标签:def 字段 cto mod uuid inf ping 默认值 single
请求体的数据校验是使用Pydantic来进行声明,然后校验的。
from typing import Optional from fastapi import FastAPI from pydantic import BaseModel class Item(BaseModel): name: str description: Optional[str] = None price: float tax: Optional[float] = None app = FastAPI() @app.post("/items/") async def create_item(item: Item): print(item.name) # 获取请求体中的值 return item
请求体内容通过Item类提前定义好,内容包含4个字段,其中description和tax为可选字段,所以请求体内容为:
{ "name": "hello", "price": 30.2 }
也是可行的。值得注意的是声明参数时将其申明为定义好的Item类型。
如果调用方对于请求体不知道如何使用,可以通过额外的配置项进行说明:
... class Item(BaseModel): name: str description: Optional[str] = None price: float tax: Optional[float] = None class Config: schema_extra = { "example": { "name": "apple", "description": "this is a fruit ...", "price": 3.14, "tax": 1.2 } } ...
这样在API接口处会有对应的示例说明:
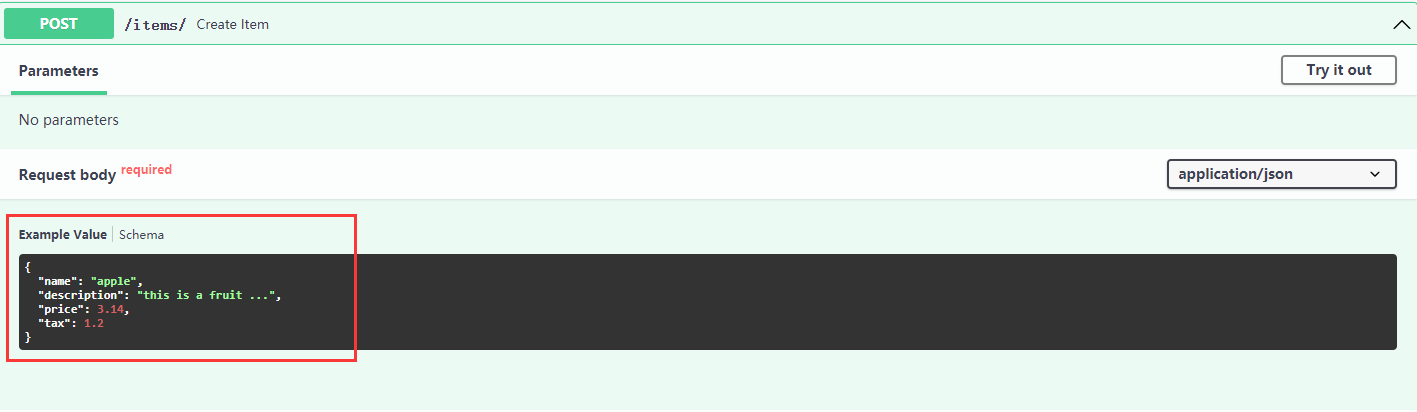
与使用Query、Path的方式相同,Field在Pydantic模型内部声明校验和元数据。
from typing import Optional from pydantic import BaseModel, Field class Item(BaseModel): name: str description: Optional[str] = Field(None, title="the description ...", max_length=20) price: float = Field(..., ge=2, description="price") tax: Optional[float] = None class Config: schema_extra = { "example": { "name": "apple", "description": "this is a fruit ...", "price": 3.14, "tax": 1.2 } } ...
注意,Field时从Pydantic中导入,这与Path与Query不同。
Field可以传递校验的参数:
def Field( default: Any = Undefined, *, default_factory: Optional[NoArgAnyCallable] = None, alias: str = None, title: str = None, description: str = None, const: bool = None, gt: float = None, ge: float = None, lt: float = None, le: float = None, multiple_of: float = None, min_items: int = None, max_items: int = None, min_length: int = None, max_length: int = None, allow_mutation: bool = True, regex: str = None, **extra: Any, ) -> Any: ...
