标签:bool bit main display chosen 开始 com 排列 cout
一个实际问题的各种可能情况构成的集合通常称为“状态空间”,而程序的运行则是对于状态空间的遍历,算法和数据结构则通过划分,归纳,提取,抽象来帮助程序提高遍历状态空间的效率。递推和递归则是两种遍历状态空间的基本方式。
我们有如下几种枚举 / 遍历方式:
| 枚举形式 | 状态空间规模 | 一般遍历方式 |
|---|---|---|
| 多项式 | \(n ^ k\),\(k\) 为常数 | 循环,递推 |
| 指数 | \(k ^ n\),\(k\) 为常数 | 递归,位运算 |
| 排列 | \(n!\) | 递归,\(\operatorname{next\_permutation}\) |
| 组合 | \(C_n^m\) | 递归+剪枝 |
从 \(1 \sim n\) 这 \(n(n \lt 20)\) 个数中选取任意多个,输出所有可能的选择方案。
这等价于每个数选或不选,所有可能方案共 \(2 ^ n\) 种,使用指数型枚举。时间复杂度 \(\operatorname{O}(2 ^ n \times n)\)。
vector<int> chosen;
void calc(int x) {
if (x > n) {
for (int i = 0; i < chosen.size(); ++i) {
cout << chosen[i] << ‘ ‘;
}
puts("");
return ;
}
calc(x + 1);
chosen.push_back(x);
calc(x + 1);
chosen.pop_back();
}
从 \(1 \sim n\) 这 \(n\) 个整数中随机选出 \(m (0 \leq m \leq n \lt 20)\) 个,输出所有的可能选择方案。
我们只需要在上面的代码开头添加
if (chosen.size() > m || chosen.size() + (n - x + 1) < m) {
return 0;
}
即可。
这就是剪枝,它保证当我们进入无解的分支( 已经超出 \(m\) 个或即使全部选上也没有 \(m\) 个)时立即返回,防止无用搜索。所以时间复杂度是 \(\operatorname{O}\left(C_n^m \times m\right)\)。
把 \(1 \sim n\) 这 \(n (n \leq 10)\) 个整数排成一行后随机打乱顺序,输出所有可能的次序。
该问题即全排列问题。所有可能的方案共 \(n!\) 种。时间复杂度 \(\operatorname{O}(n! \times n)\)。
const int kMaxN = 15;
int order[kMaxN];
bool vis[kMaxN];
void calc(int x) {
if (x > n){
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
cout << order[i] << ‘ ‘;
}
puts("");
return ;
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
if (vis[i]) continue;
order[x] = i;
vis[i] = 1;
calc(x + 1);
vis[i] = 0;
}
}
顺便提一句,在 \(\texttt{C++}\) 中可以直接使用函数 \(\operatorname{next\_permutation}\)。
在一个 \(5 \times 5\) 的 \(0 / 1\) 矩阵中,点击任意一个位置,该位置以及其上下左右的位置都会变化。问:最少需要多少次点击才能使得其变为全 \(1\) 矩阵?
我们注意到性质:
每个位置最多只会被点击 \(1\) 次。
若第 \(1\) 行的点击方案确定,其他位置的合法点击方案最多 \(1\) 种。
点击的先后顺序并不影响结果。
因此,我们可以枚举第一行的点击方式(使用位运算,共 \(32\) 种),再根据第一行来点击,最后判断合法并更新答案。
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int kMaxN = 7;
bool a[kMaxN][kMaxN], b[kMaxN][kMaxN];
int n;
void Change(int x, int y) {
b[x][y] ^= 1;
b[x - 1][y] ^= 1;
b[x + 1][y] ^= 1;
b[x][y - 1] ^= 1;
b[x][y + 1] ^= 1;
}
bool check() {
for (int i = 1; i <= 5; ++i) {
for (int j = 1; j <= 5; ++j) {
if (!b[i][j]) return 1;
}
}
return 0;
}
int Solve(int f) {
memcpy(b, a, sizeof(a));
int step = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= 5; ++i) {
if ((f >> (i - 1)) & 1) {
++step;
Change(1, i);
}
}
for (int line = 1; line <= 4; ++line) {
for (int col = 1; col <= 5; ++col) {
if (!b[line][col]) {
Change(line + 1, col);
++step;
}
}
}
if (check()) return 8;
return step;
}
int Solve() {
int minstep = 9;
for (int firststate = 0; firststate <= 32; ++firststate) {
int ans = Solve(firststate);
minstep = min(minstep, ans);
}
return (minstep <= 6 ? minstep : -1);
}
int main() {
cin >> n;
while (n--) {
for (int i = 1; i <= 5; ++i) {
for (int j = 1; j <= 5; ++j) {
char x; cin >> x; a[i][j] = (x == ‘1‘);
}
getchar();
}
cout << Solve() << endl;
}
return 0;
}
我们设 \(d_i\) 为求解 \(n\) 盘 \(3\) 塔的最少步数,则有 \(d_i = 2 ^ i - 1\)。我们设 \(f_i\) 为求解 \(i\) 盘 \(4\) 塔问题的最少步数,则有递推公式
其中 \(f_1 = 1\)。上式的含义:先把 \(i\) 个盘子移到 \(\texttt{B}\)(四塔),再将 \(n - i\) 个盘子移到 \(\texttt{D}\)(三塔),最后将 \(i\) 个盘子移回 \(\texttt{D}\)(四塔)。
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int kMaxN = 15;
