数,在后面的运算中要将其转换成其的相反数输出时 也进行一次转换。
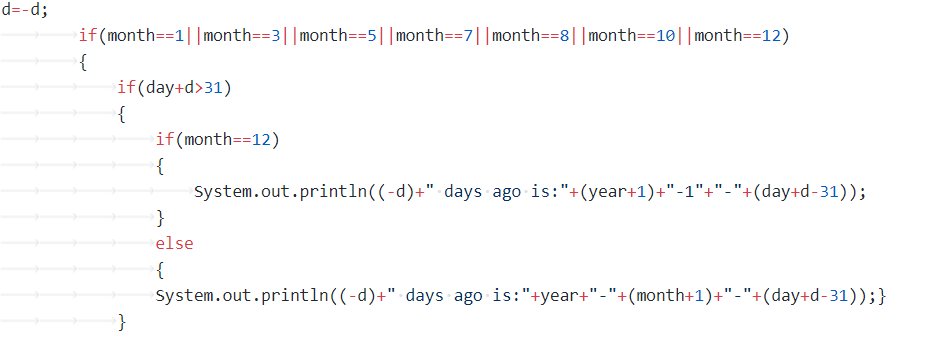
心得:与前一题查不多,要着重注意输入日期的判断,所用的结构与上一题也大同小异。虽然如此但我认为这题是比较上一题时更难一点的,更多了一步判断用户的输入前进日期。
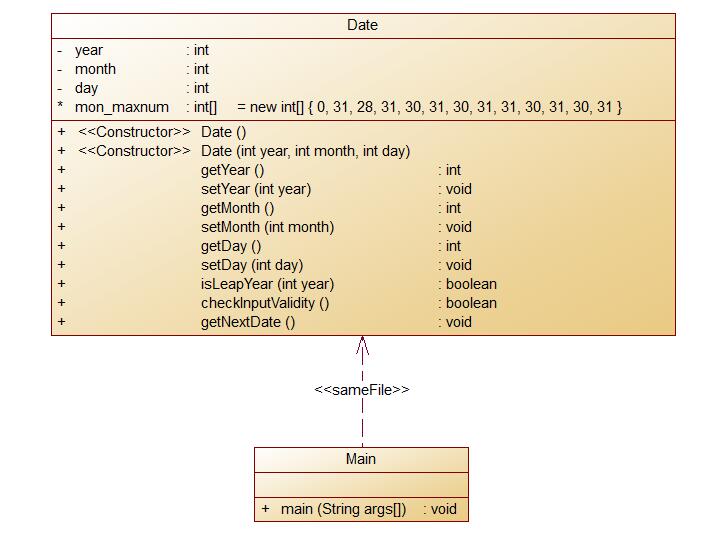
定义一个类Date,包含三个私有属性年(year)、月(month)、日(day),均为整型数,其中:年份的合法取值范围为[1900,2000] ,月份合法取值范围为[1,12] ,日期合法取值范围为[1,31] 。 注意:不允许使用Java中和日期相关的类和方法,否则按0分处理。
要求:Date类结构如下图所示:
在一行内输入年月日的值,均为整型数,可以用一到多个空格或回车分隔。
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
1912 12 25在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
Next day is:1912-12-26在这里给出一组输入。例如:
2001 2 30在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
Date Format is Wrong
本题代码如下:
1 import java.util.Scanner; 2 3 public class Main { 4 5 public static void main(String[] args) { 6 Scanner in=new Scanner(System.in); 7 Date da=new Date(in.nextInt(),in.nextInt(),in.nextInt()); 8 if(!da.checklnputValidity()) 9 { 10 System.out.println("Date Format is Wrong"); 11 } 12 else 13 { 14 da.getNextDate(); 15 } 16 } 17 18 } 19 class Date 20 { 21 private int day,month,year; 22 int mon_maxnum[]=new int[] {0,31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31}; 23 Date(int year,int month,int day) 24 { 25 this.day=day; 26 this.month=month; 27 this.year=year; 28 } 29 boolean checklnputValidity() 30 { 31 if(this.isleapYear(this.year)) 32 { 33 mon_maxnum[2]++; 34 } 35 if(year<1900||year>2000||month>12||month<1||day<1) 36 { 37 return false; 38 } 39 if(day>mon_maxnum[month]) 40 { 41 return false; 42 } 43 return true; 44 } 45 void setterDay(int day) 46 { 47 this.day=day; 48 } 49 void setterMonth(int month) 50 { 51 this.month=month; 52 } 53 void setterYear(int year) 54 { 55 this.year=year; 56 } 57 int getterDay() 58 { 59 return day; 60 } 61 int getterMonth() 62 { 63 return month; 64 } 65 int getterYear() 66 { 67 return year; 68 } 69 boolean isleapYear(int year) 70 { 71 if((year%100!