标签:数据 持久 virtual 可用性 producer weixin header 类型 imp
RabbitMQ 相较于其他消息队列,有一系列防止消息丢失的措施,拥有强悍的高可用性能,它的吞吐量可能没有其他消息队列大,但是其消息的保障性出类拔萃,被广泛用于金融类业务。
AMQP: Advanced Message Queuing Protocol 高级消息队列协议
AMQP定义:是具有现代特征的二进制协议。是一个提供统一消息服务的应用层标准高级消息队列协议,是应用层协议的一个开放标准,为面向消息的中间件设计。
Erlang语言最初在于交换机领域的架构模式,这样使得RabbitMQ在Broker之间进行数据交互的性能是非常优秀的,Erlang的优点: Erlang有着和原生Socket一样的延迟。
RabbitMQ是一个开源的消息代理和队列服务器,用来通过普通协议在完全不同的应用之间共享数据, RabbitMQ是使用Erlang语言来编写的,并且RabbitMQ是基于AMQP协议的。关注公众号Java技术栈获取系列RabbitMQ教程。
生产者发送消息到指定的 Exchange,Exchange 依据自身的类型(direct、topic等),根据 routing key 将消息发送给 0 - n 个 队列,队列再将消息转发给了消费者。
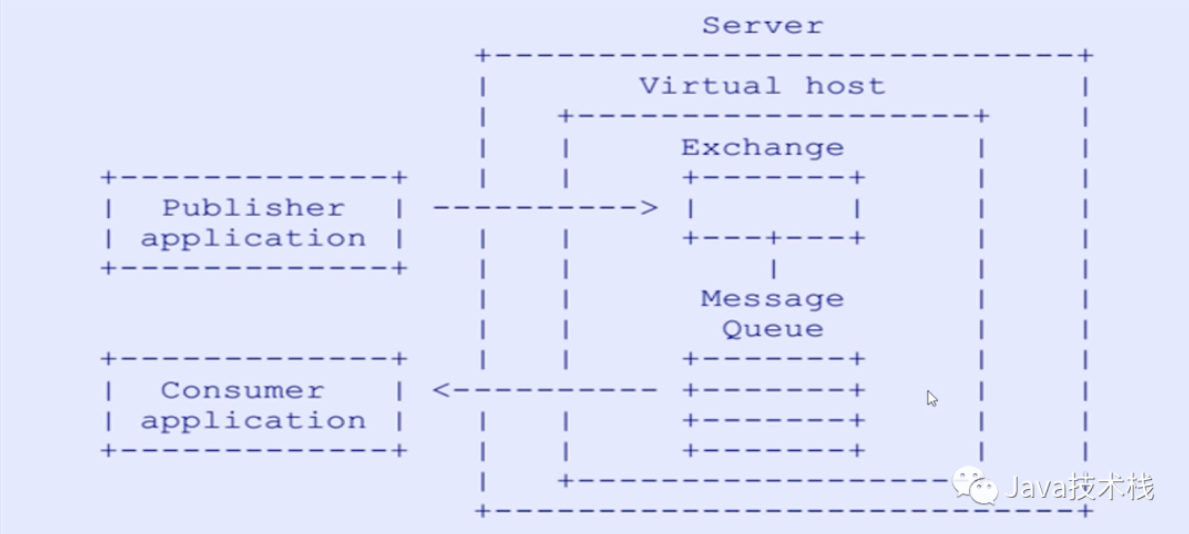
Server: 又称Broker, 接受客户端的连接,实现AMQP实体服务,这里指RabbitMQ 服务器
Connection: 连接,应用程序与Broker的网络连接。
Channel: 网络信道,几乎所有的操作都在 Channel 中进行,Channel是进行消息读写的通道。客户端可建立多个Channel:,每个Channel代表一个会话任务。
Virtual host: 虚似地址,用于迸行逻辑隔离,是最上层的消息路由。一个 Virtual Host 里面可以有若干个 Exchange和 Queue ,同一个 VirtualHost 里面不能有相同名称的 Exchange 或 Queue。权限控制的最小粒度是Virtual Host。
Binding: Exchange 和 Queue 之间的虚拟连接,binding 中可以包含 routing key。
Routing key: 一 个路由规则,虚拟机可用它来确定如何路由一个特定消息,即交换机绑定到 Queue 的键。
Queue: 也称为Message Queue,消息队列,保存消息并将它们转发给消费者。
消息,服务器和应用程序之间传送的数据,由 Properties 和 Body 组成。Properties 可以对消息进行修饰,比如消息的优先级、延迟等高级特性;,Body 则就 是消息体内容。
properties 中我们可以设置消息过期时间以及是否持久化等,也可以传入自定义的map属性,这些在消费端也都可以获取到。
import com.rabbitmq.client.AMQP;
import com.rabbitmq.client.Channel;
import com.rabbitmq.client.Connection;
import com.rabbitmq.client.ConnectionFactory;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
public class MessageProducer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//1. 创建一个 ConnectionFactory 并进行设置
ConnectionFactory factory = new ConnectionFactory();
factory.setHost("localhost");
factory.setVirtualHost("/");
factory.setUsername("guest");
factory.setPassword("guest");
//2. 通过连接工厂来创建连接
Connection connection = factory.newConnection();
//3. 通过 Connection 来创建 Channel
Channel channel = connection.createChannel();
//4. 声明 使用默认交换机 以队列名作为 routing key
String queueName = "msg_queue";
/**
* deliverMode 设置为 2 的时候代表持久化消息
* expiration 意思是设置消息的有效期,超过10秒没有被消费者接收后会被自动删除
* headers 自定义的一些属性
* */
//5. 发送
Map<String, Object> headers = new HashMap<String, Object>();
headers.put("myhead1", "111");
headers.put("myhead2", "222");
AMQP.BasicProperties properties = new AMQP.BasicProperties().builder()
.deliveryMode(2)
.contentEncoding("UTF-8")
.expiration("100000")
.headers(headers)
.build();
String msg = "test message";
channel.basicPublish("", queueName, properties, msg.getBytes());
System.out.println("Send message : " + msg);
//6. 关闭连接
channel.close();