int d[kMaxN], f[kMaxN];
int main() {
for (int i = 1; i <= 12; ++i) {
d[i] = 2 * d[i - 1] + 1;
}
memset(f, 0x3f, sizeof(f));
f[1] = 1;
puts("1");
for (int i = 2; i <= 12; ++i) {
for (int j = 1; j < i; ++j) {
f[i] = min(f[i], 2 * f[j] + d[i - j]);
}
cout << f[i] << endl;
}
return 0;
}
分治把一个问题划分为若干个规模更小的同类子问题,对这些子问题递归求解,然后在回溯时通过它们推导出原问题的解。
求 \(A ^ B\) 的所有约数之和 \(\bmod \ 9901 (0 \leq A, B \leq 5 \times 10 ^ 7)\)。
设
则 \(A ^ B\) 的约数之和为
问题转化为:求 \(\operatorname{sum}(p, c) = 1 + p + p ^ 2 + \dots + p ^ c\)。
我们考虑:
\(c\) 为奇数:\(\operatorname{sum}(p, c) = \left(1 + p^\dfrac{c+1}{2}\right)\times \operatorname{sum}\left(p, \dfrac{c-1}{2}\right)\)
\(c\) 为偶数:\(\operatorname{sum}(p, c) = \left(1 + p ^ \dfrac{c}{2}\right)\times \operatorname{sum}\left(p, \dfrac{c}{2} - 1\right) + p^c\)
配合快速幂即可在 \(\operatorname{O}(\log_2c)\) 的时间求出 \(\operatorname{sum}\)。
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int kMod = 9901;
int a, b;
int Power(int a, int b) {
int res = 1;
for (; b; b >>= 1) {
if (b & 1) res = 1ll * res * a % kMod;
a = 1ll * a * a % kMod;
}
return res;
}
int sum(int p, int c) {
if (!c) {
return 1;
}
if (c & 1) {
return (1 + Power(p, (c + 1) / 2)) * sum(p, (c - 1) / 2) % kMod;
}
return ((1 + Power(p, c / 2)) * sum(p, c / 2 - 1) + Power(p, c)) % kMod;
}
int main() {
cin >> a >> b;
if (!a) {
return puts("0"), 0;
}
int ans = 1;
for (int i = 2; i * i <= a; ++i) {
int s = 0;
while (a % i == 0) {
s += b;
a /= i;
}
if (s) {
ans *= sum(i, s);
ans %= kMod;
}
}
if (a > 1) {
ans *= sum(a, b);
ans %= kMod;
}
cout << ans;
return 0;
}
当城区规模扩大之后,Fractal 的解决方案是把和原来城区结构一样的区域按照图中的方式建设在城市周围,提升城市的等级。
对于任意等级的城市,我们把正方形街区从左上角开始按照道路标号。
虽然这个方案很烂,Fractal 规划部门的人员还是想知道,如果城市发展到了等级 \(n\), 编号为 \(A, B\) 的两个街区的直线距离是多少。
街区的距离指的是街区的中心点之间的距离,每个街区都是边长为 \(10\) 米的正方形。
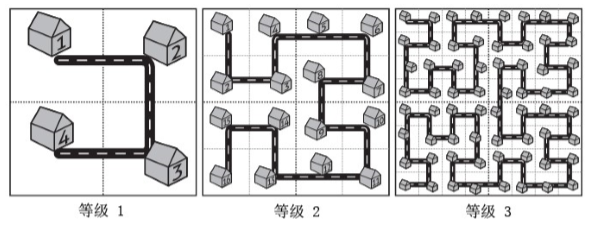
这就是通过一定规律无限包含自身的“分形图”。
我们设计子问题 \(\operatorname{calc}(n, m)\) 为问题“编号为 \(m\)(从 \(0\) 开始编号)在 \(n\) 级城市中的位置”。
我们先递归求解子问题 \(\operatorname{calc}(n - 1 , m \bmod (2^{2n-2}))\),设坐标为 \((x, y)\):
\(m\) 在左上角:答案为 \((y, x)\)
\(m\) 在右上角:答案为 \((x, y + 2^{n-1})\)
\(m\) 在左下角:答案为 \((2^n-y-1, 2^{n-1}-x-1)\)
\(m\) 在右下角:答案为 \((x+2^{n-1},y+2^{n-1})\)
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define pll pair<long long, long long>
using namespace std;
long long k, n, a, b;
pll calc(int n, long long m) {
if (!n) return make_pair(0ll, 0ll);
long long len = 1ll << (n - 1), cnt = 1ll << (2 * n - 2);
pll pos = calc(n - 1, m % cnt);
long long x = pos.first, y = pos.second;
long long z = m / cnt;
if (z == 0) return make_pair(y, x);
if (z == 1) return make_pair(x, y + len);
if (z == 2) return make_pair(x + len, y + len);
if (z == 3) return make_pair(2 * len - y - 1, len - x - 1);
}
long double dis(pll a, pll b) {
long long x = a.first - b.first, y = a.second - b.second;
return (long double)sqrt(x * x + y * y);
}
int main() {
cin >> k;
for (int i = 1; i <= k; ++i) {
cin >> n >> a >> b;
--a, --b;
cout << (long long)(1ll * 10 * dis(calc(n, a), calc(n, b)) + 0.5) << endl;
}
return 0;
}
标签:bool bit main display chosen 开始 com 排列 cout
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/reliauk/p/0x02.html