=0&&year%4==0)||(year%400==0)) 72 { 73 return true; 74 } 75 return false; 76 } 77 void getNextDate() 78 { 79 if(this.isleapYear(this.year)) 80 { 81 mon_maxnum[2]=29; 82 } 83 if(day==mon_maxnum[this.month]) 84 { 85 if(month==12) 86 { 87 System.out.println("Next day is:"+(year+1)+"-1-1"); 88 } 89 else 90 { 91 System.out.println("Next day is:"+year+"-"+(month+1)+"-1"); 92 } 93 } 94 else 95 { 96 System.out.println("Next day is:"+year+"-"+month+"-"+(day+1)); 97 } 98 } 99 }
本题分析本题要求要构建名为Data的类,并要求用该类创建一个对象,并运用该对象实现相应的功能。具体的算法与上两题差不多,但我做出了一小部分的改进。,该题的关键在于类的构建于对象的创建于使用
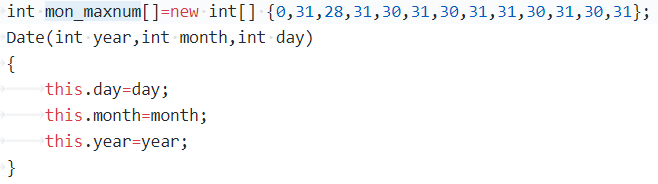
运用该结构可以快速判断输入的月份于日期。
以下是对象的构建与使用:
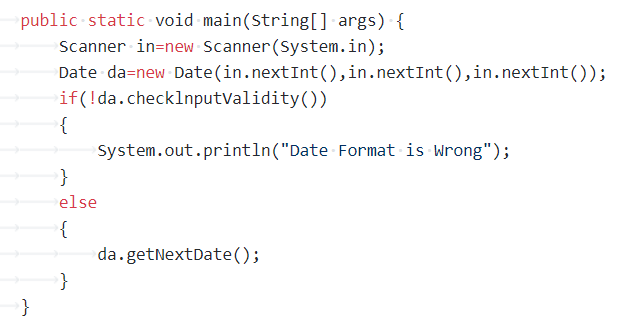
心得:对于类的构建有多种方法,构造好类,并建立相应的对象可以大大减少代码的行数于是代码的结构更加的简单。
编写程序性,实现对简单多项式的导函数进行求解。详见作业指导书。 OO作业3-3题目说明.pdf
在一行内输入一个待计算导函数的表达式,以回车符结束。
输出格式见输入输出示例。
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
-2* x^-2+ 5*x^12-4*x+ 12在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
4*x^-3+60*x^11-4在这里给出一组输入。例如:
2*x^6-0*x^7+5在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
Wrong Format代码如下:
1 import java.util.Scanner; 2 import java.util.regex.Matcher; 3 import java.util.regex.Pattern; 4 public class Main { 5 6 public static void main(String[] args) { 7 Scanner in=new Scanner(System.in); 8 String s = in.nextLine(); 9 String input=new String (s.replace(" ","")); 10 input=input.replace("-x","-1*x"); 11 12 Cef ce = new Cef(); 13 String totalRegex = "([-+]?([1-9]+[0-9]*(\\*)?)?x?(\\^[+-]?[1-9]+[0-9]*)?)+"; 14 String sbuRegex = "[-+]?([1-9]+[0-9]*(\\*)?)?x?(\\^[+-]?