标签:des style blog http io color ar os sp
整理上次写的题目:
A:
For a positive integer n let‘s define a function f:
f(n) = - 1 + 2 - 3 + .. + ( - 1)nn
Your task is to calculate f(n) for a given integer n.
The single line contains the positive integer n (1 ≤ n ≤ 10^15).
题目简洁。可以看出规律。。。分下奇偶就可以了。
B:
Let‘s define logical OR as an operation on two logical values (i. e. values that belong to the set {0, 1}) that is equal to 1 if either or both of the logical values is set to 1, otherwise it is 0. We can define logical OR of three or more logical values in the same manner:
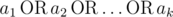 where
where 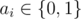 is equal to 1 if some ai = 1, otherwise it is equal to 0.
is equal to 1 if some ai = 1, otherwise it is equal to 0.
Nam has a matrix A consisting of m rows and n columns. The rows are numbered from 1 to m, columns are numbered from 1 to n. Element at row i (1 ≤ i ≤ m) and column j (1 ≤ j ≤ n) is denoted as Aij. All elements of A are either 0 or 1. From matrix A, Nam creates another matrix B of the same size using formula:
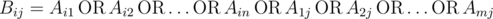 .
.
(Bij is OR of all elements in row i and column j of matrix A)
Nam gives you matrix B and challenges you to guess matrix A. Although Nam is smart, he could probably make a mistake while calculating matrix B, since size of A can be large.
The first line contains two integer m and n (1 ≤ m, n ≤ 100), number of rows and number of columns of matrices respectively.
The next m lines each contain n integers separated by spaces describing rows of matrix B (each element of B is either 0 or 1).
In the first line, print "NO" if Nam has made a mistake when calculating B, otherwise print "YES". If the first line is "YES", then also print mrows consisting of n integers representing matrix A that can produce given matrix B. If there are several solutions print any one.
题目比较烦。
但是我们可以得出这样一个规律:先预设定所有数为1,然后按得出的答案去把数变为0.然后验证是否满足答案。。
明白这一点 就简单了。

1 #include<iostream> 2 #include<cmath> 3 #include<cstdio> 4 #include<vector> 5 #include<string> 6 typedef long long ll; 7 using namespace std; 8 9 int a[123][123]; 10 int b[123][123]; 11 int main() 12 { 13 int m,n; 14 cin>>m>>n; 15 for (int i=1;i<=m;i++) 16 for (int j=1;j<=n;j++) b[i][j]=1; 17 for (int i=1;i<=m;i++) 18 for (int j=1;j<=n;j++) 19 cin>>a[i][j]; 20 21 for (int i=1;i<=m;i++) 22 for (int j=1;j<=n;j++) 23 if (a[i][j]==0){ 24 for (int k=1;k<=n;k++) 25 b[i][k]=0; 26 for (int k=1;k<=m;k++) 27 b[k][j]=0; 28 } 29 30 for (int i=1;i<=m;i++) 31 for (int j=1;j<=n;j++) 32 if (a[i][j]==1) 33 { 34 int tmp=0; 35 for (int k=1;k<=n;k++) 36 tmp|=b[i][k]; 37 for (int k=1;k<=m;k++) 38 tmp|=b[k][j]; 39 if (tmp==0) 40 { 41 cout<<"NO"; 42 return 0; 43 } 44 } 45 46 47 48 cout<<"YES"<<endl; 49 for (int i=1;i<=m;i++){ 50 for (int j=1;j<=n;j++) 51 cout<<b[i][j]<<" "; 52 cout<<endl; 53 } 54 return 0; 55 }
同样很繁琐的题目,但是我们可以贪心之。
贪心策略:1,先计算字符串的一半值。。。比如abcbcc
对应的值应当是211112.我们发现对半分的字符串所需最少的步数是对称的。还有我们要计算出最少步数。这里具体见代码。
然后当p在左半部分是就只做左半部分。同理右半部份。。。我们不可能p<=(n+1)/2,去做右半部份。
然后抽象认为这样的题目:数组为1 2 3 0 2的数组。当p在某个位置时。求全部变为0最少的步数。。。
这里用贪心或者啥的。我用了一个比较巧的办法。
然后因为写的太繁琐。露了条件。。。一直WA。。真是菜