connection.close();
}
}
import com.rabbitmq.client.*;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.Map;
public class MessageConsumer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
//1. 创建一个 ConnectionFactory 并进行设置
ConnectionFactory factory = new ConnectionFactory();
factory.setHost("localhost");
factory.setVirtualHost("/");
factory.setUsername("guest");
factory.setPassword("guest");
factory.setAutomaticRecoveryEnabled(true);
factory.setNetworkRecoveryInterval(3000);
//2. 通过连接工厂来创建连接
Connection connection = factory.newConnection();
//3. 通过 Connection 来创建 Channel
Channel channel = connection.createChannel();
//4. 声明
String queueName = "msg_queue";
channel.queueDeclare(queueName, false, false, false, null);
//5. 创建消费者并接收消息
Consumer consumer = new DefaultConsumer(channel) {
@Override
public void handleDelivery(String consumerTag, Envelope envelope,
AMQP.BasicProperties properties, byte[] body)
throws IOException {
String message = new String(body, "UTF-8");
Map<String, Object> headers = properties.getHeaders();
System.out.println("head: " + headers.get("myhead1"));
System.out.println(" [x] Received ‘" + message + "‘");
System.out.println("expiration : "+ properties.getExpiration());
}
};
//6. 设置 Channel 消费者绑定队列
channel.basicConsume(queueName, true, consumer);
}
}
Exchange 就是交换机,接收消息,根据路由键转发消息到绑定的队列。有很多的 Message 进入到 Exchange 中,Exchange 根据 Routing key 将 Message 分发到不同的 Queue 中。
RabbitMQ 中的 Exchange 有多种类型,类型不同,Message 的分发机制不同,如下:
/**
* Declare an exchange, via an interface that allows the complete set of
* arguments.
* @see com.rabbitmq.client.AMQP.Exchange.Declare
* @see com.rabbitmq.client.AMQP.Exchange.DeclareOk
* @param exchange the name of the exchange
* @param type the exchange type
* @param durable true if we are declaring a durable exchange (the exchange will survive a server restart)
* @param autoDelete true if the server should delete the exchange when it is no longer in use
* @param internal true if the exchange is internal, i.e. can‘t be directly
* published to by a client.
* @param arguments other properties (construction arguments) for the exchange
* @return a declaration-confirm method to indicate the exchange was successfully declared
* @throws java.io.IOException if an error is encountered
*/
Exchange.DeclareOk exchangeDeclare(String exchange,
String type,boolean durable,
boolean autoDelete,boolean internal,
Map<String, Object> arguments) throws IOException;
标签:数据 持久 virtual 可用性 producer weixin header 类型 imp
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/123-shen/p/14780564.html