[1-9]+[0-9]*)?"; 15 int i = 0; 16 long quotiety = 0; 17 long index = 0; 18 String a[] = new String [100]; 19 if(ce.isconstant(input)) 20 { 21 System.out.println(0); 22 } 23 else 24 { 25 boolean bl=Pattern.matches(totalRegex, input); 26 if(bl==true) 27 { 28 Pattern pattern = Pattern.compile(sbuRegex); 29 Matcher matcher=pattern.matcher(input); 30 while(matcher.find()) 31 { 32 i++; 33 String tmp=matcher.group(); 34 a[i]=tmp; 35 int begin=matcher.start(); 36 int end=matcher.end(); 37 //System.out.println("项:"+tmp+" begin:"+begin+" end:"+ (end-1)); 38 if(end==input.length()) 39 { 40 break; 41 } 42 } 43 int x=0,y=0; 44 int e=0; 45 int t=1; 46 int p=1; 47 //System.out.println(a[t].charAt((int)a[t].length()-1)==‘x‘); 48 for(t=1;t<=i;t++) 49 { 50 if(a[t].equals("x")) 51 { 52 a[t]=a[t].replace("x","1*x"); 53 } 54 if(ce.isconstant(a[t])) 55 { 56 p++; 57 continue; 58 } 59 e=0; 60 x=0; 61 y=0; 62 e=a[t].indexOf("x",-1); 63 if(a[t].indexOf("x",-1)!=-1) 64 { 65 if(ce.isture(a[t].substring(0,1))) 66 { 67 x=1; 68 } 69 quotiety = ce.number(a[t].substring(x,(a[t].indexOf("x",-1)-1)),a[t].charAt(0)); 70 71 if(a[t].charAt((int)a[t].length()-1)==‘x‘) 72 { 73 if(quotiety>0) 74 { 75 if(t==1) 76 System.out.println(quotiety); 77 else 78 System.out.println("+"+quotiety); 79 } 80 else 81 System.out.println(quotiety); 82 continue; 83 } 84 else 85 { 86 if(ce.isture(a[t].substring((e+2),(e+3)))) 87 { 88 y=1; 89 } 90 index = ce.number(a[t].substring((e+2+y),a[t].length()),a[t].charAt(e+2)); 91 } 92 } 93 if((quotiety*index)>0&&t!=p) 94 { 95 if(index-1!=1) 96 System.out.print("+"+(quotiety*index)+"*x^"+(index-1)); 97 else 98 System.out.print("+"+(quotiety*index)+"*x"); 99 } 100 if((quotiety*index)<0&&t!=p) 101 { 102 if((index-1)!=1) 103 System.out.print((quotiety*index)+"*x^"+(index-1)); 104 else 105 System.out.print((quotiety*index)+"*x"); 106 } 107 if(t==p) 108 { 109 if(index-1!