1 #include<bits/stdc++.h> 2 using namespace std; 3 #define N 123456 4 string s; 5 int a[N]; 6 int n,p; 7 8 9 int main() 10 { 11 cin>>n>>p; 12 cin>>s; 13 for (int i=0;i<s.size();i++){ 14 int tmp1=abs(s[i]-s[n-i-1]); 15 int tmp2; 16 if (s[i]>s[n-i-1]) tmp2=abs(s[i]-26-s[n-i-1]); 17 else tmp2=abs(s[n-i-1]-s[i]-26); 18 a[i+1]=min(tmp1,tmp2); 19 } 20 21 int mid=(n+1)/2; 22 int ans=0x3f3f3f; 23 24 25 if (p<=mid) 26 { 27 int ans1=0; 28 int tmpp=p; 29 for (int i=1;i<=mid;i++) 30 if (a[i]) 31 { 32 ans1+=a[i]; 33 ans1+=abs(tmpp-i); 34 tmpp=i; 35 } 36 ans=min(ans1,ans); 37 38 ans1=0; 39 tmpp=p; 40 for(int i=mid;i>=1;i--) 41 if (a[i]) 42 { 43 ans1+=a[i]; 44 ans1+=abs(tmpp-i); 45 tmpp=i; 46 } 47 ans=min(ans1,ans); 48 } 49 50 else 51 { 52 53 int ans1=0; 54 int tmpp=p; 55 for (int i=mid+1;i<=n;i++) 56 if (a[i]) 57 { 58 ans1+=a[i]; 59 ans1+=abs(tmpp-i); 60 tmpp=i; 61 } 62 ans=min(ans1,ans); 63 ans1=0; 64 tmpp=p; 65 for(int i=n;i>mid;i--) 66 if (a[i]) 67 { 68 ans1+=a[i]; 69 ans1+=abs(tmpp-i); 70 tmpp=i; 71 } 72 ans=min(ans,ans1); 73 } 74 75 cout<<ans<<endl; 76 return 0; 77 }
D题:不是原创。
我们可以这样处理。
每次枚举第I个数。并且默认为根节点。且权值最大。然后我们的目的是找到多少个其子树是满足max-min<=d;
这里用DFS就好了。

1 #include<bits/stdc++.h> 2 #define N 12345 3 #define mod 1000000007 4 typedef long long ll; 5 using namespace std; 6 int a[N]; 7 int con; 8 vector<int> mp[N]; 9 int d; 10 11 ll dfs(int p,int pre) 12 { 13 ll tot=1; 14 for (int i=0;i<mp[p].size();i++) 15 { 16 int v=mp[p][i]; 17 if (pre==v||a[con]<a[v]||a[con]-a[v]>d||(a[con]==a[v]&&v<con)) continue; 18 tot=tot*(dfs(v,p)+1)%mod; 19 } 20 return tot; 21 } 22 23 int main() 24 { 25 int n; 26 cin>>d; 27 cin>>n; 28 for (int i=1;i<=n;i++) cin>>a[i]; 29 for (int i=1;i<n;i++) 30 { 31 int x,y; 32 cin>>x>>y; 33 mp[x].push_back(y); 34 mp[y].push_back(x); 35 } 36 ll ans=0; 37 for (int i=1;i<=n;i++) 38 { 39 con=i; 40 ans=(ans+dfs(i,-1))%mod; 41 } 42 cout<<ans; 43 }
E:继续补
Codeforces Round #277 (Div. 2)
标签:des style blog http io color ar os sp
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/forgot93/p/4095880.html