一个请求中可能有路径参数、查询参数以及请求体,当它们混合在一起又是如何处理的呢?不过在说明这个问题之前,需要注意的请求体中可能有多个请求体参数以及单个请求体参数。
from typing import Optional from fastapi import FastAPI from pydantic import BaseModel, Field from datetime import date class Item(BaseModel): name: str description: Optional[str] = Field(None, title="the description ...", max_length=20) price: float = Field(..., ge=2, description="price") tax: Optional[float] = None class Config: schema_extra = { "example": { "name": "apple", "description": "this is a fruit ...", "price": 3.14, "tax": 1.2 } } class User(BaseModel): username: str full_name: Optional[str] = None birthday: date app = FastAPI() @app.post("/items/") async def create_item(item: Item, user: User): return {"item": item, "user": user}
上面声明两两个请求体参数的模型,并且在返回过程中,键值分别时定义好的,所以被期望的返回值就是类似下面的:
{ "item": { "name": "apple", "description": "this is a fruit ...", "price": 3.14, "tax": 1.2 }, "user": { "username": "san", "full_name": "zhangsan", "birthday": "2021-06-03" } }
注意birthday字段的类型时date类型,也就是除了常用的数据类型:
也可以定义其它复杂的数据类型:
在正常情况下,如果只有一个请求体模型,被期望的返回值应该是这样的:
{ "name": "apple", "description": "this is a fruit ...", "price": 3.14, "tax": 1.2 }
但是如果希望达到和上面的多个请求体一样的效果,外面存在一个键,内部是请求体的json内容,就需要使用Body中的embled参数了。
from typing import Optional from fastapi import FastAPI, Body from pydantic import BaseModel, Field class Item(BaseModel): name: str description: Optional[str] = Field(None, title="the description ...", max_length=20) price: float = Field(..., ge=2, description="price") tax: Optional[float] = None class Config: schema_extra = { "example": { "name": "apple", "description": "this is a fruit ...", "price": 3.14, "tax": 1.2 } } app = FastAPI() @app.post("/items/") async def create_item(item: Item = Body(..., embed=True)): return {"item": item}
其返回的结果就是:
{ "item": { "name": "apple", "description": "this is a fruit ...", "price": 3.14, "tax": 1.2 } }
如果请求中是一个单值或者是请求体的一部分,单值不会像上述请求体一样进行Pydantic模型设定,但是如果在函数的接受值中进行声明,显然FastAPI会将其当作一个查询参数,这时需要使用Body,这与Query和Path类似。
from fastapi import FastAPI, Body app = FastAPI() @app.post("/single/value") async def single_value(importance: int = Body(...)): return {"importance": importance}