=1) 110 System.out.print((quotiety*index)+"*x^"+(index-1)); 111 else 112 System.out.print((quotiety*index)+"*x"); 113 } 114 115 116 } 117 118 } 119 else 120 { 121 System.out.println("Wrong Format"); 122 } 123 } 124 125 } 126 127 } 128 class Cef 129 { 130 boolean isconstant(String s) 131 { 132 return s.matches("^[-+]?[0-9]*\\.?[0-9]*"); 133 } 134 boolean isture(String s) 135 { 136 return s.matches("[+-]+"); 137 } 138 long number(String str,char f) 139 { 140 int r=1; 141 if(f==‘-‘) 142 { 143 r=-1; 144 } 145 int n=0; 146 int ia[] = new int[str.length()]; 147 for(int i=0;i<str.length();i++) 148 { 149 char c = str.charAt(i); 150 } 151 for(int j=0;j<str.length();j++){ 152 char c = str.charAt(j); 153 ia[j]=(int)(c-‘0‘); 154 } 155 for(int k = 0;k<str.length();k++) 156 { 157 n=(int) (n+ia[k]*Math.pow(10,str.length()-1-k)); 158 } 159 return (n*r); 160 } 161 }
题目分析:
该题的主要思想由有几步
①消去用户输入字符串中的空格
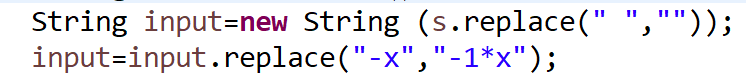
②运用正则表达式来判断用户的输入是否符合规则。

③分割客户输入的字符串并将其储存下来。

④运用字符串的相应操作将其单个表达式的符号位于数字为识别出来,并转成数值
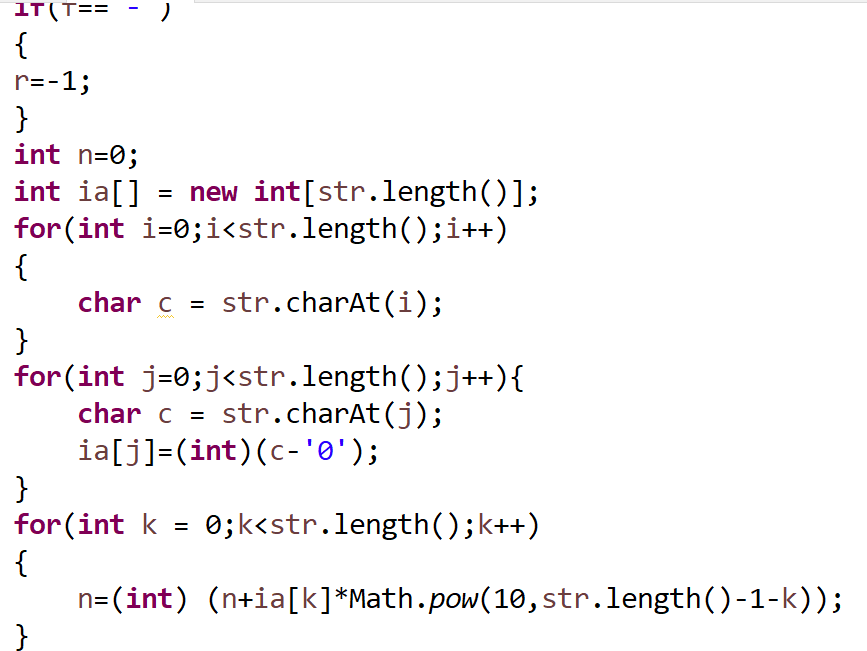
⑤最后在再来运算并进行相应的输出
心得:该题对于刚学习正则表达式和字符串操作的我们来说难度是比较高的,我的代码也只能实现一部分功能,并非所有测试点都能通过,其中有一部分要用到JAVA中的大数操作,但在本代码中并未使用
我觉得实现本题功能的关键在于对于正则表达式的运用,还有字符串的相应操作。
踩坑心得:三次题目集做下来进一步对JAVA的编写体系有所了解,在编写JAVA代码中遇到运行错误于逻辑错误,其实都是一些小错误,大括号的问题,格式输出的问题,问题较多的
其实还是在输入的判断上,有时会有逻辑上的冲突,导致代码的运行错误。还有一些特殊的错误,比如在最后一题会因为字符串的判断出现问题而引起字符串数组的溢出非法访问。
还有前集体的输入判断出现问题。
改进建议:对于我的部分代码我觉得可以在后期的学习后进一步进行优化改进。很多的成分都有赘余,在后期很多的结构可以多优化,还有最后一题,我的功能其实并没有完全实现,在后期
也可以慢慢完善。但对于PTA我也觉得有些可以多有改进
比如运行超时问题。
总结:对于这三次题目集我觉得是一个循序渐进的过程,从C语言过度到面向对象的一个过成,我觉得这样每周独有习题是挺不错的,但到最后题目的难度的确增长的太快了,到了最后一题能拿到满分的任已经是屈指可数了,
因此我希望以后的较难题目可以由老师在课堂上进行相应的讲解这样我相信我们可以学到更多的知识。
标签:index rap ann 语言 ack item bre inpu cas
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/zhangyukun233250/p/14616803.html