这样,importance这个值会从请求体中传递给后台,而不是以查询参数的输入方式。
from typing import Optional from fastapi import FastAPI, Body, Path from pydantic import BaseModel, Field from datetime import date class Item(BaseModel): name: str description: Optional[str] = Field(None, title="the description ...", max_length=20) price: float = Field(..., ge=2, description="price") tax: Optional[float] = None class Config: schema_extra = { "example": { "name": "apple", "description": "this is a fruit ...", "price": 3.14, "tax": 1.2 } } class User(BaseModel): username: str full_name: Optional[str] = None birthday: date app = FastAPI() @app.post("/multi/params/{item_id}") async def multi_params( *, item_id: int = Path(..., title="item id ...", ge=1, le=10), q: Optional[str] = None, item: Optional[Item] = None, user: User, importance: int = Body(...) ): results = {"item_id": item_id, "user": user, "importance": importance} if q: results.update({"q": q}) if item: results.update({"item": item}) return results
上述视图函数中包含路径参数、请求参数、多个请求体参数、单值请求体参数,接口中:
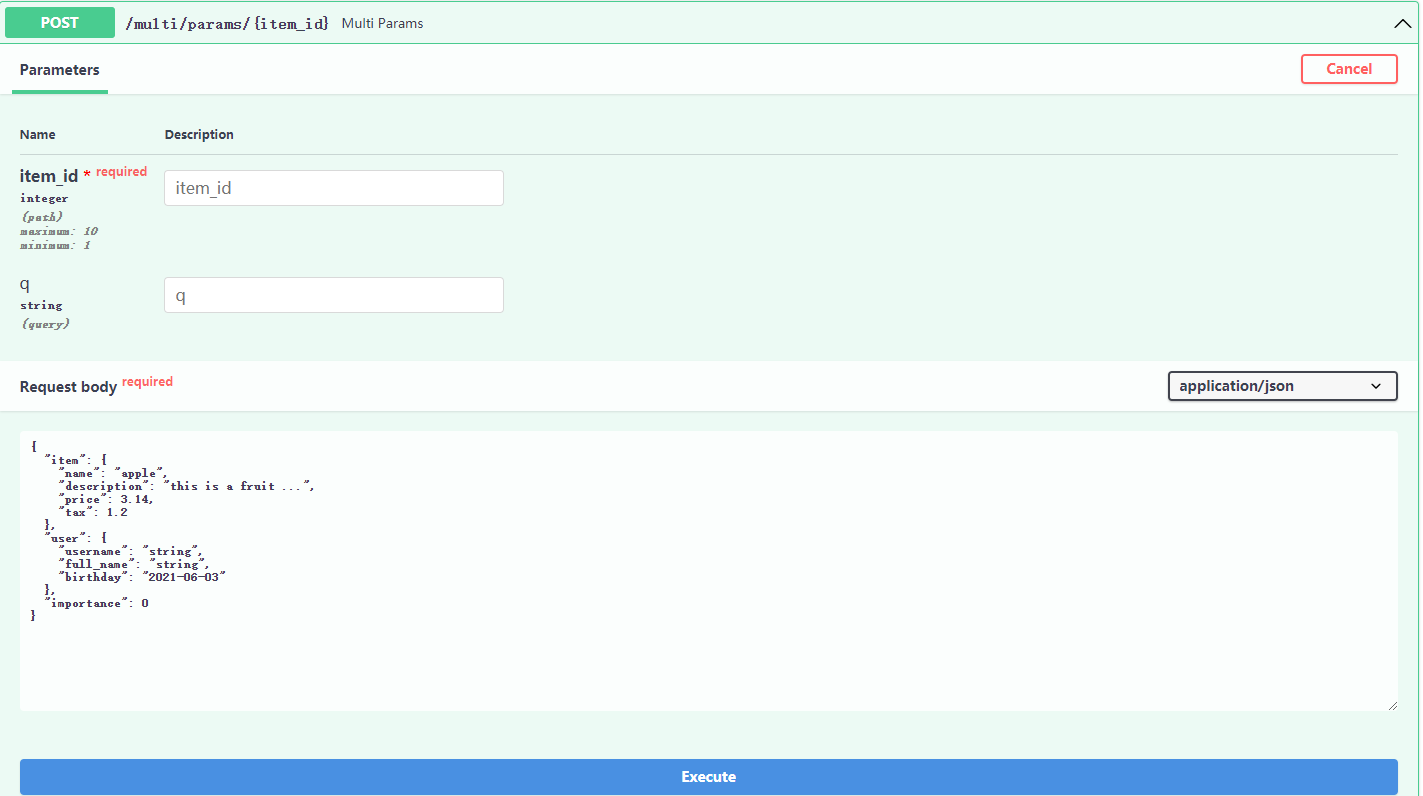
注意,第一个参数"*",Python不会对"*"做任何事情,但是之后所有的参数都应作为关键字(键值对),也被称为kwargs来调用,即使它们没有默认值。
from typing import Optional, List, Set from fastapi import FastAPI from pydantic import BaseModel, HttpUrl app = FastAPI() class Image(BaseModel): url: HttpUrl # 对http进行验证 name: str class Item(BaseModel): name: str description: Optional[str] = None price: float tax: Optional[float] = None tags: Set[str] = set() images: Optional[List[Image]] = None @app.put("/items/{item_id}") async def update_item(item_id: int, item: Item): return {"item_id": item_id, "item": item}
上述的请求体被期待这样的请求格式:
{ "name": "item name", "description": "this is item...", "price": 0, "tax": 0, "tags": [], "images": [ { "url": "http://127.0.0.1:8000/docs", "name": "zhangsan" }, { "url": "http://127.0.0.1:8000/docs", "name": "lisi" } ] }
上述模型中:
标签:def 字段 cto mod uuid inf ping 默认值 single
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/shenjianping/p/14843994.html